Abstract
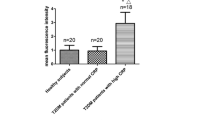
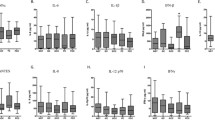
Low-grade systemic chronic inflammation is a very well-known feature of diabetes mellitus (DM). The purpose of this study was the assessment of the proinflammatory cytokine secretion profile in long-standing diabetes along with the presence of features of systemic inflammation. Metabolic parameters and serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α levels were determined in 20 patients with type 1 DM and 21 patients with type 2 DM and compared to 34 healthy subjects. The number of cytokine-secreting peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), before and after mitogenic stimulation, was also determined in the same groups. Adverse lipid profile, higher levels of inflammatory markers, and higher count of cytokine-secreting cells were observed more prevalently in type 2 diabetics than in controls. After stimulation, the increase in number of cytokine-secreting cells was higher in controls. In conclusion, patients with DM have evidence of low-grade inflammation and abnormal PBMC function that could be related to long-term sequelae, the accelerated atherosclerotic process, and the susceptibility to infections.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pickup JC, Crook MA. Is type II diabetes mellitus a disease of the innate immune system? Diabetologia 1998;41:1241–8.
Rabinovitch A, Suarez-Pinzon WL. Role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diabetes mellitus. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 2003;4:291–9.
Xing Z, Gauldie J, Cox G, Baumann H, Jordana M, Lei XF, Achong MK. IL-6 is an antiinflammatory cytokine required for controlling local or systemic acute inflammatory responses. J Clin Invest 1998;101:311–20.
Targher G, Zenari L, Bertolini L, Muggeo M, Zoppini G. Elevated levels of interleukin-6 in young adults with type 1 diabetes without clinical evidence of microvascular and macrovascular complications. Diabetes Care 2001;24:956–7.
Rıfai N, Joubran R, Yu H, Asmi M, Jouma M. Inflammatory markers in men with angiographically documented coronary heart disease. Clin Chem 1999;45:1967–73.
Pereira FO, Frode TS, Medeiros YS. Evaluation of tumour necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-2 soluble receptor, nitric oxide metabolites, and lipids as inflammatory markers in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Mediators Inflamm 2006;2006:39062.
Pickup JC, Mattock MB, Chusney GD, Burt D. NIDDM as a disease of the innate immune system: association of acute-phase reactants and interleukin-6 with metabolic syndrome X. Diabetologia 1997;40:1286–92.
Leibovich SJ, Ross R. The role of the macrophage in wound repair. A study with hydrocortisone and antimacrophage serum. Am J Pathol 1975;78:71–100.
Cassatella MA. Neutrophil-derived proteins: selling cytokines by the pound. Adv Immunol 1999;73:369–509.
Erbagci AB, Tarakcioglu M, Coskun Y, Sivasli E, Sibel Namiduru E. Mediators of inflammation in children with type I diabetes mellitus: cytokines in type I diabetic children. Clin Biochem 2001;34:645–50.
Tchorzewski H, Glowacka E, Banasik M, Lewkowicz P, Szalapska-Zawodniak M. Activated T lymphocytes from patients with high risk of type I diabetes mellitus have different ability to produce interferon-gamma, interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 and undergo anti-CD95 induced apoptosis after insulin stimulation. Immunol Lett 2001;75:225–34.
Rapoport MJ, Mor A, Vardi P, Ramot Y, Winker R, Hindi A, Bistritzer T. Decreased secretion of Th2 cytokines precedes up-regulated and delayed secretion of Th1 cytokines in activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Autoimmun 1998;11:635–42.
Eisenbarth GS. Type I diabetes mellitus. A chronic autoimmune disease. N Engl J Med 1986;314:1360–8.
El-Nawawy A, Soliman T, el-Azzouni O, Abbassy AA, Massoud MN, Marzouk S, Ibrahim F, Helal L. Interleukin-1- beta, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, insulin secretion and oral glucose tolerance in non-diabetic siblings of children with IDDM. Indian J Pediatr 1998;65:455–60.
Ozer G, Teker Z, Cetiner S, Yilmaz M, Topaloglu AK, Onenli-Mungan N, Yuksel B. Serum IL-1, IL-2, TNFalpha and INFgamma levels of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and their siblings. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 2003;16:203–10.
Kushner I. Regulation of the acute phase response by cytokines. Perspect Biol Med 1993;36:611–22.
Ventre J, Doebber T, Wu M, MacNaul K, Stevens K, Pasparakis M, Kollias G, Moller DE. Targeted disruption of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene: metabolic consequences in obese and nonobese mice. Diabetes 1997;46:1526–31.
Hotamisligil GS, Spiegelman BM. Tumor necrosis factor alpha: a key component of the obesity-diabetes link. Diabetes 1994;43:1271–8.
Akira S, Taga T, Kishimoto T. Interleukin-6 in biology and medicine. Adv Immunol 1993;54:1–78.
Hatanaka E, Monteagudo PT, Marrocos MS, Campa A. Neutrophils and monocytes as potentially important sources of proinflammatory cytokines in diabetes. Clin Exp Immunol 2006;146:443–7.
Zykova SN, Svartberg J, Seljelid R, Iversen H, Lund A, Svistounov DN, Jenssen TG. Release of TNF-alpha from in vitro-stimulated monocytes is negatively associated with serum levels of apolipoprotein B in patients with type 2 diabetes. Scand J Immunol 2004;60:535–42.
Geerlings SE, Brouwer EC, van Kessel KC, Gaastra W, Stolk RP, Hoepelman AI. Cytokine secretion is impaired in women with diabetes mellitus. Eur J Clin Invest 2000;30:995–1001.
Dogan Y, Akarsu S, Ustundag B, Yilmaz E, Gurgoze MK. Serum IL-1beta, IL-2, and IL-6 in insulin-dependent diabetic children. Mediators Inflamm 2006;2006:59206.
Celi F, Bini V, Papi F, Santilli E, Castellani MS, Ferretti A, Mencacci M, Berioli MG, De Giorgi G, Falorni A. Circulating adipocytokines in non-diabetic and Type 1 diabetic children: relationship to insulin therapy, glycaemic control and pubertal development. Diabet Med 2006;23:660–5.
Ohno Y, Aoki N, Nishimura A. In vitro production of interleukin- 1, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1993;77:1072–7.
Mooradian AD, Reed RL, Meredith KE, Scuderi P. Serum levels of tumor necrosis factor and IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta in diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 1991;14:63–5.
Netea MG, Hancu N, Blok WL, Grigorescu-Sido P, Popa L, Popa V, van der Meer JW. Interleukin 1 beta, tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin 1 receptor antagonist in newly diagnosed insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: comparison to long-standing diabetes and healthy individuals. Cytokine 1997;9:284–7.
Kulseng B, Skjak-Braek G, Folling I, Espevik T. TNF production from peripheral blood mononuclear cells in diabetic patients after stimulation with alginate and lipopolysaccharide. Scand J Immunol 1996;43:335–40.
Pickup JC, Chusney GD, Thomas SM, Burt D. Plasma interleukin-6, tumour necrosis factor alpha and blood cytokine production in type 2 diabetes. Life Sci 2000;67:291–300.
Desfaits AC, Serri O, Renier G. Normalization of plasma lipid peroxides, monocyte adhesion, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in NIDDM patients after gliclazide treatment. Diabetes Care 1998;21:487–93.
Katsuki A, Sumida Y, Murashima S, Murata K, Takarada Y, Ito K, Fujii M, Tsuchihashi K, Goto H, Nakatani K, Yano Y. Serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha are increased in obese patients with noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998;83:859–62.
Pfeiffer A, Janott J, Möhlig M, Ristow M, Rochlitz H, Busch K, Schatz H, Schifferdecker E. Circulating tumor necrosis factor alpha is elevated in male but not in female patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Horm Metab Res 1997;29:111–4.
American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2004;27:S5–10.
Jaatela M. Biologic activities and mechanisms of action of tumor necrosis factor-alpha/cachectin. Lab Invest 1991;64:724–42.
Feingold KR, Grunfeld C. Role of cytokines in inducing hyperlipidemia. Diabetes 1992;41(Suppl 2):97–101.
Mantovani A Bussolino F, Introna M. Cytokine regulation of endothelial cell function: from molecular level to the bedside. Immunol Today 1997;18:231–40.
Kroder G, Bossenmaier B, Kellerer M, Capp E, Stoyanov B, Mühlhöfer A, Berti L, Horikoshi H, Ullrich A, Häring H. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha- and hyperglycemia-induced insulin resistance. Evidence for different mechanisms and different effects on insulin signaling. J Clin Invest 1996;97:1471–7.
Hotamisligil GS, Budavari A, Murray D, Spiegelman BM. Reduced tyrosine kinase activity of the insulin receptor in obesity-diabetes. Central role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Clin Invest 1994;94:1543–9.
Ebeling P, Koistinen HA, Koivisto VA. Insulin-independent glucose transport regulates insulin sensitivity. FEBS Lett 1998;436:301–3.
Murdolo G, Smith U. The dysregulated adipose tissue: a connecting link between insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2006;16:S35–8.
Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet 1998;352:837–53.
Wang Y, Goodman M, Lumerman J, Sussman KE, Dahl R, Lafferty KJ, Draznin B. In vivo administration of interleukin-1 inhibits glucose-stimulated insulin release. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 1989;7:205–11.
Baggiolini M, Dewald B, Moser B. Human chemokines: an update. Annu Rev Immunol 1997;15:675–705.
Pociot F, Mølvig J, Wogensen L, Worsaae H, Dalbøge H, Baek L, Nerup J. A tumour necrosis factor beta gene polymorphism in relation to monokine secretion and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Scand J Immunol 1991;33:37–49.
Westendorp RG, Langermans JA, Huizinga TW, Elouali AH, Verweij CL, Boomsma DI, Vandenbroucke JP. Genetic influence on cytokine production and fatal meningococcal disease. Lancet 1997;349:170–3.
Buzzetti R, Quattrocchi CC, Nistico L. Dissecting the genetics of type 1 diabetes: relevance for familial clustering and differences in incidence. Diabetes Metab Rev 1998;14:111–28.
Wilson AG, de Vries N, Pociot F, di Giovine FS, van der Putte LB, Duff GW. An allelic polymorphism within the human tumor necrosis factor alpha promoter region is strongly associated with HLA A1, B8, and DR3 alleles. J Exp Med 1993;177:557–60.
Luger A, Schernthaner G, Urbanski A, Luger TA. Cytokine production in patients with newly diagnosed insulin-dependent (type I) diabetes mellitus. Eur J Clin Invest 1988;18:233–6.
Vlassara H, Brownlee M, Manogue KR, Dinarello CA, Pasagian A. Cachectin/TNF and IL-1 induced by glucose-modified proteins: role in normal tissue remodeling. Science 1988;240:1546–8.
Giulietti A, Stoffels K, Decallonne B, Overbergh L, Mathieu C. Monocytic expression behavior of cytokines in diabetic patients upon inflammatory stimulation. Ann NY Acad Sci 2004;1037:74–8.
Sahdev I, Fort P, Herry A. Macrophage-released interleukin-1 in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Acta Paediatr 1992;81:935–6.
Ciampolillo A, Guastamacchia E, Caragiulo L, Lollino G, De Robertis O, Lattanzi V, Giorgino R. In vitro secretion of interleukin-1 beta and interferon-gamma by peripheral blood lymphomononuclear cells in diabetic patients. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 1993;21:87–93.
Aarnes M, Schønberg S, Grill V. Fatty acids potentiate interleukin-1beta toxicity in the beta-cell line INS-1E. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002;296:189–93.
Mohamed-Ali V, Goodrick S, Rawesh A, Katz DR, Miles JM, Yudkin JS, Klein S, Coppack SW. Subcutaneous adipose tissue releases interleukin-6, but not tumor necrosis factor-alpha, in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997;82:4196–200.
Gabay C, Kushner I. Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J Med 1999;340:448–54.
Acknowledgements
Dr K. Alexandraki has been awarded with a scholarship from Alexander S. Onassis, public benefit foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alexandraki, K.I., Piperi, C., Ziakas, P.D. et al. Cytokine Secretion in Long-standing Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 and 2: Associations with Low-grade Systemic Inflammation. J Clin Immunol 28, 314–321 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-007-9164-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-007-9164-1