Abstract
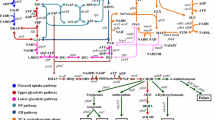
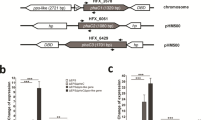
Natural phenazines are versatile secondary metabolites that are mainly produced by Pseudomonas and Streptomyces. All phenazine-type metabolites originate from two precursors: phenazine-1-carboxylic acid (PCA) in Pseudomonas or phenazine-1,6-dicarboxylic acid (PDC) in Streptomyces and other bacteria. Although the biosynthesis of PCA in Pseudomonas has been extensively studied, the origin of PDC still remains unclear. Comparing the phenazine biosynthesis operons of different species, we found that the phzA gene was restricted to Pseudomonas in which PCA is produced. By generating phzA-inactivated mutant, we found a new compound obviously accumulated; it was then isolated and identified as PDC. Protein sequence alignment showed that PhzA proteins from Pseudomonas form a separate group that is recognized by H73L and S77L mutations. Generating mutations of L73 into H73 and L77 into S77 resulted in a significant increase in PDC production. These findings suggest that phzA may act as a shunt switch of PDC biosynthesis in Pseudomonas and distinguish the pathway producing only PCA from the pathway forming PCA plus PDC. Using real-time PCR analysis, we suggested that the phzA, phzB, and phzG genes either directly or indirectly regulate the production of PDC, and phzA plays the most significant regulatory role. This is the first description of phzA in the biosynthesis of PDC, and the first-time substantial PDC was obtained in Pseudomonas. Therefore, this study not only provides valuable clues to better understand the biosynthesis of PCA and PDC in Pseudomonas but also introduces a method to produce PDC derivatives by genetically engineered strains.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahuja EG, Janning P, Mentel M, Graebsch A, Breinbauer R, Hiller W, Costisella B, Thomashow LS, Mavrodi DV, Blankenfeldt W (2008) PhzA/B catalyzes the formation of the tricycle in phenazine biosynthesis. J Am Chem Soc 130:17053–17061. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja806325k
Arnold K, Bordoli L, Kopp J, Schwede T (2006) The SWISS-MODEL workspace: a web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 22:195–201. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bti770
Blankenfeldt W (2013) The biosynthesis of phenazines. In: Chincholkar S, Thomashow L (eds) Microbial Phenazines: Biosynthesis, Agriculture and Health, 1rd edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 1–17
Blankenfeldt W, Parsons JF (2014) The structural biology of phenazine biosynthesis. Curr Opin Struct Biol 26–33. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2014.08.013
Blankenfeldt W, Kuzin AP, Skarina T, Korniyenko Y, Tong L, Bayer P, Janning P, Thomashow LS, Mavrodi DV (2004) Structure and function of the phenazine biosynthetic protein PhzF from Pseudomonas fluorescens. Proc Natl Acad of Sci USA 101:16431–16436. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0407371101
Chin-A-Woeng TF, van den Broek D, de Voer G, van der Drift KM, Tuinman S, Thomas-Oates JE, Lugtenberg BJ, Bloemberg GV (2001) Phenazine-1-carboxamide production in the biocontrol strain Pseudomonas chlororaphis PCL1391 is regulated by multiple factors secreted into the growth medium. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 14:969–979. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI.2001.14.8.969
Cimmino A, Evidente A, Mathieu V, Andolfi A, Lefranc F, Kornienko A, Kiss R (2012) Phenazines and cancer. Nat Prod Rep 29:487–501. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2np00079b
Dasgupta D, Kumar A, Mukhopadhyay B, Sengupta TK (2015) Isolation of phenazine 1,6-di-carboxylic acid from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain HRW.1-S3 and its role in biofilm-mediated crude oil degradation and cytotoxicity against bacterial and cancer cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:8653–8665. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6707-x
DeLano WL, Bromberg S (2004) PyMOL user’s guide. DeLano Scientific LLC, San Carlos, California
Du XL, Li YQ, Zhou WP, Zhou Q, Liu HM, YQ X (2013) Phenazine-1-carboxylic acid production in a chromosomally non-scar triple-deleted mutant Pseudomonas aeruginosa using statistical experimental designs to optimize yield. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:7767–7778. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4921-y
Geiger A, Keller-Schierlein W, Brandl M, Zähner H (1988) Metabolites of microorganisms. 247. Phenazines from Streptomyces antibioticus, strain Tü 2706. J Antibiot 41:1542–1551
Gerber NN (1969) New microbial phenazines. J Heterocycl Chem 6:297–300
Giddens SR, Feng Y, Mahanty HK (2002) Characterization of a novel phenazine antibiotic gene cluster in Erwinia herbicola Eh1087. Mol Microbiol 45:769–783. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03048.x
Guttenberger N, Blankenfeldt W, Breinbauer R (2017) Recent developments in the isolation, biological function, biosynthesis, and synthesis of phenazine natural products. Bioorg Med Chem S0968-0896:31180–31844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2017.01.002
Jin KM, Zhou L, Jiang HX, Sun S, Fang YL, Liu JH, Zhang XH, He YW (2015) Engineering the central biosynthetic and secondary metabolic pathways of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PA1201 to improve phenazine-1-carboxylic acid production. Metab Eng 32:30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2015.09.003
Jin XJ, Peng HS, HB H, Huang XQ, Wei W, Zhang XH (2016) iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis reveals potential factors associated with the enhancement of phenazine-1-carboxamide production in Pseudomonas chlororaphis P3. Sci Rep 6:27393. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27393
Karuppiah V, Li YX, Sun W, Feng GF, Li ZY (2015) Functional gene-based discovery of phenazines from the actinobacteria associated with marine sponges in the South China Sea. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:5939–5950. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6547-8
Kovach ME, Elzer PH, Hill DS, Robertson GT, Farris MA, Roop RM, Peterson KM (1995) Four new derivatives of the broad-host-range cloning vector pBBR1MCS, carrying different antibiotic-resistance cassettes. Gene 166:175–176
Laursen JB, Nielsen J (2004) Phenazine natural products: biosynthesis, synthetic analogues, and biological activity. Chem Rev 104:1663–1686. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr020473j
Liu KQ, Hu HB, Wang W, Zhang XH (2016) Genetic engineering of Pseudomonas chlororaphis GP72 for the enhanced production of 2-Hydroxyphenazine. Microb Cell Factories 15:131. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-016-0529-0
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C (T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Mavrodi DV, Blankenfeldt W, Thomashow LS (2006) Phenazine compounds in fluorescent Pseudomonas spp. biosynthesis and regulation. Annu Rev Phytopathol 44:417–445. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.phyto.44.013106.145710
Mavrodi DV, Peever TL, Mavrodi OV, Parejko JA, Raaijmakers JM, Lemanceau P, Mazurier S, Heide L, Blankenfeldt W, Weller DM, Thomashow LS (2010) Diversity and evolution of the phenazine biosynthesis pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:866–879. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02009-09
Mcdonald M, Wilkinson B, Van’t Land CW, Mocek U, Lee S, Floss HG (1999) Biosynthesis of phenazine antibiotics in Streptomyces antibioticus: stereochemistry of methyl transfer from carbon-2 of acetate. J Am Chem Soc 121:5619–5624
Mcdonald M, Mavrodi DV, Thomashow LS, Floss HG (2001) Phenazine biosynthesis in Pseudomonas fluorescens: branchpoint from the primary shikimate biosynthetic pathway and role of phenazine-1,6-dicarboxylic acid. J Am Chem Soc 123:9459–9460
Mentel M, Ahuja EG, Mavrodi DV, Breinbauer R, Thomashow LS, Blankenfeldt W (2009) Of two make one: the biosynthesis of phenazines. Chembiochem 10:2295–2304. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.200900323
Messenger AJ, Turner JM (1983) Phenazine-1, 6-dicarboxylate and its dimethyl ester as precursors of other phenazines in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 18:65–68
Parsons JF, Song F, Parsons L, Calabrese K, Eisenstein E, Ladner JE (2004) Structure and function of the phenazine biosynthesis protein PhzF from Pseudomonas fluorescens 2-79. Biochemistry 43:12427–12435. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi049059z
Pierson LS, Pierson EA (2010) Metabolism and function of phenazines in bacteria: impacts on the behavior of bacteria in the environment and biotechnological processes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:1659–1670. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2509-3
Podojil M, Gerber NN (1967) The biosynthesis of 1,6-phenazinediol 5,10-dioxide (Iodinin) by Brevibacterium iodinum. Biochemistry 6:2701–2705
Robert X, Gouet P (2014) Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res 42(Web Server issue):W320–W324. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku316
Rui Z, Ye M, Wang SG, Fujikawa K, Akerele B, Aung M, Floss HG, Zhang WJ, TW Y (2012) Insights into a divergent phenazine biosynthetic pathway governed by a plasmid-born esmeraldin gene cluster. Chem Biol 19:1116–1125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2012.07.025
Rusman Y, Oppegard LM, Hiasa H, Gelbmann C, Salomon CE (2013) Solphenazines A-F, glycosylated phenazines from Streptomyces sp. strain DL-93. J Nat Prod 76:91–96. https://doi.org/10.1021/np3007606
Schäfer A, Tauch A, Jäger W, Kalinowski J, Thierbach G, Pühler A (1994) Small mobilizable multi-purpose cloning vectors derived from the Escherichia coli plasmids pK18 and pK19: selection of defined deletions in the chromosome of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Gene 145:69–73
Sletta H, Degnes KF, Herfindal L, Klinkenberg G, Fjærvik E, Zahlsen K, Brunsvik A, Nygaard G, Aachmann FL, Ellingsen TE, Døskeland SO, Zotchev SB (2014) Anti-microbial and cytotoxic 1,6-dihydroxyphenazine-5,10-dioxide (iodinin) produced by Streptosporangium sp. DSM 45942 isolated from the fjord sediment. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:603–610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5320-0
Turner JM, Messenger AJ (1986) Occurrence, biochemistry and physiology of phenazine pigment production. Adv Microb Physiol 27:211–275
Wu DQ, Jing Y, Ou HY, Xue W, Huang XQ, He YW, Xu YQ (2011) Genomic analysis and temperature-dependent transcriptome profiles of the rhizosphere originating strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa M18. BMC Genomics 12:438. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-438
Wu CS, Van Wezel GP, Hae Choi Y (2015) Identification of novel endophenaside antibiotics produced by Kitasatospora sp. MBT66. J Antibiot 68:445–452. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2015.14
Zeyhle P, Bauer JS, Kalinowski J, Shin-ya K, Gross H, Heide L (2014) Genome-based discovery of a novel membrane-bound 1,6-dihydroxyphenazine prenyltransferase from a marine actinomycete. PLoS One 9:e99122. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0099122
Zhang CX, Sheng CL, Wang W, HB H, Peng HS, Zhang XH (2015) Identification of the lomofungin biosynthesis gene cluster and associated flavin-dependent monooxygenase gene in Streptomyces lomondensis S015. PLoS One 10:e0136228. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0136228
Zhao YY, Qian GL, Ye YH, Wright S, Chen H, Shen YM, Liu FQ, LC D (2016) Heterocyclic aromatic N-oxidation in the biosynthesis of phenazine antibiotics from Lysobacter antibioticus. Org Lett 18:2495–2498. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.6b01089
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31670033). The authors are grateful to Dr. Hang Wang at Instrumental Analysis Center of Shanghai Jiao Tong University for kindly providing assistance in analyzing the LC-MS results.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1454 kb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, S., Wang, Y., Dai, B. et al. PhzA, the shunt switch of phenazine-1,6-dicarboxylic acid biosynthesis in Pseudomonas chlororaphis HT66. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 7165–7175 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8474-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8474-3