Abstract
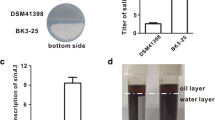
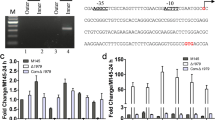
Salinomycin, a polyether antibiotic produced by Streptomyces albus, is widely used in animal husbandry as an anticoccidial drug and growth promoter. Situated within the salinomycin biosynthetic gene cluster, slnR encodes a LAL-family transcriptional regulator. The role of slnR in salinomycin production in S. albus was investigated by gene deletion, complementation, and overexpression. Gene replacement of slnR from S. albus chromosome results in almost loss of salinomycin production. Complementation of slnR restored salinomycin production, suggesting that SlnR is a positive regulator of salinomycin biosynthesis. Overexpression of slnR in S. albus led to about 25 % increase in salinomycin production compared to wild type. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis revealed that the expression of most sal structural genes was downregulated in the ΔslnR mutant but upregulated in the slnR overexpression strain. Electrophoretic mobility gel shift assays (EMSAs) also revealed that SlnRDBD binds directly to the three intergenic regions of slnQ-slnA1, slnF-slnT1, and slnC-slnB3. The SlnR binding sites within the three intergenic regions were determined by footprinting analysis and identified a consensus-directed repeat sequence 5′-ACCCCT-3′. These results indicated that SlnR modulated salinomycin biosynthesis as an enhancer via interaction with the promoters of slnA1, slnQ, slnF, slnT1, slnC, and slnB3 and activates the transcription of most of the genes belonging to the salinomycin gene cluster but not its own transcription.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoszczak M, Huczynski A (2015) Anticancer activity of polyether lonophore-salinomycin. Anti Cancer Agents Med Chem 5:575–591
Arias P, Fernandez-Moreno MA, Malpartida F (1999) Characterization of the pathway-specific positive transcriptional regulator for actinorhodin biosynthesis in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) as a DNA-binding protein. J Bacteriol 181:6958–6968
Bate N, Stratigopoulos G, Cundliffe E (2002) Differential roles of two SARP-encoding regulatory genes during tylosin biosynthesis. Mol Microbiol 43:449–458
Bibb M (2005) Regulation of secondary metabolism in Streptomyces. Curr Option Microbiol 8:208–215
Challis GL, Hopwood DA (2003) Synergy and contingency as driving forces for the evolution of multiple secondary metabolite production by Streptomyces species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:14555–14561
Chen Y, Wendt E, Shen B (2008) Identification and utility of FdmR1 as a Streptomyces antibiotic regulatory protein activator for fredericamycin production in Streptomyces griseus ATCC49344 and heterologous hosts. J Bacteriol 190:5587–5596
Guo J, Zhao J, Li L, Chen Z, Wen Y, Li J (2010) The pathway-specific regulator AveR from Streptomyces avermitilis positively regulates avermectin production while it negatively affects oligomycin biosynthesis. Mol Gen Genomics 283:123–133
Gupta PB, Onder TT, Jiang G, Tao K, Kuperwasser C, Weinberg RA, Lander ES (2009) Identification of selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput screening. Cell 4:645–659
Gust B, Challis GL, Fowler K, Kieser T, Chater KF (2003) PCR-targeted Streptomyces gene replacement identifies a protein domain needed for biosynthesis of the sesquiterpene soil odor geosmin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 4:1541–1546
He W, Lei J, Liu Y, Wang Y (2008) The LuxR family members GdmRI and GdmRII are positive regulators of geldanamycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces hygroscopicus 17997. Arch Microbiol 189:501–510
He X, Li R, Pan Y, Liu G, Tan H (2010) SanG,a transcriptional activator, controls nikkomycin biosynthesis through binding to the sanN-sanO intergenic region in Streptomyces ansochromogenes. Microbiology 156:828–837
Jiang C, Wang H, Kang Q, Liu J, Bai L (2012) Cloning and characterization of the polyether salinomycin biosynthesis gene cluster of Streptomyces albus XM211. Appl Environ Microbiol 4:994–1003
Kieser TBM, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. The John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Kitani S, Ikeda H, Sakamoto T, Noguchi S, Nihira T (2009) Characterization of a regulatory gene, aveR, for the biosynthesis of avermectin in Streptomyces avermitilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:1089–1096
Kuscer E, Coates N, Challis J, Gregory M, Wilkinson B, Sheridan R, Petkovie H (2007) Role of rapH and rapG in positive regulation of rapamycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces hygroscopicus. J Bacteriol 189:4756–4763
Liu S-P, Yu P, Yuan P-H, Zhou Z-X, Bu Q-T, Mao X-M, Li Y-Q (2015) Sigma factor WhiGch positively regulates natamycin production in Streptomyces chattanoogensis L10. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:2715–2726
Martin JF, Liras P (2010) Engineering of the regulatory cascades and networks controlling antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces. Curr Option Microbiol 13:263–273
Mizuno T, Tanaka I (1997) Structure of the DNA-binding domain of the OmpR family of response regulators. Mol Microbiol 24:665–667
Mo SJ, JiYoo Y, Ban YH, Lee S-K, Kim E, Suh J-W, Yoon YJ (2012) Roles of fkbN in positive regulation and tcs7 in negative regulation of FK506 biosynthesis in Streptomyces sp. strain KCTC 1604BP. Appl Environ Microbiol 7:2249–2255
Molnar J, Aparicio JF, Haydock SF, Khaw LE, Schwecke T, konig A, Staunton J, Leadlay PF (1996) Organisation of the biosynthetic gene cluster for raamycin in Streptomyces hygroscopicus: analysis of genes flanking the polyketide synthase. Gene 169:1–7
Narva KE, Feitelson JS (1990) Nucelotide sequence and transcriptional analysis of the redD locus of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol 172:326–333
Pan Y, Wang A, He X, Tian Y, Liu G, Tan H (2011) SabR enhances nikkomycin production via regulating the transcriptional level of sang, a pathway-specific regulatory gene in Streptomyces ansochromogenes. BMC Microbiol 11:164–170
Richet E, Raibaud O (1989) MalT, the regulatory protein of the Escherichia coli maltose system, is an ATP-dependent transcriptional activator. EMBO J 8:981–987
Riddell FG (2002) Structure, conformation, and mechanism in the membrane transport of alkali metal ions by ionophoric antibiotics. Chirality 14:121–125
Rost B, Yachday G, Liu J (2004) The PredictProtein server. Nucleic Acids Res 32:W321–W326
Santo-Aberturas J, Vicente CM, Guerra SM, Payero TD, Martin JF, Aparicio JF (2011) Molecular control of polyene macrolide biosynthesis direct binding of the regulator PimM to eight promoters of pimaricin genes and identification of binding boxes. J Biol Chem 286:9150–9161
Santos-Aberturas J, Payero TD, Vicente CM, Guerra SM, Cañibano C, Martín JF, Aparicio JF (2011) Functional conservation of PAS-LuxR transcriptional regulators in polyene macrolide biosynthesis. Metab Eng 13:756–767
Sun J, Kelemen GH, Fernández-Abalos JM, Bibb MJ (1999) Green fluorescent protein as a reporter for spatial and temporal gene expression in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Microbiology 145(9):2221–2227
Walker JE, Saraste M, Runswick MJ, Gay NJ (1982) Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J 1:945–951
Widdick DA, Dodd HM, Barraille P, White J, Stein TH, Chater KF, Gasson MJ, Bibb MJ (2003) Cloning and engineering of the cinnamycin biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces cinnamoneus DSM40005. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 7:4316–4321
Wietzorrek A, Bibb M (1997) A novel family of proteins that regulates antibiotic production in stretomycetes appears to contain an OmpR-like DNA-binding fold. Mol Microbiol 25:1177–1184
Wilson DJ, Xue Y, Reynolds KA, Sherman DH (2001) Characterization and analysis of the PikD regulatory factor in the pikromycin biosynthetic pathway of streptomyces venezuelae. J Bacteriol 183:3468–3475
Xie C, Deng J-J, Wang H-X (2015) Identification of AstG1, a LAL family regulator that positively controls ansatrienins production in Streptomyces sp.XZQH13. Curr Microbiol 70:859–864
Yurkovich ME, Tyrakis PA, Hong H, Sun Y, Samborskyy M, Kamiya K, Leadlay PF (2012) A late-stage intermediate in salinomycin biosynthesis is revealed by specific mutation in the biosynthetic gene cluster. Chembiochem 13:67–71
Zianni M, Tessanne K, Merighi M, Laguna R, Tabita FR (2006) Identification of the DNA bases of a DNase I footprint by the use of dye primer sequencing on an automated capillary DNA analysis instrument. J Biomol Tech 17:103–113
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2012CB721005), National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2012AA022107), and Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. LY16C010001, LZ12C01001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 962 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Z., Li, H., Yu, P. et al. SlnR is a positive pathway-specific regulator for salinomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces albus . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 1547–1557 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7918-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7918-5