Abstract
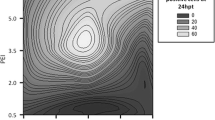
HIV-1 virus-like particles (VLPs) have great potential as new-generation vaccines. The novel CAP-T cell line is used for the first time to produce Gag-GFP HIV-1 VLPs by means of polyethylenimine (PEI)-mediated transient transfection. CAP-T cells are adapted to grow to high cell densities in serum-free medium, and are able to express complex recombinant proteins with human post-translational modifications. Furthermore, this cell line is easily transfected with PEI, which offers the flexibility to rapidly generate and screen a number of candidates in preclinical studies. Transient transfection optimization of CAP-T cells has been performed systematically in this work. It is determined that for optimal production, cells need to be growing at mid-exponential phase, Protein Expression Medium (PEM) medium has to be added post-transfection, and cells can be transfected by independent addition of DNA and PEI with no prior complexation. A Box-Behnken experimental design is used to optimize cell density at time of transfection, DNA/cell and PEI/cell ratios. The optimal conditions determined are transfection at a density of 3.3E + 06 cells/mL with 0.5 pg of DNA/cell and 3 pg of PEI/cell. Using the optimized protocol, 6 × 1010 VLP/mL are obtained, demonstrating that CAP-T is a highly efficient cell line for the production of HIV-1 VLPs and potentially other complex viral-based biotherapeutics.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansorge S, Lanthier S, Transfiguracion J, Durocher Y, Henry O, Kamen A (2009) Development of a scalable process for high-yield lentiviral vector production by transient transfection of HEK293 suspension cultures. J Gene Med 11(10):868–876. doi:10.1002/jgm.1370
Backliwal G, Hildinger M, Chenuet S, Wulhfard S, De Jesus M, Wurm FM (2008a) Rational vector design and multi-pathway modulation of HEK 293E cells yield recombinant antibody titers exceeding 1 g/l by transient transfection under serum-free conditions. Nucleic Acids Res 36(15):e96. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn423
Backliwal G, Hildinger M, Hasija V, Wurm FM (2008b) High-density transfection with HEK-293 cells allows doubling of transient titers and removes need for a priori DNA complex formation with PEI. Biotechnol Bioeng 99(3):721–727. doi:10.1002/bit.21596
Baldi L, Hacker DL, Adam M, Wurm FM (2007) Recombinant protein production by large-scale transient gene expression in mammalian cells: state of the art and future perspectives. Biotechnol Lett 29(5):677–684. doi:10.1007/s10529-006-9297-y
Bandaranayake AD, Almo SC (2014) Recent advances in mammalian protein production. FEBS Lett 588(2):253–260. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2013.11.035
Buonaguro L, Tagliamonte M, Visciano ML, Tornesello ML, Buonaguro FM (2013) Developments in virus-like particle-based vaccines for HIV. Expert Rev Vaccines 12(2):119–127. doi:10.1586/erv.12.152
Carpentier E, Paris S, Kamen AA, Durocher Y (2007) Limiting factors governing protein expression following polyethylenimine-mediated gene transfer in HEK293-EBNA1 cells. J Biotechnol 128(2):268–280. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2006.10.014
Cervera L, Fuenmayor J, Gonzalez-Dominguez I, Gutierrez-Granados S, Segura MM, Godia F (2015) Selection and optimization of transfection enhancer additives for increased virus-like particle production in HEK293 suspension cell cultures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. doi:10.1007/s00253-015-6842-4
Cervera L, Gutierrez-Granados S, Martinez M, Blanco J, Godia F, Segura MM (2013) Generation of HIV-1 Gag VLPs by transient transfection of HEK 293 suspension cell cultures using an optimized animal-derived component free medium. J Biotechnol 166(4):152–165
Circu ML, Aw TY (2010) Reactive oxygen species, cellular redox systems, and apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med 48(6):749–762. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.12.022
Chen Y, Wu B, Musier-Forsyth K, Mansky LM, Mueller JD (2009) Fluorescence fluctuation spectroscopy on viral-like particles reveals variable gag stoichiometry. Biophys J 96(5):1961–1969. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2008.10.067
Daramola O, Stevenson J, Dean G, Hatton D, Pettman G, Holmes W, Field R (2014) A high-yielding CHO transient system: coexpression of genes encoding EBNA-1 and GS enhances transient protein expression. Biotechnol Prog 30(1):132–141. doi:10.1002/btpr.1809
Fischer S, Charara N, Gerber A, Wolfel J, Schiedner G, Voedisch B, Geisse S (2012) Transient recombinant protein expression in a human amniocyte cell line: the CAP-T(R) cell system. Biotechnol Bioeng 109(9):2250–2261. doi:10.1002/bit.24514
Garnier L, Ravallec M, Blanchard P, Chaabihi H, Bossy JP, Devauchelle G, Jestin A, Cerutti M (1995) Incorporation of pseudorabies virus gD into human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Gag particles produced in baculovirus-infected cells. J Virol 69(7):4060–4068
Geisse S (2009) Reflections on more than 10 years of TGE approaches. Protein Expr Purif 64(2):99–107. doi:10.1016/j.pep.2008.10.017
Genzel Y, Behrendt I, Rodig J, Rapp E, Kueppers C, Kochanek S, Schiedner G, Reichl U (2013) CAP, a new human suspension cell line for influenza virus production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(1):111–122. doi:10.1007/s00253-012-4238-2
Girard P, Derouazi M, Baumgartner G, Bourgeois M, Jordan M, Jacko B, Wurm FM (2002) 100-liter transient transfection. Cytotechnology 38(1–3):15–21. doi:10.1023/A:1021173124640
Grosjean F, Batard P, Jordan M, Wurm FM (2002) S-phase synchronized CHO cells show elevated transfection efficiency and expression using CaPi. Cytotechnology 38(1–3):57–62. doi:10.1023/A:1021197830091
Gutierrez-Granados S, Cervera L, Godia F, Carrillo J, Segura MM (2013) Development and validation of a quantitation assay for fluorescently tagged HIV-1 virus-like particles. J Virol Methods 193(1):85–95
Haldankar R, Li D, Saremi Z, Baikalov C, Deshpande R (2006) Serum-free suspension large-scale transient transfection of CHO cells in WAVE bioreactors. Mol Biotechnol 34(2):191–199
Hammonds J, Chen X, Zhang X, Lee F, Spearman P (2007) Advances in methods for the production, purification, and characterization of HIV-1 Gag-Env pseudovirion vaccines. Vaccine 25(47):8036–8048. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.09.016
Haynes JR, Dokken L, Wiley JA, Cawthon AG, Bigger J, Harmsen AG, Richardson C (2009) Influenza-pseudotyped Gag virus-like particle vaccines provide broad protection against highly pathogenic avian influenza challenge. Vaccine 27(4):530–541. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.11.011
Hermida-Matsumoto L, Resh MD (2000) Localization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Gag and Env at the plasma membrane by confocal imaging. J Virol 74(18):8670–8679
Kushnir N, Streatfield SJ, Yusibov V (2012) Virus-like particles as a highly efficient vaccine platform: diversity of targets and production systems and advances in clinical development. Vaccine 31(1):58–83
Liu C, Dalby B, Chen W, Kilzer JM, Chiou HC (2008) Transient transfection factors for high-level recombinant protein production in suspension cultured mammalian cells. Mol Biotechnol 39(2):141–153. doi:10.1007/s12033-008-9051-x
Montgomery DC (1997) Design and analysis of experiments. Wiley, Fourth edn
Pham PL, Kamen A, Durocher Y (2006) Large-scale transfection of mammalian cells for the fast production of recombinant protein. Mol Biotechnol 34(2):225–237. doi:10.1385/MB:34:2:225
Pillay S, Meyers A, Williamson AL, Rybicki EP (2009) Optimization of chimeric HIV-1 virus-like particle production in a baculovirus-insect cell expression system. Biotechnol Prog 25(4):1153–1160. doi:10.1002/btpr.187
Raymond C, Tom R, Perret S, Moussouami P, L’Abbe D, St-Laurent G, Durocher Y (2011) A simplified polyethylenimine-mediated transfection process for large-scale and high-throughput applications. Methods 55(1):44–51. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2011.04.002
Roldao A, Mellado MC, Castilho LR, Carrondo MJ, Alves PM (2010) Virus-like particles in vaccine development. Expert Rev Vaccines 9(10):1149–1176. doi:10.1586/erv.10.115
Sakuragi S, Goto T, Sano K, Morikawa Y (2002) HIV type 1 Gag virus-like particle budding from spheroplasts of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(12):7956–7961. doi:10.1073/pnas.082281199
Scotti N, Alagna F, Ferraiolo E, Formisano G, Sannino L, Buonaguro L, De Stradis A, Vitale A, Monti L, Grillo S, Buonaguro FM, Cardi T (2009) High-level expression of the HIV-1 Pr55gag polyprotein in transgenic tobacco chloroplasts. Planta 229(5):1109–1122. doi:10.1007/s00425-009-0898-2
Schiedner G, Hertel S, Kochanek S (2000) Efficient transformation of primary human amniocytes by E1 functions of Ad5: generation of new cell lines for adenoviral vector production. Hum Gene Ther 11(15):2105–2116. doi:10.1089/104303400750001417
Schlaeger EJ, Christensen K (1999) Transient gene expression in mammalian cells grown in serum-free suspension culture. Cytotechnology 30(1–3):71–83. doi:10.1023/A:1008000327766
Schwartz S, Campbell M, Nasioulas G, Harrison J, Felber BK, Pavlakis GN (1992) Mutational inactivation of an inhibitory sequence in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 results in Rev-independent gag expression. J Virol 66(12):7176–7182
Tagliamonte M, Visciano ML, Tornesello ML, De Stradis A, Buonaguro FM, Buonaguro L (2010) Constitutive expression of HIV-VLPs in stably transfected insect cell line for efficient delivery system. Vaccine 28(39):6417–6424. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.07.054
Tagliamonte M, Visciano ML, Tornesello ML, De Stradis A, Buonaguro FM, Buonaguro L (2011) HIV-Gag VLPs presenting trimeric HIV-1 gp140 spikes constitutively expressed in stable double transfected insect cell line. Vaccine 29(31):4913–4922. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.05.004
Thompson BC, Segarra CR, Mozley OL, Daramola O, Field R, Levison PR, James DC (2012) Cell line specific control of polyethylenimine-mediated transient transfection optimized with “Design of experiments” methodology. Biotechnol Prog 28(1):179–187. doi:10.1002/btpr.715
Transfiguracion J, Jaalouk DE, Ghani K, Galipeau J, Kamen A (2003) Size-exclusion chromatography purification of high-titer vesicular stomatitis virus G glycoprotein-pseudotyped retrovectors for cell and gene therapy applications. Hum Gene Ther 14(12):1139–1153. doi:10.1089/104303403322167984
Tuvesson O, Uhe C, Rozkov A, Lullau E (2008) Development of a generic transient transfection process at 100 L scale. Cytotechnology 56(2):123–136. doi:10.1007/s10616-008-9135-2
Valley-Omar Z, Meyers AE, Shephard EG, Williamson AL, Rybicki EP (2011) Abrogation of contaminating RNA activity in HIV-1 Gag VLPs. Virol J 8:462. doi:10.1186/1743-422X-8-462
Vink T, Oudshoorn-Dickmann M, Roza M, Reitsma JJ, de Jong RN (2014) A simple, robust and highly efficient transient expression system for producing antibodies. Methods 65(1):5–10. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2013.07.018
Wolfel J, Essers R, Bialek C, Hertel S, Scholz-Neumann N, Schiedner G (2011) CAP-T cell expression system: a novel rapid and versatile human cell expression system for fast and high yield transient protein expression. BMC Proc 5 Suppl 8:P133. doi:10.1186/1753–6561-5-S8-P133
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Cevec Pharmaceuticals for kindly providing the CAP-T cell line as well as for valuable comments and discussions. The following reagent was obtained through the NIH AIDS Reagent Program, Division of AIDS, NIAID, NIH: pGag-EGFP (Cat#11468) from Dr. Marilyn Resh. The help of Pablo Castro and Meritxell Vendrell from Servei de Microscòpia of UAB is greatly appreciated. We would also like to thank Dr. Salvador Bartolomé (Departament de Bioquímica i de Biologia Molecular, UAB), Manuela Costa (Institut de Biotecnologia i Biomedicina, UAB), and Jose Amable Bernabé (ICMAB, CSIC) for the assistance with fluorometry, cytometry, and NTA, respectively. The authors acknowledge the support with the scientific equipment and scientific and technical assistance of Dr. Camille Roesch (Izon Science Europe Ltd., Magdalen Centre, The Oxford Science Park, Oxford, UK). This work is supported by a grant of SEIDI-Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad of Spain (BIO2012-31251) and Generalitat de Catalunya (2014 SGR 1544). Sonia Gutiérrez-Granados is a recipient of a FPU grant from the Ministerio de Educación y Deportes of Spain. Laura Cervera was a recipient of a PIF scholarship from UAB.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
Jens Wölfel is an employee of CEVEC Pharmaceuticals, the company that has developed the CAP-T cell line and has contributed with scientific advice to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gutiérrez-Granados, S., Cervera, L., Segura, M. et al. Optimized production of HIV-1 virus-like particles by transient transfection in CAP-T cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 3935–3947 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7213-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7213-x