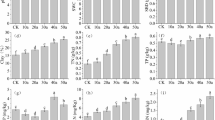
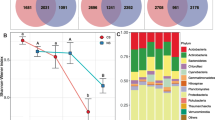
Abstract
Soil microbial autotrophs play a significant role in CO2 fixation in terrestrial ecosystem, particularly in vegetation-constrained ecosystems with environmental stresses, such as the Tibetan Plateau characterized by low temperature and high UV. However, soil microbial autotrophic communities and their driving factors remain less appreciated. We investigated the structure and shift of microbial autotrophic communities and their driving factors along an elevation gradient (4400–5100 m above sea level) in alpine grassland soils on the Tibetan Plateau. The autotrophic microbial communities were characterized by quantitative PCR, terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism (T-RFLP), and cloning/sequencing of cbbL genes, encoding the large subunit for the CO2 fixation protein ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RubisCO). High cbbL gene abundance and high RubisCO enzyme activity were observed and both significantly increased with increasing elevations. Path analysis identified that soil RubisCO enzyme causally originated from microbial autotrophs, and its activity was indirectly driven by soil water content, temperature, and NH4 + content. Soil autotrophic microbial community structure dramatically shifted along the elevation and was jointly driven by soil temperature, water content, nutrients, and plant types. The autotrophic microbial communities were dominated by bacterial autotrophs, which were affiliated with Rhizobiales, Burkholderiales, and Actinomycetales. These autotrophs have been well documented to degrade organic matters; thus, metabolic versatility could be a key strategy for microbial autotrophs to survive in the harsh environments. Our results demonstrated high abundance of microbial autotrophs and high CO2 fixation potential in alpine grassland soils and provided a novel model to identify dominant drivers of soil microbial communities and their ecological functions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfreider A, Vogt C, Geiger-Kaiser M, Psenner R (2009) Distribution and diversity of autotrophic bacteria in groundwater systems based on the analysis of RubisCO genotypes. Syst Appl Microbiol 32(2):140–150. doi:10.1016/j.syapm.2008.11.005
Babalola OO, Kirby BM, Le Roes-Hill M, Cook AE, Cary SC, Burton SG, Cowan DA (2009) Phylogenetic analysis of actinobacterial populations associated with Antarctic Dry Valley mineral soils. Environ Microbiol 11(3):566–576. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01809.x
Borodina E, Cox MJ, McDonald IR, Murrell JC (2005) Use of DNA-stable isotope probing and functional gene probes to investigate the diversity of methyl chloride-utilizing bacteria in soil. Environ Microbiol 7(9):1318–1328. doi:10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00819.x
Chen DY, Yan XJ, Xu JL, Su XL, Li LJ (2013) Lipidomic profiling and discovery of lipid biomarkers in Stephanodiscus sp. under cold stress. Metabolomics 9(5):949–959. doi:10.1007/s11306-013-0515-z
Ding YJ, Liu SY, Li J, Shangguan DH (2006) The retreat of glaciers in response to recent climate warming in western China. In: MosleyThompson E, Thompson LG (eds) Annals of glaciology, vol 43. Int Glaciological Soc, Cambridge, pp 97–105
Elsaied H, Naganuma T (2001) Phylogenetic diversity of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase large-subunit genes from deep-sea microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(4):1751–1765. doi:10.1128/aem.67.4.1751-1765.2001
Fierer N, Jackson RB (2006) The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. PNAS 103(3):626–631. doi:10.1073/pnas.0507535103
Ge T, Yuan H, Zhu H, Wu X, Sa N, Liu C, Tong C, Wu J, Brookes P (2012) Biological carbon assimilation and dynamics in a flooded rice-soil system. Soil Biol Biochem 48:39–46. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.01.009
Gourion B, Delmotte N, Bonaldi K, Nouwen N, Vorholt JA, Giraud E (2011) Bacterial RuBisCO is required for efficient Bradyrhizobium/Aeschynomene symbiosis. PLoS One 6(7), e21900. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0021900
Guo GX, Deng H, Qiao M, Yao HY, Zhu YG (2013a) Effect of long-term wastewater irrigation on potential denitrification and denitrifying communities in soils at the watershed scale. Environ Sci Technol 47(7):3105–3113. doi:10.1021/es304714a
Guo Q, Kelt DA, Sun Z, Liu H, Hu L, Ren H, Wen J (2013b) Global variation in elevational diversity patterns. Sci Rep 3 doi:10.1038/srep03007
Han JI, Choi HK, Lee SW, Orwin PM, Kim J, LaRoe SL, Tg K, O’Neil J, Leadbetter JR, Lee SY, Hur CG, Spain JC, Ovchinnikova G, Goodwin L, Han C (2011) Complete genome sequence of the metabolically versatile plant growth-promoting endophyte Variovorax paradoxus S110. J Bacteriol 193(5):1183–1190. doi:10.1128/jb.00925-10
Hart KM, Kulakova AN, Allen CCR, Simpson AJ, Oppenheimer SF, Masoom H, Courtier-Murias D, Soong R, Kulakov LA, Flanagan PV, Murphy BT, Kelleher BP (2013) Tracking the fate of microbially sequestered carbon dioxide in soil organic matter. Environ Sci Technol 47(10):5128–5137. doi:10.1021/es3050696
Janatkova K, Rehakova K, Dolezal J, Simek M, Chlumska Z, Dvorsky M, Kopecky M (2013) Community structure of soil phototrophs along environmental gradients in arid Himalaya. Environ Microbiol 15(9):2505–2516. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.12132
Jin Z, Zhuang Q, He J-S, Luo T, Shi Y (2013) Phenology shift from 1989 to 2008 on the Tibetan Plateau: an analysis with a process-based soil physical model and remote sensing data. Clim Chang 119(2):435–449. doi:10.1007/s10584-013-0722-7
John DE, Wang ZA, Liu X, Byrne RH, Corredor JE, Lopez JM, Cabrera A, Bronk DA, Tabita FR, Paul JH (2007) Phytoplankton carbon fixation gene (RuBisCO) transcripts and air-sea CO2 flux in the Mississippi River plume. ISME J 1(6):517–531. doi:10.1038/ismej.2007.70
Kong WD, Ream DC, Priscu JC, Morgan-Kiss RM (2012a) Diversity and expression of RubisCO genes in a perennially ice-covered Antarctic lake during the polar night transition. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(12):4358–4366. doi:10.1128/aem.00029-12
Kong WD, Dolhi JM, Chiuchiolo A, Priscu J, Morgan-Kiss RM (2012b) Evidence of form II RubisCO (cbbM) in a perennially ice-covered Antarctic lake. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 82(2):491–500. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2012.01431.x
Lukow T, Dunfield PF, Liesack W (2000) Use of the T-RFLP technique to assess spatial and temporal changes in the bacterial community structure within an agricultural soil planted with transgenic and non-transgenic potato plants. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 32(3): 241–247
Lutz AF, Immerzeel WW, Shrestha AB, Bierkens MFP (2014) Consistent increase in High Asia’s runoff due to increasing glacier melt and precipitation. Nat Clim Chang 4:587–592. doi:10.1038/nclimate2237
Miltner A, Richnow HH, Kopinke FD, Kastner M (2004) Assimilation of CO2 by soil microorganisms and transformation into soil organic matter. Org Geochem 35(9):1015–1024. doi:10.1016/j.orggeochem.2004.05.001
Mosier AC, Li Z, Thomas BC, Hettich RL, Pan C, Banfield JF (2015) Elevated temperature alters proteomic responses of individual organisms within a biofilm community. ISME J 9:180–194. doi:10.1038/ismej.2014.113
Nagashima S, Kamimura A, Shimizu T, Nakamura-Isaki S, Aono E, Sakamoto K, Ichikawa N, Nakazawa H, Sekine M, Yamazaki S, Fujita N, Shimada K, Hanada S, Nagashima KVP (2012) Complete genome sequence of phototrophic Betaproteobacterium Rubrivivax gelatinosus IL144. J Bacteriol 194(13):3541–3542. doi:10.1128/jb.00511-12
Nanba K, King GM, Dunfield K (2004) Analysis of facultative lithotroph distribution and diversity on volcanic deposits by use of the large subunit of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Appl Environ Microbiol 70(4):2245–2253. doi:10.1128/aem.70.4.2245-2253.2004
Nogues-Bravo D, Araujo MB, Romdal T, Rahbek C (2008) Scale effects and human impact on the elevational species richness gradients. Nature 453(7192):216–219, http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v453/n7192/suppinfo/nature06812_S1.html
Paul JH, Alfreider A, Kang JB, Stokes RA, Griffin D, Campbell L, Ornolfsdottir E (2000) Form IA rbcL transcripts associated with a low salinity/high chlorophyll plume (‘Green River’) in the eastern Gulf of Mexico. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 198:1–8. doi:10.3354/meps198001
Ren W, Tan HC, Wu J, Deng YC, Wu YB, Tang YH, Cui XY (2010) UV light spectral response of photosynthetic photochemical efficiency in alpine mosses. J Plant Ecol 3(1):17–24. doi:10.1093/jpe/rtp029
Rousk J, Baath E, Brookes PC, Lauber CL, Lozupone C, Caporaso JG, Knight R, Fierer N (2010) Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J 4(10):1340–1351. doi:10.1038/ismej.2010.58
Saros JE, Michel TJ, Interlandi SJ, Wolfe AP (2005) Resource requirements of Asterionella formosa and Fragilaria crotonensis in oligotrophic alpine lakes: implications for recent phytoplankton community reorganizations. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 62(7):1681–1689. doi:10.1139/f05-077
Satola B, Wübbeler J, Steinbüchel A (2013) Metabolic characteristics of the species Variovorax paradoxus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(2):541–560. doi:10.1007/s00253-012-4585-z
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB (2009) Introducing mothur: open source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541. doi:10.1128/aem.01541-09
Selesi D, Schmid M, Hartmann A (2005) Diversity of green-like and red-like ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase large-subunit genes (cbbL) in differently managed agricultural soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(1):175–184. doi:10.1128/aem.71.1.175-184.2005
Shen C, Xiong J, Zhang H, Feng Y, Lin X, Li X, Liang W, Chu H (2013) Soil pH drives the spatial distribution of bacterial communities along elevation on Changbai Mountain. Soil Biol Biochem 57:204–211. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.07.013
Shen MG, Zhang GX, Cong N, Wang SP, Kong WD, Piao SL (2014) Increasing altitudinal gradient of spring vegetation phenology during the last decade on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric For Meteorol 189:71–80. doi:10.1016/j.agrformet.2014.01.003
Shipley B (2000) Cause and correlation in biology: a user’s guide to path analysis, structural equations, and causal inference. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Singh J, Tabita FR (2010) Roles of RubisCO and the RubisCO-like protein in 5-methylthioadenosine metabolism in the nonsulfur purple bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Bacteriol 192(5):1324–1331. doi:10.1128/jb.01442-09
Su YG, Wu L, Zhou ZB, Liu YB, Zhang YM (2013) Carbon flux in deserts depends on soil cover type: a case study in the Gurbantunggute desert, north China. Soil Biol Biochem 58:332–340. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2012.12.006
Tabita FR, Satagopan S, Hanson TE, Kreel NE, Scott SS (2008) Distinct form I, II, III, and IV Rubisco proteins from the three kingdoms of life provide clues about Rubisco evolution and structure/function relationships. J Exp Bot 59(7):1515–1524. doi:10.1093/jxb/erm361
Takai K, Campbell BJ, Cary SC, Suzuki M, Oida H, Nunoura T, Hirayama H, Nakagawa S, Suzuki Y, Inagaki F, Horikoshi K (2005) Enzymatic and genetic characterization of carbon and energy metabolisms by deep-sea hydrothermal chemolithoautotrophic isolates of Epsilonproteobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(11):7310–7320. doi:10.1128/aem.71.11.7310-7320.2005
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30(12):2725–2729. doi:10.1093/molbev/mst197
Tan KH (2005) Soil sampling, preparation and analysis. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Thomas EK, Huang Y, Morrill C, Zhao J, Wegener P, Clemens SC, Colman SM, Gao L (2014) Abundant C-4 plants on the Tibetan Plateau during the Lateglacial and early Holocene. Quat Sci Rev 87:24–33. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2013.12.014
Tolli J, King GM (2005) Diversity and structure of bacterial chemolithotrophic communities in pine forest and agroecosystem soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(12):8411–8418. doi:10.1128/aem.71.12.8411-8418.2005
Vetaas OR, Grytnes J-A (2002) Distribution of vascular plant species richness and endemic richness along the Himalayan elevation gradient in Nepal. Glob Ecol Biogeogr 11(4):291–301. doi:10.1046/j.1466-822X.2002.00297.x
Videmšek U, Hagn A, Suhadolc M, Radl V, Knicker H, Schloter M, Vodnik D (2009) Abundance and diversity of CO2-fixing bacteria in grassland soils close to natural carbon dioxide springs. Microb Ecol 58(1):1–9. doi:10.1007/s00248-008-9442-3
Wang B, Bao Q, Hoskins B, Wu G, Liu Y (2008) Tibetan plateau warming and precipitation changes in East Asia. Geophys Res Lett 35(14). doi:10.1029/2008gl034330
Wang Y, Julio Camarero J, Luo T, Liang E (2012) Spatial patterns of Smith fir alpine treelines on the south-eastern Tibetan Plateau support that contingent local conditions drive recent treeline patterns. Plant Ecolog Divers 5(3):311–321. doi:10.1080/17550874.2012.704647
Wang Z, Luo T, Li R, Tang Y, Du M (2013) Causes for the unimodal pattern of biomass and productivity in alpine grasslands along a large altitudinal gradient in semi-arid regions. J Veg Sci 24(1):189–201. doi:10.1111/j.1654-1103.2012.01442.x
Wang JT, Cao P, Hu HW, Li J, Han LL, Zhang LM, Zheng YM, He JZ (2015) Altitudinal distribution patterns of soil bacterial and archaeal communities along Mt. Shegyla on the Tibetan Plateau. Microb Ecol 69(1):135–145. doi:10.1007/s00248-014-0465-7
Wu X, Ge T, Yuan H, Li B, Zhu H, Zhou P, Sui F, O’Donnell AG, Wu J (2014a) Changes in bacterial CO2 fixation with depth in agricultural soils. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(5):2309–2319. doi:10.1007/s00253-013-5179-0
Wu X, Ge T, Yuan H, Zhou P, Chen X, Chen S, Brookes P, Wu J (2014b) Evaluation of an optimal extraction method for measuring d-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RubisCO) in agricultural soils and its association with soil microbial CO2 assimilation. Pedobiologia 57(4–6):277–284. doi:10.1016/j.pedobi.2014.06.002
Xiao KQ, Bao P, Bao QL, Jia Y, Huang FY, Su JQ, Zhu YG (2014a) Quantitative analyses of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RubisCO) large-subunit genes (cbbL) in typical paddy soils. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 87(1):89–101. doi:10.1111/1574-6941.12193
Xiao KQ, Nie SA, Bao P, Wang FH, Bao QL, Zhu YG (2014b) Rhizosphere effect has no effect on marker genes related to autotrophic CO2 fixation in paddy soils? J Soils Sediments 14(6):1082–1087. doi:10.1007/s11368-014-0864-x
Xu HH, Tabita FR (1996) Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase gene expression and diversity of Lake Erie planktonic microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 62(6):1913–1921
Yang Y, Gao Y, Wang S, Xu D, Yu H, Wu L, Lin Q, Hu Y, Li X, He Z, Deng Y, Zhou J (2014) The microbial gene diversity along an elevation gradient of the Tibetan grassland. ISME J 8(2):430–440. doi:10.1038/ismej.2013.146
Yao HY, Campbell CD, Chapman SJ, Freitag TE, Nicol GW, Singh BK (2013) Multi-factorial drivers of ammonia oxidizer communities: evidence from a national soil survey. Environ Microbiol 15(9):2545–2556. doi:10.1111/1462-2920.12141
Yuan HZ, Ge TD, Chen CY, O’Donnell AG, Wu JS (2012a) Significant role for microbial autotrophy in the sequestration of soil carbon. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(7):2328–2336. doi:10.1128/aem.06881-11
Yuan HZ, Ge TD, Wu XH, Liu SL, Tong CL, Qin HL, Wu MN, Wei WX, Wu JS (2012b) Long-term field fertilization alters the diversity of autotrophic bacteria based on the ribulose-1,5-biphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RubisCO) large-subunit genes in paddy soil. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95(4):1061–1071. doi:10.1007/s00253-011-3760-y
Yuan Y, Si G, Wang J, Luo T, Zhang G (2014) Bacterial community in alpine grasslands along an altitudinal gradient on the Tibetan Plateau. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 87(1):121–132. doi:10.1111/1574-6941.12197
Zhang LM, Wang M, Prosser JI, Zheng YM, He JZ (2009) Altitude ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in soils of Mount Everest. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 70(2):208–217. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2009.00775.x
Zheng Y, Yang W, Hu H-W, Kim YC, Duan JC, Luo CY, Wang SP, Guo LD (2014) Ammonia oxidizers and denitrifiers in response to reciprocal elevation translocation in an alpine meadow on the Tibetan Plateau. J Soils Sediments 14(6):1189–1199. doi:10.1007/s11368-014-0867-7
Acknowledgments
This project was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41401287 to GG and 41471054 to WK), Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZZD-EW-TZ-14 and XDB15010203 to WK), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2014 M550095 to GG and 2014M550849 to JL). We thank Dr. Tianxiang Luo for the thoughtful discussions and suggestions. Reagents for RubisCO enzyme activity assay were partially provided by Dr. Baichen Wang.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 740 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, G., Kong, W., Liu, J. et al. Diversity and distribution of autotrophic microbial community along environmental gradients in grassland soils on the Tibetan Plateau. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 8765–8776 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6723-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6723-x