Abstract
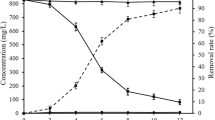
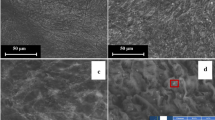
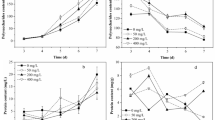
Extensive studies have been operated on the biosorption of heavy metal using white-rot fungi, whereas information on the stability of the sorbed metal species has never been taken into consideration, which is important for the later disposal of the used biomass. In this study, the growing cells of Phanerochaete chrysosporium were used to remove Pb from the fungal living environment. The bioremoval of Pb proceeded continually until 121 h. The bioremoved Pb was found to be stabilized at the first time P. chrysosporium was exposed to Pb ions. The extractable rate of removed Pb decreased constantly and kept at a stable level around 20 % after 121 h. The results indicated that the growing biomass is efficient for the stabilization of Pb, and the used biomass was suitable to be separated for further disposal at 121 h. With environment scanning electron microscopy coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray analysis (ESEM-EDAX) and X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) analysis, the stabilized Pb species were identified to be lead oxalate and lead chloride phosphate. Further, it is found that the stabilization of Pb by growing P. chrysosporium is not strictly limited in the aspect of pH when pH in the environment is in the range of 4–6.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldrian P (2003) Interactions of heavy metals with white-rot fungi. Enzyme Microb Technol 32:78–91
Barr DP, Aust SD (1994) Mechanisms white rot fungi use to degrade pollutants. Environ Sci Technol 28:78A–87A
Chisholm JE, Jones GC, Purvis OW (1987) Hydrated copper oxalate, moolooite, in lichens. Mineral Mag 51:715–718
Connolly JH, Jellison J (1995) Calcium translocation, calcium oxalate accumulation, and hyphal sheath morphology in the white-rot fungus Resinicium bicolor. Can J Bot 73:927–936
Gadd GM (1993) Interactions of fungi with toxic metals. New Phytol 124:25–60
Gadd GM (2010) Metals, minerals and microbes: geomicrobiology and bioremediation. Microbiology 156:609–643
Gomes P, Lennartsson P, Persson NK, Taherzadeh M (2014) Heavy metal biosorption by Rhizopus sp. biomass immobilized on textiles. Water Air Soil Pollut 225:1–10
Hashim MA, Mukhopadhyay S, Sahu JN, Sengupta B (2011) Remediation technologies for heavy metal contaminated groundwater. J Environ Manage 92:2355–2388
Horsfall MJ, Spiff AI (2004) Studies on the effect of pH on the sorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions from aqueous solutions by Caladium bicolor (wild cocoyam) biomass. Electron J Biotechnol 7:313–323
Huang DL, Zeng GM, Feng CL, Hu S, Jiang XY, Tang L, Su FF, Zhang Y, Zeng W, Liu HL (2008) Degradation of lead-contaminated lignocellulosic waste by Phanerochaete chrysosporium and the reduction of lead toxicity. Environ Sci Technol 42:4946–4951
Jarosz-Wilkołazka A, Malarczyk E, Pirszel J, Skowroński T, Leonowicz A (2002) Uptake of cadmium ions in white-rot fungus Trametes versicolor: effect of Cd(II) ions on the activity of laccase. Cell Biol Int 26:605–613
Jarosz-Wilkołazka A, Grąz M, Braha B, Menge S, Schlosser D, Krauss G-J (2006) Species-specific Cd-stress response in the white rot basidiomycetes Abortiporus biennis and Cerrena unicolor. Biometals 19:39–49
Kahraman S, Erdemoglu S, Yesilada O (2005) Biosorption of copper (II) by live and dried biomass of the white rot fungi Phanerochaete chrysosporium and Funalia trogii. Eng Life Sci 5:72–77
Kim C, Lee Y, Ong SK (2003) Factors affecting EDTA extraction of lead from lead-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 51:845–853
Kim SJ, Jeong HJ, Myung NY, Kim M, Lee JH, So H, Park RK, Kim HM, Um JY, Hong SH (2008) The protective mechanism of antioxidants in cadmium-induced ototoxicity in vitro and in vivo. Environ Health Perspect 116:854–862
Lesmana SO, Febriana N, Soetaredjo FE, Sunarso J, Ismadji S (2009) Studies on potential applications of biomass for the separation of heavy metals from water and wastewater. Biochem Eng J 44:19–41
Lestan D, Udovic M (2011) Mobility and availability of toxic metals after soil washing with chelating agents. In: Khan MS, Zaidi A, Goel R, Goel R, Musarrat J (eds) Biomanagement of metal-contaminated soils. 20. Springer, Netherlands, pp 343–364
Li NJ, Zeng GM, Huang DL, Hu S, Feng CL, Zhao MH, Lai C, Huang C, Wei Z, Xie GX (2011) Oxalate production at different initial Pb2+ concentrations and the influence of oxalate during solid-state fermentation of straw with Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Bioresour Technol 102:8137–8142
Lo IC, Yang XY (1999) EDTA extraction of heavy metals from different soil fractions and synthetic soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 109:219–236
Nriagu JO (1974) Lead orthophosphates-IV. Formation and stability of chloropyromorphite at 25 °C. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 37:367–377
Rhee Young J, Hillier S, Gadd Geoffrey M (2012) Lead transformation to pyromorphite by fungi. Curr Biol 22:237–241
Say R, Denizli A, Yakup Arıca M (2001) Biosorption of cadmium (II), lead(II) and copper(II) with the filamentous fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Bioresour Technol 76:67–70
Wang JL, Chen C (2009) Biosorbents for heavy metals removal and their future. Biotechnol Adv 27:195–226
Xu P, Zeng GM, Huang DL, Lai C, Zhao MH, Wei Z, Li NJ, Huang C, Xie GX (2012) Adsorption of Pb (II) by iron oxide nanoparticles immobilized Phanerochaete chrysosporium: equilibrium, kinetic, thermodynamic and mechanisms analysis. Chem Eng J 203:423–431
Xu P, Zeng GM, Huang DL, Hu S, Feng CL, Lai C, Zhao MH, Huang C, Li NJ, Wei Z (2013) Synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles and their application in Phanerochaete chrysosporium immobilization for Pb(II) removal. Colloid Surface A 419:147–155
Zheng S, Huang H, Zhang R, Cao L (2014) Removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions by fruiting bodies of the jelly fungus (Auricularia polytricha). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:8729–8736
Acknowledgments
The study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51039001, 51278176, 51378190, and 51408206), the Environmental Protection Technology Research Program of Hunan (2007185), the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20100161110012), New Century Excellent Talents in University (NECT-13-0186), the Young Teacher Growth Program of Hunan University, Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (521293050), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Hunan University Fund for Multidisciplinary Developing (531107040762), and the Hunan Provincial Innovation Foundation for Postgraduate (CX2014B141).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 163 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, G., Li, N., Huang, D. et al. The stability of Pb species during the Pb removal process by growing cells of Phanerochaete chrysosporium . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99, 3685–3693 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6275-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6275-5