Abstract
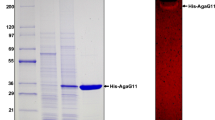
Alteromonas sp. GNUM-1 is known to degrade agar, the main cell wall component of red macroalgae, for their growth. A putative agarase gene (agaG1) was identified from the mini-library of GNUM-1, when extracellular agarase activity was detected in a bacterial transformant. The nucleotide sequence revealed that AgaG1 had significant homology to GH16 agarases. agaG1 encodes a primary translation product (34.7 kDa) of 301 amino acids, including a 19-amino-acid signal peptide. For intracellular expression, a gene fragment encoding only the mature form (282 amino acids) was cloned into pGEX-5X-1 in Escherichia coli, where AgaG1 was expressed as a fusion protein with GST attached to its N-terminal (GST-AgaG1). GST-AgaG1 purified on a glutathione sepharose column had an apparent molecular weight of 59 kDa on SDS-PAGE, and this weight matched with the estimated molecular weight (58.7 kDa). The agarase activity of the purified protein was confirmed by the zymogram assay. GST-AgaG1 could hydrolyze the artificial chromogenic substrate, p-nitrophenyl-β-d-galactopyranoside but not p-nitrophenyl-α-d-galactopyranoside. The optimum pH and temperature for GST-AgaG1 activity were identified as 7.0 and 40 °C, respectively. GST-AgaG1 was stable up to 40 °C (100 %), and it retained more than 70 % of its initial activity at 45 °C after heat treatment for 30 min. The K m and V max for agarose were 3.74 mg/ml and 23.8 U/mg, respectively. GST-AgaG1 did not require metal ions for its activity. Thin layer chromatography analysis, mass spectrometry, and 13C-nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry of the GST-AgaG1 hydrolysis products revealed that GST-AgaG1 is an endo-type β-agarase that hydrolyzes agarose and neoagarotetraose into neoagarobiose.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allouch J, Jam M, Helbert W, Barbeyron T, Kloareg B, Henrissat B, Czjzek M (2003) The three dimensional structures of two beta agarases. J Biol Chem 278:47171–47180
Aoki T, Araki T, Kitamikado M (1990) Purification and characterization of a novel beta-agarase from Vibrio sp. AP-2. Eur J Biochem 187:461–465
Araki C (1959) Seaweed polysaccharides. In: Wolfrom ML (ed) Carbohydrate chemistry of substances of biological interest. Pergamon, London, pp 15–30
Chi WJ, Chang YK, Hong SK (2012) Agar degradation by microorganisms and agar-degrading enzymes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94:917–930
Correc G, Hehemann J-H, Czjzek M, Helbert W (2011) Structural analysis of the degradation products of porphyran digested by Zobellia galactanivorans β-porphyranase A. Carbohydr Polym 83:277–283
Gauthier G, Gauthier M, Christen R (1995) Phylogenetic analysis of the genera Alteromonas, Shewanella, and Moritella using genes coding for small-subunit rRNA sequences and division of the genus Alteromonas into two genera, Alteromonas (emended) and Pseudoalteromonas gen. nov, and proposal of twelve new species combinations. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45:755–761
Hassairi I, Ben Amar R, Nonus M, Gupta BB (2001) Production and separation of alpha-agarase from Altermonas agarlyticus strain GJ1B. Bioresour Technol 29:47–51
Hayase N, Sogabe T, Itou R, Yamamori N, Sunamori J (2003) Polymer film produced by a marine bacterium. J Biosci Bioeng 95:72–76
Hehemann JH, Correc G, Barbeyron T, Helbert W, Czjzek M, Michel G (2010) Transfer of carbohydrate-active enzymes from marine bacteria to Japanese gut microbiota. Nature 464:908–912
Kim J, Hong SK (2012) Isolation and characterization of an agarase-producing bacterial strain, Alteromonas sp. GNUM-1, from the West Sea, Korea. J Microbiol Biotechnol 23:1621–1628, Erratum (2013) 23:136
Kirimura K, Masuda N, Iwasaki Y, Nakagawa H, Kobayashi R, Usai S (1999) Purification and characterization of a novel β-agarase from an alkalophilic bacterium, Alteromonas sp. E-1. J Biosci Bioeng 87:436–441
Knutsen SH, Myslabodski DE, Larsen B, Usov AI (1994) A modified system of nomenclature for red algal galactans. Bot Mar 37:163–169
Kobayashi R, Takisada M, Suzuki T, Kirimura K, Usami S (1997) Neoagarobiose as a novel moisturizer with whitening effect. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 61:162–163
Kodama K, Shiozawa H, Ishii A (1993) Alteromonas rava sp. nov, a marine bacterium that produces a new antibiotic, thiomarinol. Ann Rep Sankyo Res Lab 45:131–136
Leon O, Quintana L, Peruzzo G, Slebe JC (1992) Purification and properties of an extracellular agarase from Alteromonas sp. strain C-1. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:4060–4063
Lineweaver H, Burk D (1934) The determination of enzyme dissociation constants. J Amer Chem Soc 56:658–666
Martinez-Checa F, Bejar V, Llamas I, Del Moral A, Quesada E (2005) Alteromonas hispanica sp. nov, a polyunsaturated fatty acid producing, halophilic bacterium isolated from Fuente de Piedra, southern Spain. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:2385–2390
Morrice LM, McLean MW, Williamson FB, Long WF (1983) Beta-agarase I and II from Pseudomonas atlantica purifications and some properties. Eur J Biochem 135:553–558
Oh C, Zoysa MD, Kwon YK, Heo SJ, Affan A, Jung WK, Park HS, Lee J, Son SK, Yoon KT, Kang DH (2011) Complete genome sequence of the agarase-producing marine bacterium strain S89, representing a novel species of the genus Alteromonas. J Bacteriol 193:5538–5538
Ohta Y, Hatada Y, Miyazaki M, Nogi Y, Ito S, Horikoshi K (2005) Purification and characterization of a novel α-agarase from a Thalassomonas sp. Curr Microbiol 50:212–216
Potin P, Richard C, Rochas C, Kloareg B (1993) Purification and characterization of the alpha-agarase from Alteromonas agarlyticus (Cataldi) comb. nov, strain GJ1B. Eur J Biochem 214:599–607
Raguenes G, Cambon-Bonavita MA, Lohier JF, Boisset C, Guezennec J (2003) A novel, highly viscous polysaccharide excreted by an Alteromonas isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent shrimp. Curr Microbiol 46:448–452
Rochas C, Lahaye M, Yaphe W (1986) 13C-N.M.R.-spectroscopic investigation of agarose oligomers. Carbohydr Res 148:199–207
Rochas C, Potin P, Kloareg B (1994) NMR spectroscopic investigation of agarose oligomers produced by an alpha-agarase. Carbohydr Res 253:69–77
Segel IH (1976) Enzyme kinetics. In Biochemical calculations. How to solve mathematical problems in general biochemistry, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 214–229
Temuujin U, Chi WJ, Lee SY, Chang YK, Hong SK (2011) Overexpression and biochemical characterization of DagA from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2): an endo-type β-agarase producing neoagarotetraose and neoagarohexaose. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92:749–59
Temuujin U, Chi WJ, Chang YK, Hong SK (2012) Identification and biochemical characterization of Sco3487 from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2), an exo- and endo-type β-agarase-producing neoagarobiose. J Bacteriol 194:142–149
Usov AI (1998) Structural analysis of red seaweed galactans of agar and carrageenan groups. Food Hydrocoll 12:301–308
van de Velde F, Knutsen SH, Usov AI, Rollema HS, Cerezo AS (2002) 1H and 13C high resolution NMR spectroscopy of carrageenans: application in research and industry. Trends Food Sci Technol 13:73–92
Wang J, Mou H, Jiang X, Guan H (2006) Characterization of a novel β-agarase from marine Alteromonas sp. SY37-12 and it degrading products. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:833–839
Xiao TF, Kim SM (2010) Agarase: review of major sources, categories, purification method, enzyme characteristics and applications. Mar Drugs 8:200–218
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant no. 2012-R1A1B3002174 from the Basic Research Program of the National Research Foundation (KRF) of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chi, WJ., Park, D.Y., Seo, Y.B. et al. Cloning, expression, and biochemical characterization of a novel GH16 β-agarase AgaG1 from Alteromonas sp. GNUM-1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 4545–4555 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5510-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5510-4