Abstract
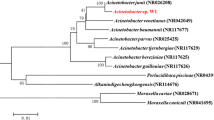
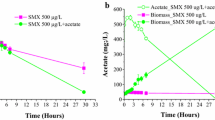
Sulfamethoxazole is a common antibiotic that is frequently detected in wastewater and surface water. This study investigated the biodegradation and metabolic pathway of sulfamethoxazole by Pseudomonas psychrophila HA-4, a cold-adapted bacterium. Strain HA-4, which uses sulfamethoxazole as its sole source of carbon and energy, was isolated at a low temperature (10 °C) and identified as P. psychrophila by physico-biochemical characterization and 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis. Strain HA-4 removed sulfamethoxazole at temperatures ranging from 5.0 °C to 30 °C, with the maximal removal rate at 10 °C. The maximal removal rate of sulfamethoxazole by strain HA-4 was 34.30 % after 192 h at 10 °C. The highest percentage of unsaturated fatty acid was determined to be 23.03 % at 10 °C, which adheres to the characteristic for cold-adapted psychrophiles and psychrotrophs. At low concentrations of sulfamethoxazole, the growth kinetics correlated well with the Haldane model. The single-substrate parameter values of sulfamethoxazole on cell growth were determined to be μ max = 0.01 h−1, K s = 20.91 mg/l and K i = 170.60 mg/l. Additionally, the major intermediates from sulfamethoxazole biodegradation by strain HA-4, including aniline, 3-amino-5-methylisoxazole, 4-aminothiophenol and sulfanilamide, were identified by GC-MS and high-resolution mass spectrometry (HR-MS) analysis. The results demonstrate that strain HA-4 has the potential to degrade sulfamethoxazole at low temperatures.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahsan S, Kaneco S, Ohta K, Mizuno T, Kani K (2001) Use of some natural and waste materials for waste water treatment. Water Res 35(15):3738–3742
Akhtar J, Amin NS, Aris A (2011) Combined adsorption and catalytic ozonation for removal of sulfamethoxazole using Fe2O3/CeO2 loaded activated carbon. Chem Eng J 170:136–144
Arutchelvan V, Kanakasabai V, Elangovan R, Nagarajan S, Muralikrishnan V (2006) Kinetics of high strength phenol degradation using Bacillus brevis. J Hazard Mater 129(1–3):216–222
Autschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EM, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215(3):403–410
Banerjee I, Modak JM, Bandopadhyay K, Das D, Maiti BR (2001) Mathematical model for evaluation of mass transfer limitations in phenol biodegradation by immobilized Pseudomonas putida. J Biotechnol 87(3):211–223
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cavicchioli R, Siddiqui KS, Andrews D, Sowers KR (2002) Low-temperature extremophiles and their applications. Curr Opin Biotechnol 13(3):253–261
Chintalapati S, Kiran MD, Shivaji S (2004) Role of membrane lipid fatty acids in cold adaptation. Mol Cell Biol 50(5):631–642
Clara M, Kreuzinger N, Strenn B, Gans O, Kroiss H (2005) The solids retention time—a suitable design parameter to evaluate the capacity of wastewater treatment plants to remove micropollutants. Water Res 39(1):97–106
Claußen M, Schmidt S (1998) Biodegradation of phenol and p-cresol by the hyphomycete Scedosporium apiospermum. Res Microbiol 149:399–406
Dantas RF, Contreras S, Sans C, Esplugas S (2008) Sulfamethoxazole abatement by means of ozonation. J Hazard Mater 150(3):790–794
Dirany A, Aaron SE, Oturan N, Sirés I, Oturan MA, Aaron JJ (2011) Study of the toxicity of sulfamethoxazole and its degradation products in water by a bioluminescence method during application of the electro-Fenton treatment [J]. Anal Bioanal Chem 400(2):353–360
Drillia P, Dokianakis SN, Fountoulakis MS (2005) On the occasional biodegradation of pharmaceuticals in the activated sludge process: the example of the antibiotic sulfamethoxazole. J Hazard Mater 122(3):259–265
Eibes G, Debernardi G, Feijoo G, Moreira M, Lema J (2011) Oxidation of pharmaceutically active compounds by a ligninolytic fungal peroxidase. Biodegradation 22(3):539–550
Garcıa-Galán MJ, Dıaz-Cruz MS, Barceló D (2009) Combining chemical analysis and ecotoxicity to determine environmental exposure and to assess risk from sulfonamides. Trends Anal Chem 28(6):804–819
Gauthier H, Yargeau V, Cooper DG (2010) Biodegradation of pharmaceuticals by Rhodococcus rhodochrous and Aspergillus niger by co-metabolism. Sci Total Environ 408(7):1701–1706
Gerday C, Aittaleb M, Bentahir M, Chessa JP, Claverie P, Collins T, D’Amico S, Dumont J, Garsoux G, Georlette D, Hoyoux A, Lonhienne T, Meuwis MA, Feller G (2000) Cold-adapted enzymes: from fundamentals to biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 18(3):103–107
González O, Sans C, Esplugas S (2007) Sulfamethoxazole abatement by photo-Fenton: toxicity, inhibition and biodegradability assessment of intermediates. J Hazard Mater 146(3):459–464
Gupta N, Roychoudhury PK, Deb JK (2005) Biotechnology of desulfurization of diesel: prospects and challenges. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66(4):356–366
Hajjouji H, Bailly JR, Winterton P, Merlina G, Revel JC, Hafidi M (2008) Chemical and spectroscopic analysis of olive mill waste water during a biological treatment. Bioresour Technol 99(11):4958–4965
Hao OJ, Kim MH, Seagren EA, Kim H (2002) Kinetics of phenol and chlorophenol utilization by Acinetobacter species. Chemosphere 46(6):797–807
Hébraud M, Potier P (1999) Cold shock response and low temperature adaptation in psychrotrophic bacteria. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 1(2):211–219
Jiang Y, Wen JP, Bai J, Jia XQ, Hu ZD (2007) Biodegradation of phenol at high initial concentration by Alcaligenes faecalis. J Hazard Mater 147:672–676
Joss A, Zabczynski S, Gobel A, Hoffmann B, Loffler D, McArdell CS, Ternes TA, Thomsen A, Siegrist H (2006) Biological degradation of pharmaceuticals in municipal wastewater treatment: proposing a classification scheme. Water Res 40(8):1686–1696
Kagle J, Porter AW, Murdoch RW, Rivera-Cancel G, Hay AG (2009) Biodegradation of pharmaceutical and personal care products. Adv Appl Microbiol 67:65–108
Larcher S, Yargeau V (2011) Biodegradation of sulfamethoxazole by individual and mixed bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91(1):211–218
Li A, Qu YY, Zhou JT, Gou M (2009a) Isolation and characteristics of a novel biphenyl-degrading bacterial strain, Dyella ginsengisoli LA-4. J Environ Sci 21(2):211–217
Li WW, Li XD, Zeng KM (2009b) Aerobic biodegradation kinetics of tannic acid in activated sludge system. Biochem Eng J 43(2):142–148
Li Y, Li J, Wang C, Wang PF (2010) Growth kinetics and phenol biodegradation of psychrotrophic Pseudomonas putida LY1. Bioresour Technol 101:6740–6744
Liu WD, Lee CY (2007) Practical identification analysis of Haldane kinetic parameters describing phenol biodegradation in batch operations. J Environ Eng Manag 17(1):71–80
Lon KC, Yu YG (2000) Kinetics of carbazole degradation by Pseudomonas putida in presence of sodium salicylate. Water Res 34(17):4131–4138
Michel H, Patrick P (1999) Cold shock response and low temperature adaptation in psychrotrophic bacteria. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 1(2):211–219
Mompelat S, LeBot B, Thomas O (2009) Occurrence and fate of pharmaceutical products and by-products, from resource to drinking water. Environ Int 35(5):803–814
Monticello DJ (2000) Biodesulfurization and the upgrading of petroleum distillates. Curr Opin Biotechnol 11(6):540–546
Neilan BA (1995) Identification and phylogeneticanalysis of toxigenic cyanobacteria by multiplex randomly amplified polymorphic DNA PCR. Appl Environ Microbiol 61(6):2286–2291
Nödler K, Licha T, Fischer S, Wagner B, Sauter M (2011) A case study on the correlation of micro-contaminants and potassium in the Leine River (Germany). Appl Geochem 26(12):2172–2180
Paxeus N (2004) Removal of selected non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), gemfibrozil, carbamazepine, beta-blockers, trimethoprim and triclosan in conventional wastewater treatment plants in five EU countries and their discharge to the aquatic environment. Water Sci Technol 50(5):253–260
Ricken B, Corvini PF, Cichocka D, Parisi M, Lenz M, Wyss D, Martínez-Lavanchy PM, Müller JA, Shahgaldian P, Tulli LG, Kohler H-PE, Kolvenbach BA (2013) ipso-Hydroxylation and subsequent fragmentation: a novel microbial strategy to eliminate sulfonamide antibiotics. Appl Environ Microbiol 79(18):5550–5558
Rodayan A, Roy R, Yargeau V (2010) Oxidation products of sulfamethoxazole in ozonated secondary effluent. J Hazard Mater 177(1):237–243
Rodrigues DF, Tiedje JM (2008) Coping with our cold planet. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(6):1677–1686
Russell NJ (1997) Psychrophilic bacteria—molecular adaptations of membrane lipids. Comp Biochem Physiol A 118:489–493
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4(4):406–425
Saravanan P, Pakshirajan K, Saha P (2008) Kinetics of phenol and m-cresol biodegradation by an indigenous mixed microbial culture isolated from a sewage treatment plant. J Environ Sci 20(12):1508–1513
Suárez S, Carballa M, Omil F, Lema J (2008) How are pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) removed from urban wastewater. Rev Environ Sci Bio/Technol 7(2):125–138
Ternes TA, Stumpf M, Mueller J, Haberer K, Wilken R, Servos M (1999) Behavior and occurrence of estrogens in municipal sewage treatment plants: I. Investigations in Germany, Canada and Brazil. Sci Total Environ 225(102):81–90
Wang LM, Li Y, Yu P, Xie ZX, Luo YB, Lin YW (2010) Biodegradation of phenol at high concentration by a novel fungal strain Paecilomyces variotii JH6. J Hazard Mater 183(1):366–371
Watanabe N, Bergamaschi BA, Loftin KA, Meyer MT, Harter T (2010) Use and environmental occurrence of antibiotics in freestall dairy farms with manured forage fields. Environ Sci Technol 44(17):6591–6600
Watkinson AJ, Murby EJ, Kolpin DW, Costanzo SD (2009) The occurrence of antibiotics in an urban watershed: from wastewater to drinking water. Sci Total Environ 407(8):2711–2723
Xu P, Yu B, Li FL, Cai XF, Ma CQ (2006) Microbial degradation of sulfur, nitrogen and oxygen heterocycles. Trends Microbiol 14(9):398–405
Xu BJ, Mao DQ, Luo Y, Xu L (2011) Sulfamethoxazole biodegradation and biotransformation in the water–sediment system of a natural river. Bioresour Technol 102(14):7069–7076
Yamazoe A, Yagi O, Oyaizu H (2004) Degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by a newly isolated dibenzofuran-utilizing Janibacter sp. strain YY-1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65(2):211–218
Yargeau V, Huot JC, Rodayan A, Rouleau L, Roy R, Leask RL (2008) Impact of degradation products of sulfamethoxazole on mammalian cultured cells. Environ Toxicol 23:492–498
Zhang D, Pan B, Zhang H, Ning P, Xing B (2010) Contribution of different sulfamethoxazole species to their overall adsorption on functionalized carbon nanotubes. Environ Sci Technol 44(10):3806–3811
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51108120 and 51178139), the National Creative Research Group of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51121062), the 4th Special Financial Grant from the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (201104430), and the 46th China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (20090460901).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 608 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, B., Li, A., Cui, D. et al. Biodegradation and metabolic pathway of sulfamethoxazole by Pseudomonas psychrophila HA-4, a newly isolated cold-adapted sulfamethoxazole-degrading bacterium. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 4671–4681 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5488-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5488-3