Abstract
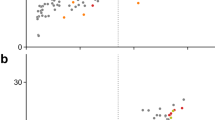
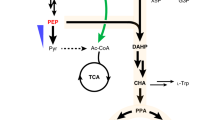
A genetically-engineered strain of the yeast Candida utilis harboring genes encoding (1) an acetoacetyl-CoA transferase from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824, (2) an acetoacetate decarboxylase, and (3) a primary–secondary alcohol dehydrogenase derived from Clostridium beijerinckii NRRL B593 produced up to 0.21 g/L of isopropanol. Because the engineered strain accumulated acetate, isopropanol titer was improved to 1.2 g/L under neutralized fermentation conditions. Optimization of isopropanol production was attempted by the overexpression and disruption of several endogenous genes. Simultaneous overexpression of two genes encoding acetyl-CoA synthetase and acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase increased isopropanol titer to 9.5 g/L. Moreover, in fed-batch cultivation, the resultant recombinant strain produced 27.2 g/L of isopropanol from glucose with a yield of 41.5 % (mol/mol). This is the first demonstration of the production of isopropanol by genetically engineered yeast.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boze H, Moulin G, Galzy P (1992) Production of food and fodder yeasts. Crit Rev Biotechnol 12:65–86
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brethauer S, Wyman CE (2010) Continuous hydrolysis and fermentation for cellulosic ethanol production. Bioresour Technol 101:4862–4874
Chen JS, Hiu SF (1986) Acetone–butanol–isopropanol production by Clostridium beijerinckii (synonym, Clostridium butylicum). Biotechnol Lett 8:371–376
De Jong-Gubbels P, van den Berg MA, Steensma HY, van Dijken JP (1997) Pronk, JT (1997) The Saccharomyces cerevisiae acetyl-coenzyme A synthetase encoded by the ACS1 gene, but not the ACS2-encoded enzyme, is subject to glucose catabolite inactivation. FEMS Microbiol Lett 153:75–81
De Virgilio C, Bürckert N, Barth G, Neuhaus JM, Boller T, Wiemken A (1992) Cloning and disruption of a gene required for growth on acetate but not on ethanol: the acetyl-coenzyme A synthetase gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 8:1043–1051
Deken DRH (1966) The Crabtree effect: a regulatory system in yeast. J Gen Microbiol 44:149–156
Dien BS, Cotta MA, Jeffries TW (2003) Bacteria engineered for fuel ethanol production: current status. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63:258–266
Dürre P (1998) New insights and novel developments in clostridial acetone/butanol/isopropanol fermentation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 49:639–648
Hanai T, Atsumi S, Liao JC (2007) Engineered synthetic pathway for isopropanol production in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:7814–7818
Hiser L, Basson ME, Rine J (1994) ERG10 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase. J Biol Chem 269:31383–31389
Ichii T, Takehara S, Konno H, Ishida T, Sato H, Suzuki A, Yamazumi K (1993) Development of a new commercial-scale airlift fermentor for rapid growth of yeast. J Ferment Bioeng 75:375–379
Ikushima S, Fujii T, Kobayashi O (2009a) Efficient gene disruption in the high-ploidy yeast Candida utilis using the Cre-loxP system. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 73:879–884
Ikushima S, Fujii T, Kobayashi O, Yoshida S, Yoshida A (2009b) Genetic engineering of Candida utilis yeast for efficient production of L-lactic acid. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 73:1818–1824
Inokuma K, Liao JC, Okamoto M, Hanai T (2010) Improvement of isopropanol production by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli using gas stripping. J Biosci Bioeng 110:696–701
Ismaiel AA, Zhu CX, Colby GD, Chen JS (1993) Purification and characterization of a primary-secondary alcohol dehydrogenase from two strains of Clostridium beijerinckii. J Bacteriol 16:5097–5105
Jojima T, Inui M, Yukawa H (2008) Production of isopropanol by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 77:1219–1224
Kondo K, Miura Y, Sone H, Kobayashi K, Iijima H (1997) High-level expression of a sweet protein, monellin, in the food yeast Candida utilis. Nat Biotechnol 15:453–457
Li Y, Wei G, Chen J (2004) Glutathione: a review on biotechnological production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66:233–242
Luong A, Hannah VC, Brown MS, Goldstein JL (2000) Molecular characterization of human acetyl-CoA synthetase, an enzyme regulated by sterol regulatory element-binding proteins. J Biol Chem 275:26458–26466
Okamura E, Tomita T, Sawa R, Nishiyama M, Kuzuyama T (2010) Unprecedented acetoacetyl-coenzyme: a synthesizing enzyme of the thiolase superfamily involved in the mevalonate pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:11265–11270
Petersen DJ, Bennett GN (1990) Purification of acetoacetate decarboxylase from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824 and cloning of the acetoacetate decarboxylase gene in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:3491–3498
Postma E, Verduyn C, Scheffers WA, Van Dijken JP (1989) Enzymic analysis of the crabtree effect in glucose-limited chemostat cultures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:468–477
Schmitt HD, Zimmermann FK (1982) Genetic analysis of the pyruvate decarboxylase reaction in yeast glycolysis. J Bacteriol 151:1146–1152
Starai VJ, Celic I, Cole RN, Boeke JD, Escalante-Semerena JC (2002) Sir2-dependent activation of acetyl-CoA synthetase by deacetylation of active lysine. Science 298:2390–2392
Tamakawa H, Ikushima S, Yoshida S (2011) Ethanol production from xylose by a recombinant Candida utilis strain expressing protein-engineered xylose reductase and xylitol dehydrogenase. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 75:1994–2000
Tamakawa H, Ikushima S, Yoshida S (2012) Efficient production of L-lactic acid from xylose by a recombinant Candida utilis strain. J Biosci Bioeng 113:73–75
Tamakawa H, Ikushima S, Yoshida S (2013) Construction of a Candida utilis strain with ratio-optimized expression of xylose-metabolizing enzyme genes by cocktail multicopy integration method. J Biosci Bioeng 115:532–539
Tomita Y, Ikeo K, Tamakawa H, Gojobori T, Ikushima S (2012) Genome and transcriptome analysis of the food-yeast Candida utilis. PLoS One 7:e37226
Van den Berg MA, Steensma HY (1995) ACS2, a Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene encoding acetyl coenzyme A synthetase, essential for growth on glucose. Eur J Biochem 231:704–713
Wiesenborn DP, Rudolph FB, Papoutsakis ET (1988) Thiolase from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824 and its role in the synthesis of acids and solvents. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:2717–2722
Wiesenborn DP, Rudolph FB, Papoutsakis ET (1989) Coenzyme A transferase from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824 and its role in the uptake of acids. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:323–329
Yamada R, Taniguchi N, Tanaka T, Ogino C, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2010) Cocktail delta-integration: a novel method to construct cellulolytic enzyme expression ratio-optimized yeast strains. Microb Cell Factories 9:32
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Aruto Yoshida, Dr. Takayoshi Kirisako, Dr. Yasuyuki Tomita, Mr. Toshikazu Tsuji, Ms. Akane Misaizu, Ms. Toshiko Kutsukake, Ms. Yuki Konoeda, and Mr. Yuusei Ikegami for valuable discussions and technical assistance throughout the course of this study. Part of this work was financed by the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO), Tokyo, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tamakawa, H., Mita, T., Yokoyama, A. et al. Metabolic engineering of Candida utilis for isopropanol production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 6231–6239 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4964-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4964-0