Abstract
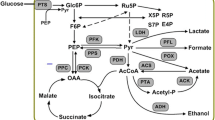
Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB), the best known polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) has been believed to change intracellular metabolic flow and oxidation/reduction state, as well as enhance stress resistance of the host. In this study, a PHB biosynthesis pathway, which contains phaCAB operon genes from Ralstonia eutropha, was introduced into an l-tryptophan producing Escherichia coli strain GPT1002. The expression of the PHB biosynthesis genes resulted in PHB accumulation inside the cells and improved the l-tryptophan production. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis showed that the transcription of tryptophan operon genes in GPT2000 increased by 1.9 to 4.3 times compared with the control, indicating that PHB biosynthesis in engineered E. coli changed the physiological state of the host. Xylose was added into the medium as co-substrate to enhance the precursor supply for PHB biosynthesis. The addition of xylose improved both extracellular l-tryptophan production and intracellular PHB accumulation. Moreover, we obtained 14.4 g l−1 l-tryptophan production and 9.7 % PHB (w/w) accumulation in GPT2000 via fed-batch cultivation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azuma S, Tsunekawa H, Okabe M, Okamoto R, Aiba S (1993) Hyper-production of l-trytophan via fermentation with crystallization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 39(4):471–476
Berry A (1996) Improving production of aromatic compounds in Escherichia coli by metabolic engineering. Trends Biotechnol 14(7):250–256
Bongaerts J, Kramer M, Muller U, Raeven L, Wubbolts M (2001) Metabolic engineering for microbial production of aromatic amino acids and derived compounds. Metab Eng 3(4):289–300
Chan E, Tsai H, Chen S, Mou D (1993) Amplification of the tryptophan operon gene in Escherichia coli chromosome to increase l-tryptophan biosynthesis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 40(2):301–305
Chavez-Bejar MI, Lara AR, Lopez H, Hernandez-Chavez G, Martinez A, Ramirez OT, Bolivar F, Gosset G (2008) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for l-tyrosine production by expression of genes coding for the chorismate mutase domain of the native chorismate mutase-prephenate dehydratase and a cyclohexadienyl dehydrogenase from Zymomonas mobilis. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(10):3284–3290
Chen Q, Wang Q, Wei G, Liang Q, Qi Q (2011) Production in Escherichia coli of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) with differing monomer compositions from unrelated carbon sources. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(14):4886–4893
de Almeida A, Catone MV, Rhodius VA, Gross CA, Pettinari MJ (2011) Unexpected stress-reducing effect of PhaP, a poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) granule-associated protein, in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(18):6622–6629
Flores S, Gosset G, Flores N, de Graaf AA, Bolivar F (2002) Analysis of carbon metabolism in Escherichia coli strains with an inactive phosphotransferase system by 13C labeling and NMR spectroscopy. Metab Eng 4(2):124–137
Gosset G (2005) Improvement of Escherichia coli production strains by modification of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system. Microb Cell Fact 4(1):14
Gosset G (2009) Production of aromatic compounds in bacteria. Curr Opin Biotechnol 20(6):651–658
Gu P, Yang F, Kang J, Wang Q, Qi Q (2012) One-step of tryptophan attenuator inactivation and promoter swapping to improve the production of l-tryptophan in Escherichia coli. Microb Cell Fact 11:30
Han M, Yoon S, Lee S (2001) Proteome analysis of metabolically engineered Escherichia coli producing poly(3-hydroxybutyrate). J Bacteriol 183:301–308
Iizuka H, Yajima T (1993) Fluorometric determination of l-tryptophan with methoxyacetaldehyde. Biol Pharm Bull 16(2):103–106
Ikeda M (2006) Towards bacterial strains overproducing l-tryptophan and other aromatics by metabolic engineering. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69(6):615–626
Juminaga D, Baidoo EE, Redding-Johanson AM, Batth TS, Burd H, Mukhopadhyay A, Petzold CJ, Keasling JD (2012) Modular engineering of l-tyrosine production in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(1):89–98
Kang Z, Gao C, Wang Q, Liu H, Qi Q (2010) A novel strategy for succinate and polyhydroxybutyrate co-production in Escherichia coli. Bioresour Technol 101(19):7675–7678
Kang Z, Du L, Kang J, Wang Y, Wang Q, Liang Q, Qi Q (2011) Production of succinate and polyhydroxyalkanoate from substrate mixture by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Bioresour Technol 102(11):6600–6604
Lee SY, Lee YK, Chang HN (1995) Stimulatory effects of amino acids and oleic acid on poly (3-hydroxybutyric acid) synthesis by recombinant Escherichia coli. J Ferment Bioeng 79(2):177–180
Lee SY, Choi J, Wong HH (1999) Recent advances in polyhydroxyalkanoate production by bacterial fermentation: mini-review. Int J Biol Macromol 25(1–3):31–36
Li R, Chen Q, Wang PG, Qi Q (2007) A novel-designed Escherichia coli for the production of various polyhydroxyalkanoates from inexpensive substrate mixture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75(5):1103–1109
Liu Q, Ouyang SP, Kim J, Chen GQ (2007) The impact of PHB accumulation on l-glutamate production by recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Biotechnol 132(3):273–279
Liu R, Liang L, Chen K, Ma J, Jiang M, Wei P, Ouyang P (2012) Fermentation of xylose to succinate by enhancement of ATP supply in metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94(4):959–968
Marx A, Eikmanns BJ, Sahm H, de Graaf AA, Eggeling L (1999) Response of the central metabolism in Corynebacterium glutamicum to the use of an NADH-dependent glutamate dehydrogenase. Metab Eng 1(1):35–48
Song S, Park C (1997) Organization and regulation of the d-xylose operons in Escherichia coli K-12: XylR acts as a transcriptional activator. J Bacteriol 179(22):7025–7032
Spiekermann P, Rehm BH, Kalscheuer R, Baumeister D, Steinbuchel A (1999) A sensitive, viable-colony staining method using Nile red for direct screening of bacteria that accumulate polyhydroxyalkanoic acids and other lipid storage compounds. Arch Microbiol 171(2):73–80
Tyo KE, Fischer CR, Simeon F, Stephanopoulos G (2010) Analysis of polyhydroxybutyrate flux limitations by systematic genetic and metabolic perturbations. Metab Eng 12(3):187–195
Wang Q, Yu H, Xia Y, Kang Z, Qi Q (2009) Complete PHB mobilization in Escherichia coli enhances the stress tolerance: a potential biotechnological application. Microb Cell Fact 8:47
Yakandawala N, Romeo T, Friesen AD, Madhyastha S (2008) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli to enhance phenylalanine production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78(2):283–291
Zhao ZJ, Zou C, Zhu YX, Dai J, Chen S, Wu D, Wu J, Chen J (2011) Development of l-tryptophan production strains by defined genetic modification in Escherichia coli. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38(12):1921–1929
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31070092), a grant of the National Basic Research Program of China (2012CB725202), a grant of Shandong Science and Technology Development Plan (2011GSF12120), and Independent Innovation Foundation of Shandong University IIFSDU (2012ZD029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, P., Kang, J., Yang, F. et al. The improved l-tryptophan production in recombinant Escherichia coli by expressing the polyhydroxybutyrate synthesis pathway. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 4121–4127 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4665-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4665-0