Abstract
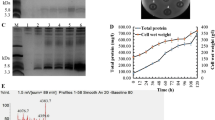
A novel specifically targeted antimicrobial peptide (STAMP) that was especially effective against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) was designed by fusing the AgrD1 pheromone to the N-terminal end of plectasin. This STAMP was named Agplectasin, and its gene was synthesized and expressed in Pichia pastoris X-33 via pPICZαA. The highest amount of total secreted protein reached 1,285.5 mg/l at 108 h during the 120-h induction. The recombinant Agplectasin (rAgP) was purified by cation exchange chromatography and hydrophobic exchange chromatography; its yield reached 150 mg/l with 94 % purity. The rAgP exhibited strong bactericidal activity against S. aureus but not Staphylococcus epidermidis or other types of tested bacteria. A bactericidal kinetics assay showed that the rAgP killed over 99.9 % of tested S. aureus (ATCC 25923 and ATCC 43300) in both Mueller–Hinton medium and human blood within 10 h when treated with 4× minimal inhibitory concentration. The rAgP caused only approximately 1 % hemolysis of human blood cells, even when the concentration reached 512 μg/ml, making it potentially feasible as a clinical injection agent. In addition, it maintained a high activity over a wide range of pH values (2.0–10.0) and demonstrated a high thermal stability at 100 °C for 1 h. These results suggested that this STAMP has the potential to eliminate MRSA strains without disrupting the normal flora.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai X, Teng D, Tian Z, Zhu Y, Yang Y, Wang J (2010) Contribution of bovine lactoferrin inter-lobe region to iron binding stability and antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus. BioMetals 23:431–439
Boman HG (2000) Innate immunity and the normal microflora. Immunol Rev 173:5–16
Chambers HF (2001) The changing epidemiology of Staphylococcus aureus? Emerg Infect Dis 7:178–182
Chandler JR, Dunny GM (2004) Enterococcal peptide sex pheromones: synthesis and control of biological activity. Peptides 25:1377–1388
Cho J, Lee DG (2011) The characteristic region of arenicin-1 involved with a bacterial membrane targeting mechanism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 405:422–427
Eckert R (2011) Road to clinical efficacy challenges and novel strategies for antimicrobial peptide development. Future Microbiol 6:635–651
Eckert R, Brady KM, Greenberg EP, Qi F, Yarbrough DK, He J, McHardy I, Anderson MH, Shi W (2006a) Enhancement of antimicrobial activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa by coadministration of G10KHc and tobramycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50:3833–3838
Eckert R, He J, Yarbrough DK, Qi F, Anderson MH, Shi W (2006b) Targeted killing of Streptococcus mutans by a pheromone-guided “smart” antimicrobial peptide. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50:3651–3657
Franzman MR, Burnell KK, Dehkordi-Vakil FH, Guthmiller JM, Dawson DV, Brogden KA (2009) Targeted antimicrobial activity of a specific IgG-SMAP28 conjugate against Porphyromonas gingivalis in a mixed culture. Int J Antimicrob Agents 33:14–20
Gottlieb C, Thomsen L, Ingmer H, Mygind P, Kristensen HH, Gram L (2008) Antimicrobial peptides effectively kill a broad spectrum of Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus strains independently of origin, sub-type, or virulence factor expression. BMC Microbiol 8:205–214
Hanberger H, Walther S, Leone M, Barie PS, Rello J, Lipman J, Marshall JC, Anzueto A, Sakr Y, Pickkers P, Felleiter P, Engoren M, Vincent JL (2011) Increased mortality associated with meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection in the intensive care unit: results from the EPIC II study. Int J Antimicrob Agents 38:331–335
Hara S, Mukae H, Sakamoto N, Ishimoto H, Amenomori M, Fujita H, Ishimatsu Y, Yanagihara K, Kohno S (2008) Plectasin has antibacterial activity and no affect on cell viability or IL-8 production. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 374:709–713
Highlander SK, Xie Y, He Y, Gehring A, Hu Y, Li Q, Tu SI, Shi X (2011) Genotypes and toxin gene profiles of Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates from china. PLoS One 6:e28276
Hsiao CH, Chuang CC, Tan HY, Ma DHK, Lin KK, Chang CJ, Huang YC (2012) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus ocular infection: a 10-Year hospital-based study. Ophthalmology 119:522–527
Jarraud S, Lyon GJ, Figueiredo AMS, Gérard L, Vandenesch F, Etienne J, Muir TW, Novick RP (2000) Exfoliatin-producing strains define a fourth agr specificity group in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 182:6517–6522
Ji G, Beavis RC, Novick RP (1995) Cell density control of staphylococcal virulence mediated by an octapeptide pheromone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:12055–10259
Jin T, Bokarewa M, Foster T, Mitchell J, Higgins J, Tarkowski A (2004) Staphylococcus aureus resists human defensins by production of staphylokinase, a novel bacterial evasion mechanism. J Immunol 172:1169–1176
Jin F, Xu X, Wang L, Zhang W, Gu D (2006) Expression of recombinant hybrid peptide cecropinA(1–8)-magainin2(1–12) in Pichia pastoris: purification and characterization. Protein Expr Purif 50:147–156
Johnson A (2003) The biology of mating in Candida albicans. Nat Rev Microbiol 1:106–116
Jones RN (2006) Microbiological features of vancomycin in the 21st century: minimum inhibitory concentration creep, bactericidal/static activity, and applied breakpoints to predict clinical outcomes or detect resistant strains. Clin Infect Dis 42:S13–S24
Ju H, Liang DC, Guo G (2003) Comparison of four methods to prepare Pichia genomic DNA for PCR. Tianjin Med J 31:270–272
Kaplan CW, Sim JH, Shah KR, Kolesnikova-Kaplan A, Shi WY, Eckert R (2011) Selective membrane disruption: mode of action of C16G2, a specifically targeted antimicrobial peptide. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55:3446–3452
Kim JM, Jang SA, Yu BJ, Sung BH, Cho JH, Kim SC (2008) High-level expression of an antimicrobial peptide histonin as a natural form by multimerization and furin-mediated cleavage. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:123–130
Kim HK, Thammavongsa V, Schneewind O, Missiakas D (2012) Recurrent infections and immune evasion strategies of Staphylococcus aureus. Curr Opin Microbiol 15:92–99
Köck R, Becker K, Cookson B, van Gemert-Pijnen J, Harbarth S, Kluytmans J, Mielke M, Peters G, Skov R, Struelens M (2010) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): burden of disease and control challenges in Europe. Euro Surveill 15:19688
Li L, Guo L, Lux R, Eckert R, Yarbrough D, He J, Anderson M, Shi W (2010) Targeted antimicrobial therapy against Streptococcus mutans establishes protective non-cariogenic oral biofilms and reduces subsequent infection. Int J Oral Sci 2:66–73
Lu X, Wan L, Yang H, Zhang J, Li S, Kang M, Li Y, Cheng J (2006) Fusion of fungicidal peptide dhvar4 to enterococcal peptide pheromone increases its bactericidal activity against Enterococcus faecalis. Chem Biol Drug Des 68:220–224
Mai J, Tian XL, Gallant JW, Merkley N, Biswas Z, Syvitski R, Douglas SE, Ling J, Li YH (2011) A novel target-specific, salt-resistant antimicrobial peptide against the cariogenic pathogen Streptococcus mutans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55:5205–5213
Marr AK, Gooderham WJ, Hancock REW (2006) Antibacterial peptides for therapeutic use: obstacles and realistic outlook. Curr Opin Pharmacol 6:468–472
Mygind PH, Fischer RL, Schnorr KM, Hansen MT, Sönksen CP, Ludvigsen S, Raventós D, Buskov S, Christensen B, De Maria L, Taboureau O, Yaver D, Elvig-Jørgensen SG, Sørensen MV, Christensen BE, Kjærulff S, Frimodt-Moller N, Lehrer RI, Zasloff M, Kristensen HH (2005) Plectasin is a peptide antibiotic with therapeutic potential from a saprophytic fungus. Nature 437:975–980
Neoh HM, Hori S, Komatsu M, Oguri T, Takeuchi F, Cui L, Hiramatsu K (2007) Impact of reduced vancomycin susceptibility on the therapeutic outcome of MRSA bloodstream infections. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 6:1–6
Neu HC (1992) The crisis in antibiotic resistance. Science 257:1064–1073
Otto M (2004) Quorum-sensing control in Staphylococci-a target for antimicrobial drug therapy? FEMS Microbiol Lett 241:135–141
Otto M (2012) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection is associated with increased mortality. Future Microbiol 7:189–191
Park Y, Park SN, Park SC, Shin SO, Kim JY, Kang SJ, Kim MH, Jeong CY, Hahm KS (2006) Synergism of Leu–Lys rich antimicrobial peptides and chloramphenicol against bacterial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1764:24–32
Perron GG, Zasloff M, Bell G (2006) Experimental evolution of resistance to an antimicrobial peptide. P Roy Soc B-Biol Sci 273:251–256
Qiu XQ, Wang H, Lu XF, Zhang J, Li SF, Cheng G, Wan L, Yang L, Zuo JY, Zhou YQ, Wang HY, Cheng X, Zhang SH, Ou ZR, Zhong ZC, Cheng JQ, Li YP, Wu GY (2003) An engineered multidomain bactericidal peptide as a model for targeted antibiotics against specific bacteria. Nat Biotechnol 21:1480–1485
Qiu XQ, Zhang J, Wang H, Wu GY (2005) A novel engineered peptide, a narrow-spectrum antibiotic, is effective against vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:1184–1189
Sader HS, Becker HK, Moet GJ, Jones RN (2010) Antimicrobial activity of daptomycin tested against Staphylococcus aureus with vancomycin MIC of 2 μg/mL isolated in the United States and European hospitals (2006–2008). Diagn Microbiol Infec Dis 66:329–331
Schägger H (2006) Tricine–SDS-PAGE. Nat Protoc 1:16–22
Schneider T, Kruse T, Wimmer R, Wiedemann I, Sass V, Pag U, Jansen A, Nielsen AK, Mygind PH, Raventos DS, Neve S, Ravn B, Bonvin AMJJ, De Maria L, Andersen AS, Gammelgaard LK, Sahl HG, Kristensen HH (2010) Plectasin, a fungal defensin, targets the bacterial cell wall precursor lipid II. Science 328:1168–1172
Skosyrev VS, Kulesskiy EA, Yakhnin AV, Temirov YV, Vinokurov LM (2003) Expression of the recombinant antibacterial peptide sarcotoxin IA in Escherichia coli cells. Protein Expr Purif 28:350–356
Soriano A, Marco F, Martínez JA, Pisos E, Almela M, Dimova VP, Alamo D, Ortega M, Lopez J, Mensa J (2008) Influence of vancomycin minimum inhibitory concentration on the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Clin Infect Dis 46:193–200
Tian ZG, Dong TT, Teng D, Yang YL, Wang JH (2009a) Design and characterization of novel hybrid peptides from LFB15(W4,10), HP(2–20), and cecropin A based on structure parameters by computer-aided method. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:1097–1103
Tian ZG, Dong TT, Yang YL, Teng D, Wang JH (2009b) Expression of antimicrobial peptide LH multimers in Escherichia coli C43(DE3). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83:143–149
van Leeuwen W, van Nieuwenhuizen W, Gijzen C, Verbrugh H, van Belkum A (2000) Population studies of methicillin-resistant and-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus strains reveal a lack of variability in the agrD gene, encoding a staphylococcal autoinducer peptide. J Bacteriol 182:5721–5729
Wang Y, Jiang Y, Gong T, Cui X, Li W, Feng Y, Wang B, Jiang Z, Li M (2010) High-level expression and novel antifungal activity of mouse beta defensin-1 mature peptide in Escherichia coli. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160:213–221
Yacoby I, Benhar I (2007) Targeted anti bacterial therapy. Infect Disord Drug Targets 7:221–229
Yang Y, Teng D, Zhang J, Tian Z, Wang S, Wang J (2011) Characterization of recombinant plectasin: solubility, antimicrobial activity and factors that affect its activity. Process Biochem 46:1050–1055
Yeaman M, Yount N (2003) Mechanisms of antimicrobial peptide action and resistance. Pharmacol Rev 55:27–55
Zasloff M (2002) Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature 415:389–395
Zhang J, Yang Y, Teng D, Tian Z, Wang S, Wang J (2011) Expression of plectasin in Pichia pastoris and its characterization as a new antimicrobial peptide against Staphyloccocus and Streptococcus. Protein Expr Purif 78:189–196
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge Prof. Shi Xianming, Ph.D., in the Bor Luh Food Safety Center, Shanghai Jiaotong University, for donating all the MRSA clinical isolates, and Prof. Yang Fuquan, Ph.D., in the Proteomics Platform Laboratory at the Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, for his coordination of the MALDI-TOF MS analysis. This study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 30771574, 30810303084, 30972125, and 31001026) and the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (nos. 5062031 and 5093030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, R., Teng, D., Wang, X. et al. Design, expression, and characterization of a novel targeted plectasin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 3991–4002 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4508-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4508-z