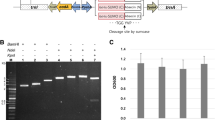
Abstract
Direct expression of an antimicrobial peptide (AMP) in Escherichia coli causes several problems such as the toxicity of AMP to the host cell, its susceptibility to proteolytic degradation, and decreased antimicrobial activity due to the additional residue(s) introduced after cleavage of AMPs from fusion partners. To overcome these problems and produce a large quantity of a potent AMP histonin (RAGLQFPVGKLLKKLLKRLKR) in E. coli, an efficient expression system was developed, in which the toxicity of histonin was neutralized by a fusion partner F4 (a truncated fragment of PurF protein) and the productivity was increased by a multimeric expression of a histonin gene. The expression level of the fusion proteins reached a maximum with a 12-mer of a histonin gene. In addition, because of the RLKR residues present at the C terminus of histonin, furin cleavage of the multimeric histonin expressed produces an intact, natural histonin. The AMP activity of the histonin produced in E. coli was identical to that of a synthetic histonin. With our expression system, 167 mg of histonin was obtained from 1 l of E. coli culture. These results may lead to a cost-effective solution for the mass production of AMPs that are toxic to a host.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cipakova I, Hostinova E, Gasperik J, Velebny V (2004) High-level expression and purification of a recombinant hBD-1 fused to LMM protein in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 37:207–212
Creemers JW, Usac EF, Bright NA, Van de Loo JW, Jansen E, Van de Ven WJ, Hutton JC (1996) Identification of a transferable sorting domain for the regulated pathway in the prohormone convertase PC2. J Biol Chem 271:25284–25291
Dhople V, Krukemeyer A, Ramamoorthy A (2006) The human beta-defensin-3, an antibacterial peptide with multiple biological functions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1758:1499–1512
Dürr UH, Sudheendra US, Ramamoorthy A (2006) LL-37, the only human member of the cathelicidin family of antimicrobial peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta 1758:1408–1425
Hancock RE, Sahl HG (2006) Antimicrobial and host-defense peptides as new anti-infective therapeutic strategies. Nat Biotechnol 24:1551–1557
Ingham AB, Moore RJ (2007) Recombinant production of antimicrobial peptides in heterologous microbial systems. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 47:1–9
Iost I, Dreyfus M (1995) The stability of Escherichia coli lacZ mRNA depends upon the simultaneity of its synthesis and translation. EMBO J 14:3252–3261
Jenssen H, Hamill P, Hancock RE (2006) Peptide antimicrobial agents. Clin Microbiol Rev 19:491–511
Kim HK, Chun DS, Kim JS, Yun CH, Lee JH, Hong SK, Kang DK (2006) Expression of the cationic antimicrobial peptide lactoferricin fused with the anionic peptide in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:330–338
Lee JH, Minn I, Park CB, Kim SC (1998) Acidic peptide-mediated expression of the antimicrobial peptide buforin II as tandem repeats in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 12:53–60
Lee JH, Kim JH, Hwang SW, Lee WJ, Yoon HK, Lee HS, Hong SS (2000) High-level expression of antimicrobial peptide mediated by a fusion partner reinforcing formation of inclusion bodies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 277:575–580
Lee JH, Kim MS, Cho JH, Kim SC (2002) Enhanced expression of tandem multimers of the antimicrobial peptide buforin II in Escherichia coli by the DEAD-box protein and trxB mutant. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58:790–796
Li L, Wang JX, Zhao XF, Kang CJ, Liu N, Xiang JH, Li FH, Sueda S, Kondo H (2005) High level expression, purification, and characterization of the shrimp antimicrobial peptide, Ch-penaeidin, in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 39:144–151
Makovitzki A, Avrahami D, Shai Y (2006) Ultrashort antibacterial and antifungal lipopeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:15997–16002
Mecke A, Lee DK, Ramamoorthy A, Orr BG, Banaszak Holl MM (2005) Membrane thinning due to antimicrobial peptide binding: an atomic force microscopy study of MSI-78 in lipid bilayers. Biophys J 89:4043–4050
Merrifield RB (1963) Solid phase peptide synthesis, I, the synthesis of a tetrapeptide. J Am Chem Soc 85:2149–2154
Molloy SS, Bresnahan PA, Leppla SH, Klimpel KR, Thomas G (1992) Human furin is a calcium-dependent serine endoprotease that recognizes the sequence Arg-X-X-Arg and efficiently cleaves anthrax toxin protective antigen. J Biol Chem 267:16396–16402
Mookherjee N, Hancock RE (2007) Cationic host defence peptides: innate immune regulatory peptides as a novel approach for treating infections. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:922–933
Moon JY, Henzler-Wildman KA, Ramamoorthy A (2006) Expression and purification of a recombinant LL-37 from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta 1758:1351–1358
Morassutti C, Amicis FD, Bandiera A, Marchetti S (2005) Expression of SMAP-29 cathelicidin-like peptide in bacterial cells by intein-mediated system. Protein Expr Purif 39:160–168
Morin KM, Arcidiacono S, Beckwitt R, Mello CM (2006) Recombinant expression of indolicidin concatamers in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70:698–704
Park CB, Yi KS, Matsuzaki K, Kim MS, Kim SC (2000) Structure–activity analysis of buforin II, a histone H2A-derived antimicrobial peptide: the proline hinge is responsible for the cell-penetrating ability of buforin II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:8245–8250
Park IY, Cho JH, Kim KS, Kim YB, Kim MS, Kim SC (2004) Helix stability confers salt resistance upon helical antimicrobial peptides. J Biol Chem 279:13896–13901
Porcelli F, Buck-Koehntop BA, Thennarasu S, Ramamoorthy A, Veglia G (2006) Structures of the dimeric and monomeric variants of magainin antimicrobial peptides (MSI-78 and MSI-594) in micelles and bilayers, determined by NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry 45:5793–5799
Ramamoorthy A, Thennarasu S, Lee DK, Tan A, Maloy L (2006) Solid-state NMR investigation of the membrane-disrupting mechanism of antimicrobial peptides MSI-78 and MSI-594 derived from magainin 2 and melittin. Biophys J 91:206–216
Rao XC, Li S, Hu JC, Jin XL, Hu XM, Huang JJ, Chen JG, Zhu JM, Hu FQ (2004) A novel carrier molecule for high-level expression of peptide antibiotics in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 36:11–18
Reddy KV, Yedery RD, Aranda C (2004) Antimicrobial peptides: premises and promises. Int J Antimicrob Agents 24:536–547
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Szynol A, de Haard JJ, Veerman EC, de Soet JJ, van Nieuw Amerongen AV (2006) Design of a peptibody consisting of the antimicrobial peptide dhvar5 and a llama variable heavy-chain antibody fragment. Chem Biol Drug Des 67:425–431
Tanaka T, Yada RY (1996) Expression of soluble cloned porcine pepsinogen A in Escherichia coli. Biochem J 315:443–446
Wei Q, Kim YS, Seo JH, Jang WS, Lee IH, Cha HJ (2005) Facilitation of expression and purification of an antimicrobial peptide by fusion with baculoviral polyhedrin in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:5038–5043
Xu X, Jin F, Yu X, Ji S, Wang J, Cheng H, Wang C, Zhang W (2007) Expression and purification of a recombinant antibacterial peptide, cecropin, from Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 53:293–301
Zasloff M (2002) Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature 415:389–395
Acknowledgments
This work was supported, in part, by grants from 21C Frontier Program of Microbial Genomics and Applications (MG05-0204-1-0), the Molecular and Cellular BioDiscovery Research Program (M1-0106-00-0200) from the Ministry of Science and Technology of Korea, the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation Grant (R01-2005-000-11010-0), and the Basic Research Program of the Korea Research Foundation Grant (KRF-2004-042-D00072).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.M., Jang, S.A., Yu, B.J. et al. High-level expression of an antimicrobial peptide histonin as a natural form by multimerization and furin-mediated cleavage. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78, 123–130 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1273-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1273-5