Abstract
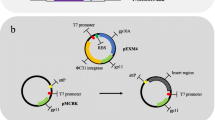
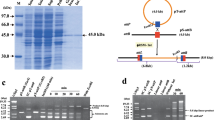
Serine-type phage integrases catalyze unidirectional site-specific recombination between the attachment sites, attP and attB, in the phage and host bacterial genomes, respectively; these integrases and DNA target sites function efficiently when transferred into heterologous cells. We previously developed an in vivo site-specific genomic integration system based on actinophage TG1 integrase that introduces ∼2-kbp DNA into an att site inserted into a heterologous Escherichia coli genome. Here, we analyzed the TG1 integrase-mediated integrations of att site-containing ∼10-kbp DNA into the corresponding att site pre-inserted into various genomic locations; moreover, we developed a system that introduces ∼10-kbp DNA into the genome with an efficiency of ∼104 transformants/μg DNA. Integrations of attB-containing DNA into an attP-containing genome were more efficient than integrations of attP-containing DNA into an attB-containing genome, and integrations targeting attP inserted near the replication origin, oriC, and the E. coli “centromere” analogue, migS, were more efficient than those targeting attP within other regions of the genome. Because the genomic region proximal to the oriC and migS sites is located at the extreme poles of the cell during chromosomal segregation, the oriC–migS region may be more exposed to the cytosol than are other regions of the E. coli chromosome. Thus, accessibility of pre-inserted attP to attB-containing incoming DNA may be crucial for the integration efficiency by serine-type integrases in heterologous cells. These results may be beneficial to the development of serine-type integrases-based genomic integration systems for various bacterial species.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boye E, Blinkova A, Walker JR (2001) Defective initiation in an Escherichia coli dnaA (Cs, Sx) mutant. Biochimie 83:25–32
Brown WR, Lee NC, Xu Z, Smith MC (2011) Serine recombinases as tools for genome engineering. Methods 53:372–379
Carrasco CD, Ramaswamy KS, Ramasubramanian TS, Golden JW (1994) Anabaena xisF gene encodes a developmentally regulated site-specific recombinase. Genes Dev 8:74–83
Christiansen B, Brondfted L, Vogensen FK, Hammer K (1996) A resolvase-like protein is required for the site-specific integration of the temperate lactococcal bacteriophage TP901-1. J Bacteriol 178:5164–5173
Fekete RA, Chattora DKA (2005) cis-acting sequence involved in chromosome in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 55:175–183
Ghosh K, Van Duyne GD (2002) Cre-loxP biochemistry. Methods 28:374–383
Gilbertson L (2003) Cre-lox recombination: Cre-active tools for plant biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 21:550–555
Gordley RM, Gersbach CA, Barbas CF III (2009) Synthesis of programmable integrases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:5053–5058
Goryshin IY, Jendrisak J, Hoffman LM, Meis R, Reznikoff WS (2000) Insertional transposon mutagenesis by electroporation of released Tn5 transposition complexes. Nat Biotechnol 18:97–100
Groth AC, Calos MP (2004) Phage integrases: biology and applications. J Mol Biol 335:667–678
Hirano N, Muroi T, Takahashi H, Haruki M (2011a) Site-specific recombinases as tools for heterologous gene integration. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92:227–239
Hirano N, Muroi T, Kihara Y, Kobayashi R, Takahashi H, Haruki M (2011b) Site-specific recombination system based on actinophage TG1 integrase for gene integration into bacterial genomes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:1877–1884
Kuhstoss S, Rao RN (1991) Analysis of the integration function of the streptomycete bacteriophage ϕC31. J Mol Biol 222:897–908
Matsuura M, Noguchi T, Yamaguchi D, Aida T, Asayama M, Takahashi H, Shirai M (1996) The sre gene (ORF469) encodes a site-specific recombinase responsible for integration of the R4 phage genome. J Bacteriol 178:3374–3376
Morita K, Yamamoto T, Fusada N, Komatsu M, Ikeda H, Hirano N, Takahashi H (2009a) The site-specific recombination system of actinophage TG1. FEMS Microbiol Lett 297:234–240
Morita K, Yamamoto T, Fusada N, Komatsu M, Ikeda H, Hirano N, Takahashi H (2009b) In vitro characterization of the site-specific recombination system based on actinophage TG1 integrase. Mol Genet Genomics 282:607–616
Morita K, Morimura K, Fusada N, Komatsu M, Ikeda H, Hirano N, Takahashi H (2012) Site-specific genome integration in alphaproteobacteria mediated by TG1 integrase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:295–304
Olivares EC, Hollis RP, Calos MP (2001) Phage R4 integrase mediates site-specific integration in human cells. Gene 278:167–176
Radman-Livaja M, Biswas T, Ellenberger T, Landy A, Aihara H (2006) DNA arms do the legwork to ensure the directionality of λ site-specific recombination. Curr Opin Struct Biol 16:42–50
Rice PA, Mouw KW, Montano SP, Boocock MR, Rowland SJ, Stark WM (2010) Orchestrating serine resolvases. Biochem Soc Trans 38:384–387
Russell JP, Chang DW, Tretiakova A, Padidam M (2006) Phage Bxb1 integrase mediates highly efficient site-specific recombination in mammalian cells. Biotechniques 40:460–464
Sato T, Samori Y, Kobayashi Y (1990) The cisA cistron of Bacillus subtilis sporulation gene spoIVC encodes a protein homologue to a site-specific recombinase. J Bacteriol 172:1092–1098
Skarstad K, Boye E, Steen HB (1986) Timing of initiation of chromosome replication in individual Escherichia coli cells. EMBO J 5:1711–1717
Smith MCM, Thorpe HM (2002) Diversity in the serine recombinases. Mol Microbiol 44:299–307
Smith MCM, Brown WRA, McEwan AR, Rowley PA (2010) Site-specific recombination by ϕC31 integrase and other large serine recombinases. Biochem Soc Trans 38:388–394
Thyagarajan B, Olivares EC, Hollis RP, Ginsburg DS, Calos MP (2001) Site-specific genomic integration in mammalian cells mediated by phage ϕC31 integrase. Mol Cell Biol 21:3926–3934
Turan S, Galla M, Ernst E, Qiao J, Voelkel C, Schiedlmeier B, Zehe C, Bode J (2011) Recombinase-mediated cassette exchange (RMCE): traditional concepts and current challenges. J Mol Biol 407:193–221
Winterberg KM, Luecke J, Bruegl AS, Reznikoff WS (2005) Phenotypic screening of Escherichia coli K-12 Tn5 insertion libraries, using whole-genome oligonucleotide microarrays. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:451–459
Xu Z, Lee NCO, Dafhnis-Calas F, Malla S, Smith MCM, Brown WRA (2008) Site-specific recombination in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and systematic assembly of a 400 kb transgene array in mammalian cells using the integrase of Streptomyces phage ϕBT1. Nucleic Acids Res 36:e9
Yamaichi Y, Niki H (2004) migS, a cis-acting site that affects bipolar positioning of oriC on the Escherichia coli chromosome. EMBO J 23:221–233
Acknowledgments
We thank M. Kyono for technical support. This work was supported by the 22nd Kato Memorial Bioscience Foundation, A-step feasibility study program AS231Z03071E from Japan Science and Technology Agency, and a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B) 22760612 and the Matching Fund Subsidy for Private Universities from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muroi, T., Kokuzawa, T., Kihara, Y. et al. TG1 integrase-based system for site-specific gene integration into bacterial genomes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 4039–4048 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4491-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4491-4