Abstract
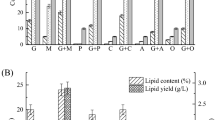
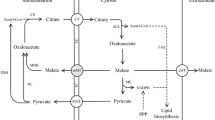
Commercial interest in microbial lipids is increasing due to their potential use as feedstock for biodiesel production. The supply of NADPH generated by malic enzyme (ME; NADP+-dependent; EC 1.1.1.40) has been postulated as being the rate-limiting step for fatty acid biosynthesis in oleaginous fungi, based mainly on data from the zygomycete Mucor circinelloides studies. This fungus contains five genes that code for six different ME isoforms. One of these genes, malA, codes for the isoforms III and IV, which have previously been associated with lipid accumulation. Following a strategy of targeted integration of an engineered malA gene, a stable strain overexpressing malA and showing high ME activity has been obtained, demonstrating the feasibility of this strategy to overexpress genes of biotechnological interest in M. circinelloides. This is the first report showing the integration and overexpression of a gene in Zygomycetes. Unexpectedly, the genetically modified strain showed a lipid content similar to that of a prototrophic non-overexpressing control strain, suggesting that another limiting step in the fatty acid synthesis pathway may have been revealed as a consequence of the elimination of malic enzyme-based bottleneck. Otherwise, the fact that prototrophic strains showed at least a 2.5-fold increase in lipid accumulation in comparison with leucine auxotrophic strains suggests that a wild-type leucine biosynthetic pathway is required for lipid accumulation. Moreover, increasing concentrations of leucine in culture medium increased growth of auxotrophs but failed to increase lipid content, suggesting that the leucine synthesized by the fungus is the only leucine available for lipid biosynthesis. These results support previous data postulating leucine metabolism as one of the pathways involved in the generation of the acetyl-CoA required for fatty acid biosynthesis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartnicki-Garcia S, Nickerson WJ (1962) Nutrition, growth, and morphogenesis of Mucor rouxii. J Bacteriol 84:841–858
Beopoulos A, Nicaud JM, Gaillardin C (2011) An overview of lipid metabolism in yeasts and its impact on biotechnological processes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:1193–1206
Chaney AL, Marbach EP (1962) Modified reagents for determination of urea and ammonia. Clin Chem 8:130–132
Courchesne NM, Parisien A, Wang B, Lan CQ (2009) Enhancement of lipid production using biochemical, genetic and transcription factor engineering approaches. J Biotechnol 141:31–41
Folch J, Lees M, Stanley GHS (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Gutierrez A, Lopez-Garcia S, Garre V (2011) High reliability transformation of the basal fungus Mucor circinelloides by electroporation. J Microbiol Methods 84:442–446
Hsu RY, Lardy HA (1967) Pigeon liver malic enzyme. II. Isolation, crystallization, and some properties. J Biol Chem 242:520–526
Kalscheuer R, Stolting T, Steinbüchel A (2006) Microdiesel: Escherichia coli engineered for fuel production. Microbiology 152:2529–2536
Kamisaka Y, Tomita N, Kimura K, Kainou K, Uemura H (2007) DGA1 (diacylglycerol acyltransferase gene) overexpression and leucine biosynthesis significantly increase lipid accumulation in the Δsnf2 disruptant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem J 408:61–68
Kerr RA (2007) Climate change. Global warming is changing the world. Science 316:188–190
Kohlhaw GB (2003) Leucine biosynthesis in fungi: entering metabolism through the back door. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 67:1–15
Kosa M, Ragauskas AJ (2011) Lipids from heterotrophic microbes: advances in metabolism research. Trends Biotechnol 29:53–61
Lasker BA, Borgia PT (1980) High-frequency heterokaryon formation by Mucor racemosus. J Bacteriol 141:565–569
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Navarro E, Sandmann G, Torres-Martinez S (1995) Mutants of the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway of Mucor circinelloides. Exp Mycol 19:186–190
Navarro E, Ruiz-Perez VL, Torres-Martinez S (2000) Overexpression of the crgA gene abolishes light requirement for carotenoid biosynthesis in Mucor circinelloides. Eur J Biochem 267:800–807
Navarro E, Lorca-Pascual JM, Quiles-Rosillo MD, Nicolas FE, Garre V, Torres-Martinez S, Ruiz-Vazquez RM (2001) A negative regulator of light-inducible carotenogenesis in Mucor circinelloides. Mol Genet Genomics 266:463–470
Nicolas FE, Torres-Martinez S, Ruiz-Vazquez RM (2003) Two classes of small antisense RNAs in fungal RNA silencing triggered by non-integrative transgenes. EMBO J 22:3983–3991
Ratledge C (1997) Microbial lipids. In: Biotechnology. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH, pp 133-197
Ratledge C (2004) Fatty acid biosynthesis in microorganisms being used for single cell oil production. Biochimie 86:807–815
Ratledge C, Wynn JP (2002) The biochemistry and molecular biology of lipid accumulation in oleaginous microorganisms. Adv Appl Microbiol 51:1–51
Roncero MI (1984) Enrichment method for the isolation of auxotrophic mutants of Mucor using the polyene antibiotic N-glycosyl-polifungin. Carlsberg Res Commun 49:685–690
Roncero MI, Jepsen LP, Stroman P, van Heeswijck HR (1989) Characterization of a leuA gene and an ARS element from Mucor circinelloides. Gene 84:335–343
Ruiz-Perez VL, Murillo FJ, Torres-Martinez S (1995) PkpA, a novel Phycomyces blakesleeanus serine/threonine protein kinase. Curr Genet 28:309–316
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, N.Y
Silva F, Navarro E, Penaranda A, Murcia-Flores L, Torres-Martinez S, Garre V (2008) A RING-finger protein regulates carotenogenesis via proteolysis-independent ubiquitylation of a white collar-1-like activator. Mol Microbiol 70:1026–1036
Song Y, Wynn JP, Li Y, Grantham D, Ratledge C (2001) A pre-genetic study of the isoforms of malic enzyme associated with lipid accumulation in Mucor circinelloides. Microbiology 147:1507–1515
Steen EJ, Kang Y, Bokinsky G, Hu Z, Schirmer A, McClure A, del Cardayre SB, Keasling JD (2010) Microbial production of fatty-acid-derived fuels and chemicals from plant biomass. Nature 463:559–562
Stephanopoulos G (2007) Challenges in engineering microbes for biofuels production. Science 315:801–804
van Heeswijck R, Roncero M (1984) High frequency transformation of Mucor with recombinant plasmid DNA. Carlsberg Res Commun 49:691–702
Velayos A, Eslava AP, Iturriaga EA (2000) A bifunctional enzyme with lycopene cyclase and phytoene synthase activities is encoded by the carRP gene of Mucor circinelloides. Eur J Biochem 267:5509–5519
Velayos A, Papp T, Aguilar-Elena R, Fuentes-Vicente M, Eslava AP, Iturriaga EA, Alvarez MI (2003) Expression of the carG gene, encoding geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase, is up-regulated by blue light in Mucor circinelloides. Curr Genet 43:112–120
Vicente G, Bautista LF, Rodriguez R, Gutierrez FJ, Sadaba I, Ruiz-Vazquez RM, Torres-Martinez S, Garre V (2009) Biodiesel production from biomass of an oleaginous fungus. Biochem Eng J 48:22–27
Vicente G, Bautista LF, Gutierrez FJ, Rodriguez R, Martinez V, Rodriguez-Frometa RA, Ruiz-Vazquez RM, Torres-Martinez S, Garre V (2010) Direct transformation of fungal biomass from submerged cultures into biodiesel. Energy Fuel 24:3173–3178
Vongsangnak W, Zhang Y, Chen W, Ratledge C, Song Y (2012) Annotation and analysis of malic enzyme genes encoding for multiple isoforms in the fungus Mucor circinelloides CBS 277.49. Biotechnol Lett 34:941–947
Vorapreeda T, Thammarongtham C, Cheevadhanarak S, Laoteng K (2012) Alternative routes of acetyl-CoA synthesis identified by comparative genomic analysis: involvement in the lipid production of oleaginous yeast and fungi. Microbiology 158:217–228
Wynn JP, Ratledge C (1997) Malic enzyme is a major source of NADPH for lipid accumulation by Aspergillus nidulans. Microbiology 143:253–257
Wynn JP, bin Abdul HA, Ratledge C (1999) The role of malic enzyme in the regulation of lipid accumulation in filamentous fungi. Microbiology 145(Pt 8):1911–1917
Zhang Y, Adams IP, Ratledge C (2007) Malic enzyme: the controlling activity for lipid production? Overexpression of malic enzyme in Mucor circinelloides leads to a 2.5-fold increase in lipid accumulation. Microbiology 153:2013–2025
Acknowledgment
We thank J. A. Madrid for technical assistance. This work was funded by the Dirección General de Investigación y Política Científica (Comunidad Autónoma de la Región de Murcia, Spain), Project BIO-BMC 07/01-0005. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez-Frómeta, R.A., Gutiérrez, A., Torres-Martínez, S. et al. Malic enzyme activity is not the only bottleneck for lipid accumulation in the oleaginous fungus Mucor circinelloides . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 3063–3072 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4432-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4432-2