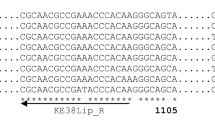
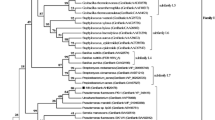
Abstract
Lipase (lip) and lipase-specific foldase (lif) genes of a biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)-synthesizing Pseudomonas resinovorans NRRL B-2649 were cloned using primers based on consensus sequences, followed by polymerase chain reaction-based genome walking. Sequence analyses showed a putative Lip gene product (314 amino acids, a.a.) with its catalytic active site (Ser111, Asp258, and His280) identified. The foldase lif gene that is located 55 bp downstream of lip codes for a putative Lif (345 a.a.). To verify the biological function of the cloned lip gene for lipase expression in P. resinovorans, we constructed a lip knock-out mutant (lip::Tn5<KAN-2>) by transposon insertion. Complementation of the lip knock-out P. resinovorans mutant with a lipase expression plasmid (pBS29-P2-lip) was performed, and its effect on lipase expression was investigated. The wild-type P. resinovorans and the lip::Tn5<KAN-2>[pBS29-P2-lip] recombinant (but not the lip::Tn5<KAN-2> mutant) showed fluorescence on rhodamine B plates indicative of lipase activity. The wild type exhibited extracellular lipase activity when grown on medium containing triacylglycerol substrates (tallow, olive oil, and tributyrin) as sole carbon sources, but the lip::Tn5<KAN-2> mutant did not show such activity. Lipase activity of various strains was also confirmed by TLC analysis of the composition of acylglycerols and free fatty acid in the extracts of the spent culture medium. We further found that tributyrin was more effective than olive oil in inducing lipase expression in P. resinovorans.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aires-Barros MR, Taipa MÂ, Cabral JMX (1994) Isolation and purification of lipases. In: Woolley P, Petersen SB (eds) lipases. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 243–270
Akiyama M, Tsuge T, Doi Y (2003) Environmental life cycle comparison of polyhydroxyalkanoates produced from renewable carbon resources by bacterial fermentation. Polym Degrad Stab 80:183–194
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Aoyama S, Yoshida N, Inouye S (1988) Cloning, sequencing and expression of the lipase gene from Pseudomonas fragi IFO-12049 in E. coli. FEBS Lett 242:36–40
Arpigny JL, Jaeger KE (1999) Bacterial lipolytic enzymes: classification and properties. Biochem J 343:177–183
Ashby RD, Foglia TA (1998) Poly(hydroxyalkanoate) biosynthesis from triglyceride substrates. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 49:431–437
Ashby RD, Foglia TA, Solaiman DKY, Liu C-K, Nunez A, Eggink G (2000) Viscoelastic properties of linseed oil-based medium chain length poly(hydroxyalkanoate) films: effects of epoxidation and curing. Int J Biol Macromol 27:355–361
Bell PJL, Sunna A, Gibbs MD, Curach NC, Nevalainen H, Bergquist PL (2002) Prospecting for novel lipase genes using PCR. Microbiology 148:2283–2291
Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, Brunak S (2004) Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J Mol Biol 340:783–795
Brandl H, Gross RA, Lenz RW, Fuller RC (1988) Pseudomonas oleovorans as a source of poly(β-hydroxyalkanoates) for potential applications as biodegradable polyesters. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:1977–1982
Brendel V, Bucher P, Nourbakhsh I, Blaisdell BE, Karlin S (1992) Methods and algorithms for statistical analysis of protein sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci 89:2002–2006
Budde CF, Ridel SL, Hűbner F, Risch S, Popović MK, Rha CK, Sinskey AJ (2011) Growth and polyhydroxybutyrate production by Ralstonia eutropha in emulsified plant oil medium. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:1611–1619
Chander H, Rangnathan B, Singh J (1979) Role of some fatty acids on the growth and lipase production by Streptococcus faecalis. J Food Sci 44:1566–1567
Chihara-Siomi M, Yoshikawa K, Oshima-Hirayama N, Yamamoto K, Sogabe Y, Nakatani T, Nishioka T, Oda J (1992) Purification, molecular cloning, and expression of lipase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Arch Biochem Biophys 296:505–513
Chung GH, Lee YP, Jeohn GH, Yoo OJ, Rhee JS (1991) Cloning and nucleotide sequence of thermostable lipase gene from Pseudomonas fluorescens SIK W1. Agric Biol Chem 55:2359–2365
Cromwick AM, Foglia T, Lenz RW (1996) The microbial production of poly(hydroxyalkanoates) from tallow. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 46:464–469
DiRusso CC, Black PN, Weimar JD (1999) Molecular inroads into the regulation and metabolism of fatty acids, lessons from bacteria. Prog Lipid Res 38:129–197
Frenken LG, Egmond MR, Batenburg AM, Bos JW, Visser C, Verrips CT (1992) Cloning of the Pseudomonas glumae lipase gene and determination of the active site residues. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:3787–3791
Gilbert EJ, Drozd JW, Jones CW (1991) Physiological regulation and optimization of lipase activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa EF2. J Gen Microbiol 137:2215–2221
Hiom K (2001) Recombination: Homologous recombination branches out. Curr Biol 11:R278–R280
Hou CT, Johnston TM (1992) Screening of lipase activities with cultures from the agricultural research service culture collection. J Am Oil Chem Soc 69:1088–1097
Ihara F, Kageyama Y, Hirata M, Nihira T, Yamada Y (1991) Purification, characterization, and molecular cloning of lactonizing lipase from Pseudomonas species. J Biol Chem 266:18135–18140
Jaeger KE, Ransac S, Koch HB, Ferrato F, Dijkstra BW (1993) Topological characterization and modeling of the 3D structure of lipase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEBS Lett 332:143–149
Jaeger KE, Ransac S, Dijkstra BW, Colson C, Heuvel M, Misset O (1994) Bacterial lipases. FEMS Microbiol Rev 15:29–63
Jorgensen S, Skov KW, Diderichsen B (1991) Cloning, sequence, and expression of a lipase gene from Pseudomonas cepacia: lipase production in heterologous hosts requires two Pseudomonas genes. J Bacteriol 173:559–567
Kim KK, Song HK, Shin DH, Hwang KY, Suh SW (1997) The crystal structure of a triacylglycerol lipase from Pseudomonas cepacia reveals a high open conformation in the absence of a bound inhibitor. Structure 5:173–185
Kim DY, Kim HW, Chung MG, Rhee YH (2007) Biosynthesis, modification, and biodegradation of bacterial medium-chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoates. J Microbiol 45:87–97
Kok RG, Nudel CB, Gonzalez RH, Nugteren-Roozant IM, Hellingwerf KH (1996) Physiological factors affecting production of extracellular lipase (LipA) in Acinetobacter calcoaceticus BD413: fatty acid repression of lipA expression and degradation of LipA. J Bacteriol 178:6025–6035
Kötting J, Eibl H (1994) Lipases and phospholipases on organic synthesis. In: Woolley P, Petersen SB (eds) Lipases. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 289–313
Kumura H, Hirose S, Sakurai H, Mikawa K, Tomita F, Shimazaki K (1998) Molecular cloning and analysis of a lipase gene from Pseudomonas fluorescens no. 33. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 62:2233–2235
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Lee JH, Akoh CC, Himmelsbach DS, Lee KT (2008) Preparation of interesterified plastic fats from fats and oils free of trans fatty acid. J Agric Food Chem 56:4039–4046
Ogino H, Katou Y, Akagi R, Mimitsuka T, Hiroshima S, Gemba Y, Doukyu N, Yasuda M, Ishimi K, Ishikawa H (2007) Cloning and expression of gene, and activation of an organic solvent-stable lipase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa LST-03. Extremophiles 11:809–817
Reeves JB, Weihrauch JL (1979) Composition of foods, fats and oils. In: Agriculture handbook no. 8–4. United States Department of Agricultural Science and Education Administration, Washington, p 15
Rosenau F, Tommassen J, Jaeger KE (2004) Lipase-specific foldases. ChemBioChem 5:152–161
Solaiman DKY (1998) Genetic transformation of Pseudomonas oleovorans by electroporation. Biotechnol Tech 12:829–832
Solaiman DKY (2000) PCR cloning of Pseudomonas resinovorans polyhydroxyalkanoate biosynthesis genes and expression in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Lett 22:789–794
Solaiman DKY, Ashby RD (2005) Genetic characterization of the poly(hydroxyalkanoate) synthases of various Pseudomonas oleovorans strains. Curr Microbiol 50:329–333
Solaiman DKY, Swingle BM (2010) Isolation of novel Pseudomonas syringae promoters and functional characterization in polyhydroxyalkanoate-producing pseudomonads. New Biotechnol 27:1–9
Tan Y, Miller KJ (1992) Cloning, expression, and nucleotide sequence of a lipase gene from Pseudomonas fluorescens B52. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:1402–1407
Tommassen J, Filloux A, Bally M, Murgier M, Lazdunski A (1992) Protein secretion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol Rev 103:73–90
Wohlfarth S, Hoesche C, Strunk C, Winkler UK (1992) Molecular genetics of the extracellular lipase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAOl. J Gen Microbiol 138:1325–1335
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported via a fellowship to JHL under the OECD Co-operative Research Programme on Biological Resource Management for Sustainable Agricultural Systems. The authors thank Nicole Crocker and Susan Lawlor for technical assistance. Mention of trade names or commercial products in this publication is solely for the purpose of providing specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J.H., Ashby, R.D., Needleman, D.S. et al. Cloning, sequencing, and characterization of lipase genes from a polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA)-synthesizing Pseudomonas resinovorans . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96, 993–1005 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4133-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4133-x