Abstract
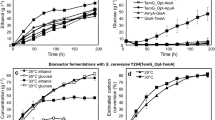
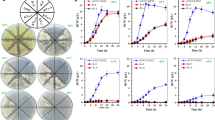
The development of a yeast that converts raw starch to ethanol in one step (called consolidated bioprocessing) could yield large cost reductions in the bioethanol industry. The aim of this study was to develop an efficient amylolytic Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain suitable for industrial bioethanol production. A native and codon-optimized variant of the Aspergillus awamori glucoamylase gene were expressed in the S. cerevisiae Y294 laboratory strain. Codon optimization resulted to be effective and the synthetic sequence sGAI was then δ-integrated into a S. cerevisiae strain with promising industrial fermentative traits. The mitotically stable recombinant strains showed high enzymatic capabilities both on soluble and raw starch (2425 and 1140 nkat/g dry cell weight, respectively). On raw corn starch, the engineered yeasts exhibited improved fermentative performance with an ethanol yield of 0.42 (g/g), corresponding to 75 % of the theoretical maximum yield.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal P, Dollimore D (1998) A thermal analysis investigation of partially hydrolyzed starch. Thermochim Acta 319:17–25
Albers E, Larsson C (2009) A comparison of stress tolerance in YPD and industrial lignocellulose-based medium among industrial and laboratory yeast strains. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:1085–1091
Allen MJ, Coutinho PM, Ford CF (1998) Stabilization of Aspergillus awamori glucoamylase by proline substitution and combining stabilizing mutations. Protein Eng 11:783–788
Bothast RJ, Schlicher MA (2005) Biotechnological processes for conversion of corn into ethanol. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:19–25
Chen HM, Ford C, Reilly PJ (1995) Identification and elimination by site-directed mutagenesis of thermolabile aspartyl bonds in Aspergillus awamori glucoamylase. Protein Eng 8:575–582
Cho KM, Yoo YJ, Kang HS (1999) δ-Integration of endo/exo-glucanase and β-glucosidase genes into the yeast chromosomes for direct conversion of cellulose to ethanol. Enzyme Microb Technol 25:23–30
de Moraes LMP, Astolfi-Filho S, Oliver SG (1995) Development of yeast strains for the efficient utilization of starch: evaluation of constructs that express alpha-amylase and glucoamylase separately or as bifunctional fusion proteins. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 43:1067–1076
Den Haan R, McBride JE, La Grange DC, Lynd LR, van Zyl WH (2007) Functional expression of cellobiohydrolases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae towards one-step conversion of cellulose to ethanol. Enzyme Microb Technol 40:1291–1299
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Favaro L, Basaglia M, Saayman M, Rose SH, van Zyl WH, Casella S (2010a) Engineering amylolytic yeasts for industrial bioethanol production. Chemical Engineering Transactions 20:97–102. doi:10.3303/CET1020017
Favaro L, Basaglia M, Trento A, Saayman M, Rose SH, van Zyl WH, Casella S (2010b) Development of raw starch hydrolysing yeasts for industrial bioethanol production. J Biotechnol 150(1):142. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2010.08.371
Fierobe HP, Mirgorodskaya E, Frandsen TP, Roepstorff P, Svensson B (1997) Overexpression and characterization of Aspergillus awamori wild-type and mutant glucoamylase secreted by the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris: comparison with wild-type recombinant glucoamylase produced using Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Aspergillus niger as hosts. Protein Expression Purif 9:159–170
Garay-Arroyo A, Covarrubias AA, Clark I, Niño I, Gosset G, Martinez A (2004) Response to different environmental stress conditions of industrial and laboratory Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63:734–741
Goto M, Ekino K, Furukawa K (1997) Expression and functional analysis of a hyperglycosylated glucoamylase in a parental host. Aspergillus awamori var. kawachi. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:2940–2943
Hayashida S, Kuroda K, Ohta K, Kuhara S, Fukuda K, Sakaki Y (1989) Molecular cloning of the glucoamylase I gene of Aspergillus awamori var. kawachi for localization of the raw-starch-affinity site. RL Agric Biol Chem 53:923–929
Hahn-Hägerdal B, Karhumaa K, Larsson CU, Gorwa-Grauslund M, Görgens J, van Zyl WH (2005) Role of cultivation media in the development of yeast strains for large scale industrial use. Microb Cells Fact 4:31
Hill J, Donald KA, Griffiths DE (1991) DMSO-enhanced whole cell yeast transformation. Nucleic Acids Res 19:5791
Kang NY, Park JN, Chin JE, Blaise LH, Im SY, Bai S (2003) Construction of an amylolytic industrial strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae containing the Schwanniomyces occidentalis α-amylase gene. Biotechnol Lett 25:1847–1851
Kern L, de Montigny J, Jund R, Lacroute F (1990) The FUR1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: cloning, structure and expression of wild-type and mutant alleles. Gene 88:149–157
Khaw TS, Katakura Y, Koh J, Kondo A, Ueda M, Shioya S (2005) Evaluation of performance of different surface-engineered yeast strains for direct ethanol production from raw starch. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70:573–579
Kim MD, Rhee SK, Seo JH (2001) Enhanced production of anticoagulant hirudin in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae by chromosomal delta-integration. J Biotechnol 85:41–48
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lee FWF, Silva NA (1997) Improved efficiency and stability of multiple cloned gene insertions at the δ sequences of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 48:339–345
Lee J, Choi SI, Jang JS, Jang K, Moon JW, Bae CS, Yang DS, Seong BL (1999) Novel secretion system of recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae using an N-terminus residue of human IL-1 beta as secretion enhancer. Biotechnol Prog 15:884–890
Martin C, Jönsson LJ (2003) Comparison of the resistance of industrial and laboratory strains of Saccharomyces and Zygosaccharomyces to lignocellulose-derived fermentation inhibitors. Enzyme Microb Technol 32:386–395
McBride JEE, Deleault KM, Lynd LR, Pronk JT (2008) Recombinant yeast strains expressing tethered cellulase enzymes. Patent PCT/US2007/085390.
Murai T, Yoshino T, Ueda M, Haranoya I, Ashikari T, Yoshizumi H, Tanaka A (1998) Evaluation of the function of arming yeast displaying glucoamylase on its cell surface by direct fermentation of corn to ethanol. J Ferment Bioeng 86:569–572
Nakamura Y, Kobayashi F, Ohnaga M, Sawada T (1997) Alcohol fermentation of starch by a genetic recombinant yeast having glucoamylase activity. Biotechnol Bioeng 53:21–25
Plüddemann A, van Zyl WH (2003) Evaluation of Aspergillus niger as host for virus-like particle production, using the hepatitis B surface antigen as a model. Curr Genet 43:439–446
Romanos MA, Scorer CA, Clare JJ (1992) Foreign gene expression in yeast: a review. Yeast 8:423–488
Sambrook J, Russel DB (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Sharp PM, Cowe E (1991) Synonymous codon usage in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 7:657–678
Shibuya I, Gomi K, Iimura Y, Takahashi K, Tamura G, Hara S (1990) Molecular cloning of the glucoamylase gene of Aspergillus shirousami and its expression in Aspergillus oryzae. RL Agric Biol Chem 54:1905–1914
van Rooyen R, Hahn-Hägerdal B, La Grange DC, van Zyl WH (2005) Construction of cellobiose-growing and fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. J Biotechnol 120:284–295
van Zyl WH, Lynd LR, den Haan R, McBride JE (2007) Consolidated Bioprocessing for bioethanol production using Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 108:205–235
Wiedemann B, Boles E (2008) Codon-optimized bacterial genes improve L-arabinose fermentation in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2043–2050
Yamada R, Bito Y, Adachi T, Tanaka T, Ogino C, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2009) Efficient production of ethanol from raw starch by a mated diploid Saccharomyces cerevisiae with integrated α-amylase and glucoamylase genes. Enzyme Microb Technol 44:344–349
Zhang J, Reddy J, Buckland B, Greasham R (2003) Toward consistent and productive complex media for industrial fermentations: studies on yeast extract for a recombinant yeast fermentation process. Biotechnol Bioeng 82:640–652
Acknowledgements
This work was partially financed by the BiotechIIbis and BiotechIII projects (Regione Veneto, Italy) and the National Research Foundation (South Africa). Dr. Lorenzo Favaro is recipient of “Assegno di ricerca Junior” grant (University of Padova). Stefania Zannoni (University of Padova) is acknowledged for HPLC analysis. Authors are grateful to Claudio Furlan (CUGAS, University of Padova) for performing SEM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Favaro, L., Jooste, T., Basaglia, M. et al. Codon-optimized glucoamylase sGAI of Aspergillus awamori improves starch utilization in an industrial yeast. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95, 957–968 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4001-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4001-8