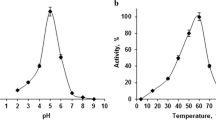
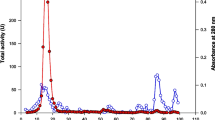
Abstract
Naringinases has attracted a great deal of attention in recent years due to its hydrolytic activities which include the production of rhamnose, and prunin and debittering of citrus fruit juices. While this enzyme is widely distributed in fungi, its production from bacterial sources is less commonly known. Fungal naringinase are very important as they are used industrially in large amounts and have been extensively studied during the past decade. In this article, production of bacterial naringinase and potential biotechnological applications are discussed. Bacterial rhamnosidases are exotype enzymes that hydrolyse terminal non-reducing α-l-rhamnosyl groups from α-l-rhamnose containing polysaccharides and glycosides. Structurally, they are classified into family 78 of glycoside hydrolases and characterized by the presence of Asp567 and Glu841 in their active site. Optimization of fermentation conditions and enzyme engineering will allow the development of improved rhamnosidases for advancing suggested industrial applications.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avila M, Jaquet M, Moine D, Requena T, Palaez C, Arigoni F (2009) Physiological and biochemical characterization of the two rhamnosidase of Lactobacillus plantarum. Microbiology 155:2739–2749
Beekwilder J, Marcozzi D, Vecchi S, deVos R, Janssen P, Francke C, Hall RD (2009) Characterization of rhamnosidases from Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus acidophilus. App Environ Microbiol 75:3447–3454
Birgisson H, Wheat JO, Hreggvidsson GO, Kristjansson JK, Mattiason B (2004) Immobilization of a recombinant E. coli producing a thermostable rhamnosidase: creation of a bioreactor for hydrolysis of naringin. Enz Microb Technol 40:1181–1187
Bok S, Jeong T, Bae KH (2000) Narigin and naringenin as inhibitors of acyl coA-cholesterol-o-acyltransferase. US Patent 6(165):984
Bornscheuer UT, Pohl M (2001) Improved biocatalysts by directed evolution and rational protein design. Curr Opin Chem Biol 5:137–143
Bourbouze R, Percheron F, Courtois JE (1976) a-l-rhamnosidase from Fagopyrum esculentum: purification and some properties. Eur J Biochem 63:331–337
Bouriche H, Arnhold J (2010) Effect of Cleome arabica leaf extract treated by naringinase on human neutrophil chemotaxis. Nat Prod Commun 5:415–418
Bram B, Solomons GL (1965) Production of the enzyme naringinase by Aspergillus niger. Appl Environ Microbiol 13:842–845
Busto MD, Meza V, Ortega N, Perez-Mateos M (2007) Immobilization of naringinase from Aspergillus niger CECT 2088 in poly (vinyl alcohol) cryogels for the debittering of fruit juices. Food Chem 104:1177–1182
Cardona ST, Mueller CL, Valvano MA (2006) Identification of essential operons with a rhamnose inducible promoter in Burkholderia cenocepacia. App Environ Microbiol 72:2547–2555
Chang HY, Lee YB, Bae HA, Huh JY, Nam SH, Sohn HS, Lee HJ, Lee SB (2011) Purification and characterization of Aspergillus sojae naringinase: the production of pruning exhibiting markedly enhanced solubility with in vitro inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase. Food Chem 124:234–241
Cui Z, Maruyama Y, Mikami B, Hashimoto W, Murata K (2006) Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic analysis of the family GH 78 α-L-rhamnosidase RhaB from Bacillus sp. GL1. Acta Cryst F62:646–648
Cui Z, Maruyama Y, Mikami B, Hashimoto W, Murata K (2007) Crystal structure of glycoside hydrolase family 78 α-l-rhamnosidase from Bacillus sp. GL1. J Mol Biol 374:384–398
Davis DW (1947) Determination of flavonones in citrus juice. Anal Chem 19:46–48
Ferreira L, Afonso C, Vila-Real H, Alfaia A, Ribeiro MHL (2008) Debittering of grapefruit juice with naringinase. Food Technol Biotechnol 46:144–148
Fukumoto J, Okada S (1973) Naringinase production by fermentation. Japanese Patent 7(306):554
Gallego MV, Pinaga F, Ramon D, Valles S (2001) Production and characterization of an Aspergillus terreus α-l-rhamnosidase of oenological interest. J Food Sci 66:204–209
Garnier P, Wang XT, Robinson MA, Perkins AC, Frier M, Davis BG (2010) Lectin directed enzyme activated prodrug therapy: synthesis and evaluation of rhamnose capped prodrugs. J Drug Targeting 18:794–802
Gaston Orillo A, Ledesmaa P, Delgadoa OD, Spagna G, Breccia JD (2007) Cold-active α-l-rhamnosidase from psychrotolerant bacteria isolated from a sub-Antarctic ecosystem. Enz Microbiol Technol 40:236–241
Giavasis I, Harvey LM, McNeil B (2000) Gellan gums. Crit Rev Biotech 20:177–211
Habelt K, Pittner F (1983) A rapid method for the determination of naringin, prunin and naringenin applied to the assay of naringinase. Anal Biochem 134:393–397
Hall D (1938) A new enzyme of the glycosidase type. Chem Ind 57:473
Han X, Ren D, Fan P, Shen T, Lou H (2008) Protective effects of narigenin-7-O-glucoside on doxorubicin induced apoptosis in H9C2 cells. Eur J Pharmacol 581:47–53
Hashimoto W, Murata K (1998) Alpha-l-rhamnosidase of Sphingomonas sp. R1 producing an unusual exopolysaccharide of sphingan. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 62:1068–1074
Hashimoto W, Miyake O, Nankai H, Murata K (2003) Molecular identification of a α-l-rhamnosidase from Bacillus sp. strain GL1 as an enzyme involved in complete metabolism of gellan. Arch Biochem Biophy 415:235–244
Jang IS, Kim DH (1996) Purification and characterization of alpha-l-rhamnosidase from Bacteroides JY-6, a human intestinal bacterium. Biol Pharm Bull 19:1546–1549
Kamiya S, Esaki S, Tanaka R (1985) Synthesis of some disaccharides containing an l-rhamnopyranosyl or l-mannopyranosyl residue, and the substrate specificity of alpha-l-rhamnosidase from Aspergillus niger. Agric Biol Chem 49:55–62
Kaul T, Middleton E, Ogra PL (1985) Antiviral effects of flavonoids on human viruses. J Med Virol 15:71–79
Kaur A, Singh RS, Puri M (2009) Strengthening of rec-rhamnosidase enhances naringin hydrolysis. J Punjab Academy Sciences 5–6:129–131
Kaur A, Singh S, Singh RS, Schwarz WH, Puri M (2010) Hydrolysis of citrus peel naringin by recombinant α-l-rhamnosidase from Clostridium stercorarium. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 85:1419–1422
Koseki T, Mese Y, Nishibori N, Masaki K, Fuhii T, Handa T, Yamane Y, Shiono Y, Murayama T, iefuji H (2008) Characterization of an α-l-rhamnosidase from Aspergillus kawachii. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 80:1007–1013
Kumar V (2010) Compartive studies on inducers in the production of naringinase from Aspergillus niger MTCC 1344. Afr J Biotechnol 9:7683–7686
Kurosawa Y, Ikeda K, Egami F (1973) a-l-rhamnosidase of the liver of Turbo cornutus and Aspergillus niger. J Biochem 73:31–37
Lei S, Xu Y, Fan G, Xiao M, Pan S (2011) Immobilization of naringinase on mesoporous molecular sieve MCM-41 and its application to debittering of white grapefruit. Appl Surface Sci 257:4096–4099
Li L, Ni H, Xiao A, Cai H (2010) Characterization of Cryptococcus sp. jmudeb008 and regulation of naringinase activity by glucose. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 50:1202–1207
Magario I, Neumann A, Oliveros E, Syldatk C (2009) Kinetic analysis and modeling of the liquid–liquid conversion of emulsified di-rhamnolipid by naringinase from P. decumbens. Biotechnol Bioeng 102:9–19
Mamma D, Kalogeris E, Kekos D, Macris BJ, Christakopoulus P (2004) Biochemical characterization of the multi-enzyme system produced by P. decumbens grown on ruitn. Food Biotechnol 18:1–18
Manzanares P, de Graaff LH, Visser J (1997) Production and characterization of an α-l-rhamnosidase from Aspergillus niger. FEMS Microbiol Lett 157:279–283
Manzanares P, van den Broeck H, de Graaff LH, Visser J (2001) Purification and characterization of two different α-l-rhamnosidase, RhaA and RhaB from Aspergillus aculeatus. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2230–2234
Manzanares P, Valles S, Ramon D, Orejas M (2007) α-l-rhamnosidase: old and new insights. In: Polaina Julio, McCabe AP (eds) Industrial enzymes: structure, function and applications. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 117–140
Mazzaferro LS, Orrillo GA, Ledesma P, Breccia JD (2008) Dose-dependent significance of monosaccharides on intracellular α-l-rhamnosidase activity from Pseudoalteromonas sp. Biotech Letts 30:2147–2150
McCarter JD, Withers SG (1994) Mechanism of enzymatic glycoside hydrolysis. Curr Opinion Struct Biol 4:885–892
McMahon H, Zoecklein BW, Fugelsang K, Jasinski Y (1999) Quantification of glycosidase activity in selected yeasts and lactic acid bacteria. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 23:198–203
Miake F, Satho T, Takesue H, Yanagida F, Kashige N, Watanabe K (2000) Purification and characterization of intracellular alpha-l-rhamnosidase from Pseudomonas paucimobilis FP2001. Arch Microbiol 173:65–70
Michlmayr H, Brandes W, Eder R, Schumann C, Hierro AM, Kulbe KD (2011) Characterization of two distinct GH family 78a-l-rhmanosidases from Pedicococcus acidilactici. Appl Environ Microbiol (in press; doi:10.1128/AEM.05317-11)
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Miyata T, Kashige N, Satho T, Yamaguchi T, Aso Y, Miake F (2005) Cloning, sequence analysis and expression of the gene encoding Sphingomonas paucimobilis FP 2001 rhamnosidase. Current Microbiol 51:105–109
Nunes MA, Vila-Real H, Fernandes PC, Ribeiro MHL (2010) Immobilization of naringinase in PVA-alginate matrix using an innovative technique. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160:2129–2147
Orejas M, Ibanez E, Ramon D (1999) The filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans produces an α-l-rhamnosidase of potential oenological interest. Lett Appl Microbiol 28:383–388
Perez-Vizcaino F, Duarte J (2010) Flavanols and cardiovascular disease. Molecular Aspects of Medicine 31:478–494
Prakash S, Singhal RS, Kulkarni PR (2002) Enzymic debittering of Indian grapefruit (Citrus paradis) juice. J Sci Food Agric 82:394–397
Puri M, Banerjee UC (2000) Production, purification and characterization of the debittering enzyme naringinase. Biotechnol Adv 18:207–217
Puri M, Kaur A (2010) Molecular identification of Staphylococcus xylosus MAK2, a new l-rhamnosidase producer. W J Microbiol Biotechnol 26:963–968
Puri M, Banerjee A, Banerjee UC (2005) Optimization of process parameters for the production of naringinase by Aspergillus niger MTCC 1344. Process Biochem 40:195–201
Puri M, Kaur A, Singh RS, Kanwar JR (2008) Immobilized enzymes for debittering citrus fruit juices, In: Busto MD, Ortega N (eds) Food Enzymes: Application of New Technologies, Transworld Research Network. Trivandrum, India, pp 91–103
Puri M, Kaur A, Singh RS, Schwarz WH, Kaur A (2010a) One step purification and immobilization of His-tagged rhamnosidase for narigin hydrolysis. Process Biochem 45:445–451
Puri M, Kaur A, Singh RS, Nahar A (2010b) Response surface optimization for the production of naringinase from Staphlococcus xylosus MAK2. Applied Biochem Biotechnol 162:181–191
Puri M, Kaur A, Barrow CJ, Singh RS (2011a) Citrus peel influences the production of an extracellular naringinase by Staphylococcus xylosus MAK 2. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:715–722
Puri M, Kaur A, Schwarz WH, Kennedy JF (2011b) Molecular characterization and enzymatic hydrolysis of naringin extracted from kinnow peel waste. Int J Biol Macromol 48:58–62
Qian S, Yu H, Zhang C, Lu M, Wang H, Jin F (2005) Purification and characterization of dioscin-α-l-rhamnosidase from pig liver. Chem Pharm Bull 53:911–914
Rajal VB, Cid AG, Ellenrieder G, Cuevas C (2009) Production, partial purification and characterization of rhamnosidase from Penicillium ulaiense. W J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:1025–1033
Ribeiro MH (2011) Naringinases: occurrences, characteristics and applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:1883–1895
Ribeiro IAC, Ribeiro MHL (2008) Kinetic modeling of naringin hydrolysis using a bitter sweet α-rhamnopyranoside immobilized in k-carragennan. J Mol Cat B Enz 51:10–18
Robinson MA, Charlton ST, Garnier P, Wang X, Davis SS (2004) LEAPT: lectin directed enzyme-activated prodrug therapy. Proc Nat Acad Sci 40:14527–14532
Rodriguez ME, Lopez CA, van Broock M, Valles S, Ramon D, Caballero AC (2004) Screening and typing of patagonian wine yeasts for glycosidase activities. J Appl Microbiol 96:84–95
Roitner M, Schalkhammer T, Pittner F (1984) Preparation of prunin with the help of immobilized naringinase pretreated with alkaline buffer. App Biochem Biotechnol 9:483–488
Romero C, Manjon A, Bastida J, Iborra JL (1985) A method for the assaying rhamnosidase activity of naringinase. Anal Biochem 149:566–571
Scaroni E, Cuevas C, Carrrillo L, Ellenrieder G (2002) Hydrolytic properties of crude α-l-rhamnosidase produced by several wild strains of mesophillic fungi. Lett Appl Microbiol 34:461–465
Shanmugam V, Yadav KDS (1995) Extracellular production of alpha-rhamnosidase by Rhizopus nigricans. Ind J Exp Biol 33:705–707
Sinnott ML (1990) Catalytic mechanisms of glycosyl transfer. Chem Rev 90:1171–1202
Suzuki H (1962) Hydrolysis of flavonoid glycosides by enzymes from Rhamnus and other sources. Arch Biochem Biophys 99:476–483
Thammawat K, Pongtanya P, Juntharasari V, Wongvithoonyaporn P (2008) Isolation, preliminary enzyme characterization and optimization of culture parameters for the production of naringinase isolated from Aspergillus niger BCC25166. Kaestsart J Nat Sci 42:61–72
Thirkettle J (2000) SB-253514 and analogues novel inhibitors of lipoprotein associated phospholipase A2 produced by Pseudomonas fluorescens M11579. III. Biotransformation using naringinase. J Antibiot 53:733–735
Thomas DW, Smythe CV, Labbee MD (1958) Enzymatic hydrolysis of naringin, the bitter principle of grapefruit. Food Res 23:591–598
Ting SV (1958) Enzymatic hydrolysis of naringin in grapefruit. J Agric Food Chem 6:546–549
Vila-Real H, Alfaia AJ, Calado ART, Ribeiro MHL (2010) Improvement of activity and stability of soluble and sol-gel immobilized naringinase in co-solvent systems. J Mol Catal B Enz 65:10–91
Wood TM, Bhat KM (1988) Methods for measuring cellulase activities. Methods Enzymol 160:87–112
Yadav V, Yadav PK, Yadav S, Yadav KDS (2010) Rhamnosidase: a review. Process Biochem 45:1226–1235
Yadav V, Yadav S, Yadav S, Ydav KDS (2011) Rhamnosidase from Aspergillus flavus MTCC 9606 isolated from lemon fruit peel. Int J Food Sci Technol 46:350–357
Yanai T, Sato M (2000) Purification and characterization of an rhamnosidase from Pichia angusta X349. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:2179–2185
Young NM, Johnston RAZ, Richards JC (1989) Purification of the α-l-rhamnosidase of Penicillium decumbens and characterisation of two glycopeptide components. Carbohydr Res 191:53–62
Yusof S, Ghazali HM, King GS (1990) Naringin content in local citrus fruits. Food Chem 37:113–121
Zverlov VV, Hertel C, Bronnernmeier K, Hroch A, Kellermann J, Schwarz WH (2000) The thermostable alpha-l-rhamnosidaseRamA of Clostridium stercorarium: biochemical characterization and primary structure of bacterial alpha-l-rhamnose hydrolase, a new type of inverting glycoside hydrolase. Mol Microbiol 35:173–179
Acknowledgement
The author would like to thank Director, Centre for Biotechnology and Interdisciplinary Sciences (CBIS), ITRI for providing the necessary facility to carry out this work at Deakin University, Australia. Some of the data presented in this write-up has emanated from the research work carried at Department of Biotechnology, Punjabi University, India.
Conflicts of interest
The author declare that he has no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Puri, M. Updates on naringinase: structural and biotechnological aspects. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93, 49–60 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3679-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3679-3