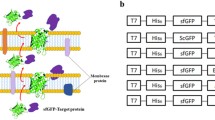
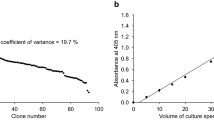
Abstract
Efficient protein secretion, the basis of large-scale production of many compounds central to the biotechnology industry, is achieved by signal peptide and propeptide optimization in addition to optimizing host factors affecting heterologous protein production. Here, we fused green fluorescent protein (GFP) to the recently identified Tat-type secretory signal peptide of CgR0949 to demonstrate a high-yield protein secretion system of Corynebacterium glutamicum. The resultant secretion vector facilitated effective secretion of active-form GFP (20 mg l−1) into C. glutamicum culture medium. The expression of GFP was enhanced 2.9-fold using the Shine–Dalgarno sequence of triosephosphate isomerase in the secretion vector. Moreover, GFP drastically accumulated in the culture supernatant upon addition of calcium chloride even though Ca2+ addition did neither enhanced the transcription of gfp nor resulted in the accumulation of cytosolic GFP. Active-form GFP concentration reached 1.8 g l−1 after 48-h incubation in a jar fermentor. Likewise, α-amylase accumulation in C. glutamicum cultures was also enhanced by Ca2+ addition, suggesting that Ca2+ may affect general protein secretion in C. glutamicum.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Billman-Jacobe H, Wang L, Kortt A, Stewart D, Radford A (1995) Expression and secretion of heterologous proteases by Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:1610–1613
Boekema BK, Beselin A, Breuer M, Hauer B, Koster M, Rosenau F, Jaeger KE, Tommassen J (2007) Hexadecane and Tween 80 stimulate lipase production in Burkholderia glumae by different mechanisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3838–3844
Daffé M (2005) The cell envelope of corynebacteria. In: Eggeling L, Bott M (eds) Handbook of Corynebacterium glutamicum. CRC Press, USA, pp 121–148
Date M, Yokoyama K, Umezawa Y, Matsui H, Kikuchi Y (2003) Production of native-type Streptoverticillium mobaraense transglutaminase in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3011–3014
Date M, Yokoyama K, Umezawa Y, Matsui H, Kikuchi Y (2004) High level expression of Streptomyces mobaraensis transglutaminase in Corynebacterium glutamicum using a chimeric pro-region from Streptomyces cinnamoneus transglutaminase. J Biotechnol 110:219–226
Date M, Itaya H, Matsui H, Kikuchi Y (2006) Secretion of human epidermal growth factor by Corynebacterium glutamicum. Lett Appl Microbiol 42:66–70
Dominguez DC (2004) Calcium signalling in bacteria. Mol Microbiol 54:291–297
Eiden-Plach A, Zagorc T, Heintel T, Carius Y, Breinig F, Schmitt MJ (2004) Viral preprotoxin signal sequence allows efficient secretion of green fluorescent protein by Candida glabrata, Pichia pastoris, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:961–966
Feilmeier BJ, Iseminger G, Schroeder D, Webber H, Phillips GJ (2000) Green fluorescent protein functions as a reporter for protein localization in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 182:4068–4076
Hansmeier N, Chao TC, Pühler A, Tauch A, Kalinowski J (2006) The cytosolic, cell surface and extracellular proteomes of the biotechnologically important soil bacterium Corynebacterium efficiens YS-314 in comparison to those of Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032. Proteomics 6:233–250
Hermann T, Pfefferle W, Baumann C, Busker E, Schaffer S, Bott M, Sahm H, Dusch N, Kalinowski J, Puhler A, Bendt AK, Kramer R, Burkovski A (2001) Proteome analysis of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Electrophoresis 22:1712–1723
Inui M, Kawaguchi H, Murakami S, Vertès AA, Yukawa H (2004a) Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for fuel ethanol production under oxygen-deprivation conditions. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 8:243–254
Inui M, Murakami S, Okino S, Kawaguchi H, Vertès AA, Yukawa H (2004b) Metabolic analysis of Corynebacterium glutamicum during lactate and succinate productions under oxygen deprivation conditions. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 7:182–196
Itaya H, Kikuchi Y (2008) Secretion of Streptomyces mobaraensis pro-transglutaminase by coryneform bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:621–625
Jollif G, Mathieu L, Hahn V, Bayan N, Duchiron F, Renaud M, Shechter E, Leblon G (1992) Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the csp1 gene encoding PS1, one of the two major secreted proteins of Corynebacterium glutamicum: the deduced NH2-terminal region of PS1 is similar to the Mycobacterium antigen 85 complex. Mol Microbiol 6:2349–2362
Kesavan J, Borisovska M, Bruns D (2007) v-SNARE actions during Ca(2+)-triggered exocytosis. Cell 131:351–363
Kikuchi Y, Date M, Umezawa Y, Yokoyama K, Heima H, Matsui H (2002) Method for the secretion and production of protein. International Patent Cooperation Treaty patent WO02/081694
Kikuchi Y, Date M, Yokoyama K, Umezawa Y, Matsui H (2003) Secretion of active-form Streptoverticillium mobaraense transglutaminase by Corynebacterium glutamicum: processing of the pro-transglutaminase by a cosecreted subtilisin-Like protease from Streptomyces albogriseolus. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:358–366
Kikuchi Y, Date M, Itaya H, Matsui K, Wu LF (2006) Functional analysis of the twin-arginine translocation pathway in Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13869. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:7183–7192
Kikuchi Y, Itaya H, Date M, Matsui K, Wu LF (2008) Production of Chryseobacterium proteolyticum protein-glutaminase using the twin-arginine translocation pathway in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:67–74
Kinoshita S (1985) Glutamic acid bacteria. In: Demain AL, Solomon NA (eds) Biology of industrial microorganisms. Cummings, London, pp 115–146
Kjaerulff S, Jensen MR (2005) Comparison of different signal peptides for secretion of heterologous proteins in fission yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 336:974–982
Lee PA, Tullman-Ercek D, Georgiou G (2006) The bacterial twin-arginine translocation pathway. Annu Rev Microbiol 60:373–395
Liebl W, Sinskey AJ (1990) Coryneform expression and secretion system. US patent 4,965,197
Liebl W, Sinskey AJ, Schleifer KH (1992) Expression, secretion, and processing of staphylococcal nuclease by Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Bacteriol 174:1854–1861
Malumbers M, Mateos ML, Martin FJ (1995) Microorganisms for amino acid production: Escherichia coli and Corynebacteria. In: Hui YH, Khachatorians GG (eds) Food biotechnology microorganisms, vol. 2. V.C.H Publishers, New York, pp 423–469
Meissner D, Vollstedt A, van Dijl JM, Freudl R (2007) Comparative analysis of twin-arginine (Tat)-dependent protein secretion of a heterologous model protein (GFP) in three different Gram-positive bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:633–642
Muller M, Klosgen RB (2005) The Tat pathway in bacteria and chloroplasts (review). Mol Membr Biol 22:113–121
Nishimura T, Teramoto H, Vertès AA, Inui M, Yukawa H (2008) ArnR, a novel transcriptional regulator, represses expression of the narKGHJI operon in Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Bacteriol 190:3264–3273
Okino S, Inui M, Yukawa H (2005) Production of organic acids by Corynebacterium glutamicum under oxygen deprivation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 68:475–480
Peyret JL, Bayan N, Joliff G, Gulik-Krzywicki T, Mathieu L, Schechter E, Leblon G (1993) Characterization of the cspB gene encoding PS2, an ordered surface-layer protein in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Mol Microbiol 9:97–109
Salim K, Haedens V, Content J, Leblon G, Huygen K (1997) Heterologous expression of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis gene encoding antigen 85A in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4392–4400
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Smith MD, Flickinger JL, Lineberger DW, Schmidt B (1986) Protoplast transformation in coryneform bacteria and introduction of an alpha-amylase gene from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens into Brevibacterium lactofermentum. Appl Environ Microbiol 51:634–639
Solem C, Koebmann B, Jensen PR (2008) Control analysis of the role of triosephosphate isomerase in glucose metabolism in Lactococcus lactis. IET Syst Boil 2:64–72
Su WW, Guan P, Bugos RC (2004) High-level secretion of functional green fluorescent protein from transgenic tobacco cell cultures: characterization and sensing. Biotechnol Bioeng 85:610–619
Thomas JD, Daniel RA, Errington J, Robinson C (2001) Export of active green fluorescent protein to the periplasm by the twin-arginine translocase (Tat) pathway in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 39:47–53
Tjalsma H, Bolhuis A, Jongbloed JD, Bron S, van Dijl JM (2000) Signal peptide-dependent protein transport in Bacillus subtilis: a genome-based survey of the secretome. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64:515–547
Vertès AA, Inui M, Kobayashi M, Kurusu Y, Yukawa H (1993) Presence of mrr- and mcr-like restriction systems in coryneform bacteria. Res Microbiol 144:181–185
Watanabe K, Tsuchida Y, Okibe N, Teramoto H, Suzuki N, Inui M, Yukawa H (2009) Scanning the Corynebacterium glutamicum R genome for high efficiency secretion signal sequences. Microbiology 155:741–750
Yang J, Moyana T, MacKenzie S, Xia Q, Xiang J (1998) One hundred seventy-fold increase in excretion of an FV fragment-tumor necrosis factor alpha fusion protein (sFV/TNF-alpha) from Escherichia coli caused by the synergistic effects of glycine and triton X-100. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2869–2874
Yukawa H, Inui M, Vertès AA (2006) Genomes and genome-level engineering of amino acid-producing bacteria. In: Wendisch VF (ed) Amino acid biosynthesis, vol. 5. Springer, Berlin, pp 349–401
Yukawa H, Omumasaba CA, Nonaka H, Kós P, Okai N, Suzuki N, Suda M, Tsuge Y, Watanabe J, Ikeda Y, Vertès AA, Inui M (2007) Comparative analysis of the Corynebacterium glutamicum group and complete genome sequence of strain R. Microbiology 153:1042–1058
Acknowledgment
We thank Dr. C. Omumasaba (internal) for critical reading of the manuscript. This study was partly funded by the New Energy and industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teramoto, H., Watanabe, K., Suzuki, N. et al. High yield secretion of heterologous proteins in Corynebacterium glutamicum using its own Tat-type signal sequence. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91, 677–687 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3281-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3281-8