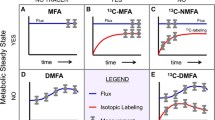
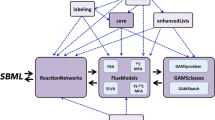
Abstract
The recent years have seen tremendous progress towards the understanding of microbial metabolism on a higher level of the entire functional system. Hereby, huge achievements including the sequencing of complete genomes and efficient post-genomic approaches provide the basis for a new, fascinating era of research—analysis of metabolic and regulatory properties on a global scale. Metabolic flux (fluxome) analysis displays the first systems oriented approach to unravel the physiology of microorganisms since it combines experimental data with metabolic network models and allows determining absolute fluxes through larger networks of central carbon metabolism. Hereby, fluxes are of central importance for systems level understanding because they fundamentally represent the cellular phenotype as integrated output of the cellular components, i.e. genes, transcripts, proteins, and metabolites. A currently emerging and promising area of research in systems biology and systems metabolic engineering is therefore the integration of fluxome data in multi-omics studies to unravel the multiple layers of control that superimpose the flux network and enable its optimal operation under different environmental conditions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoniewicz MR, Kelleher JK, Stephanopoulos G (2007a) Elementary metabolite units (EMU): a novel framework for modeling isotopic distributions. Metab Eng 9:68–86
Antoniewicz MR, Kraynie DF, Laffend LA, Gonzalez-Lergier J, Kelleher JK, Stephanopoulos G (2007b) Metabolic flux analysis in a nonstationary system: fed-batch fermentation of a high yielding strain of E. coli producing 1, 3-propanediol. Metab Eng 9:277–292
Asakura Y, Kimura E, Usuda Y, Kawahara Y, Matsui K, Osumi T, Nakamatsu T (2007) Altered metabolic flux due to deletion of odhA causes L-glutamate overproduction in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:1308–1319
Becker J, Klopprogge C, Zelder O, Heinzle E, Wittmann C (2005) Amplified expression of fructose 1, 6-bisphosphatase in Corynebacterium glutamicum increases in vivo flux through the pentose phosphate pathway and lysine production on different carbon sources. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8587–8596
Becker J, Klopprogge C, Herold A, Zelder O, Bolten CJ, Wittmann C (2007) Metabolic flux engineering of L-lysine production in Corynebacterium glutamicum-over expression and modification of G6P dehydrogenase. J Biotechnol 132:99–109
Becker J, Klopprogge C, Wittmann C (2008) Metabolic responses to pyruvate kinase deletion in lysine producing Corynebacterium glutamicum. Microb Cell Fact 7:8
Becker J, Klopprogge C, Schröder H, Wittmann C (2009) Tricarboxylic acid cycle engineering for improved lysine production in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7866–7869
Becker J, Buschke N, Bücker R, Wittmann C (2010) Systems level engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum—reprogramming translational efficiency for superior production. Chem Eng Life Sci 10:1–9
Blank LM, Kuepfer L (2010) Metabolic flux distributions: genetic information, computational predictions, and experimental validation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:1243–1255
Blank LM, Sauer U (2004) TCA cycle activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a function of the environmentally determined specific growth and glucose uptake rates. Microbiology 150:1085–1093
Blank LM, Kuepfer L, Sauer U (2005a) Large-scale 13C-flux analysis reveals mechanistic principles of metabolic network robustness to null mutations in yeast. Genome Biol 6:R49
Blank LM, Lehmbeck F, Sauer U (2005b) Metabolic-flux and network analysis in fourteen hemiascomycetous yeasts. FEMS Yeast Res 5:545–558
Bolten CJ, Kiefer P, Letisse F, Portais J-C, Wittmann C (2007) Sampling for metabolome analysis of microorganisms. Anal Chem 79:3843–3849
Bolten CJ, Heinzle E, Muller R, Wittmann C (2009) Investigation of the central carbon metabolism of Sorangium cellulosum: metabolic network reconstruction and quantification of pathway fluxes. J Microbiol Biotechnol 19:23–36
Borodina I, Scholler C, Eliasson A, Nielsen J (2005) Metabolic network analysis of Streptomyces tenebrarius, a Streptomyces species with an active Entner–Doudoroff pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:2294–2302
Borodina I, Siebring J, Zhang J, Smith CP, van Keulen G, Dijkhuizen L, Nielsen J (2008) Antibiotic overproduction in Streptomyces coelicolor A3 2 mediated by phosphofructokinase deletion. J Biol Chem 283:25186–25199
Christensen B, Nielsen J (1999) Isotopomer analysis using GC–MS. Metab Eng 1:282–290
Christensen B, Nielsen J (2000) Metabolic network analysis. A powerful tool in metabolic engineering. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 66:209–231
Dauner M, Sauer U (2000) GC–MS analysis of amino acids rapidly provides rich information for isotopomer balancing. Biotechnol Prog 16:642–649
Des Rosiers C, Chatham JC (2005) Myocardial phenotyping using isotopomer analysis of metabolic fluxes. Biochem Soc Trans 33:1413–1417
Des Rosiers C, Lloyd S, Comte B, Chatham JC (2004) A critical perspective of the use of 13C-isotopomer analysis by GCMS and NMR as applied to cardiac metabolism. Metab Eng 6:44–58
Emmerling M, Dauner M, Ponti A, Fiaux J, Hochuli M, Szyperski T, Wuthrich K, Bailey JE, Sauer U (2002) Metabolic flux responses to pyruvate kinase knockout in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 184:152–164
Fischer E, Sauer U (2003) Metabolic flux profiling of Escherichia coli mutants in central carbon metabolism using GC–MS. Eur J Biochem 270:880–891
Fischer E, Sauer U (2005) Large-scale in vivo flux analysis shows rigidity and suboptimal performance of Bacillus subtilis metabolism. Nat Genet 37:636–640
Fischer E, Zamboni N, Sauer U (2004) High-throughput metabolic flux analysis based on gas chromatography–mass spectrometry derived 13C constraints. Anal Biochem 325:308–316
Fong SS, Nanchen A, Palsson BO, Sauer U (2006) Latent pathway activation and increased pathway capacity enable Escherichia coli adaptation to loss of key metabolic enzymes. J Biol Chem 281:8024–8033
Frick O, Wittmann C (2005) Characterization of the metabolic shift between oxidative and fermentative growth in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by comparative 13C flux analysis. Microb Cell Fact 4:30
Fuhrer T, Sauer U (2009) Different biochemical mechanisms ensure network-wide balancing of reducing equivalents in microbial metabolism. J Bacteriol 191:2112–2121
Fuhrer T, Fischer E, Sauer U (2005) Experimental identification and quantification of glucose metabolism in seven bacterial species. J Bacteriol 187:1581–1590
Fürch T, Preusse M, Tomasch J, Zech H, Wagner-Dobler I, Rabus R, Wittmann C (2009) Metabolic fluxes in the central carbon metabolism of Dinoroseobacter shibae and Phaeobacter gallaeciensis, two members of the marine Roseobacter clade. BMC Microbiol 9:209
Georgi T, Rittmann D, Wendisch VF (2005) Lysine and glutamate production by Corynebacterium glutamicum on glucose, fructose and sucrose: roles of malic enzyme and fructose-1, 6-bisphosphatase. Metab Eng 7:291–301
Gombert AK, Moreira dos Santos M, Christensen B, Nielsen J (2001) Network identification and flux quantification in the central metabolism of Saccharomyces cerevisiae under different conditions of glucose repression. J Bacteriol 183:1441–1451
Heinemann M, Sauer U (2010) Systems biology of microbial metabolism. Curr Opin Microbiol 13:337–343
Hua Q, Joyce AR, Palsson BO, Fong SS (2007) Metabolic characterization of Escherichia coli strains adapted to growth on lactate. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:4639–4647
Hult K, Veide A, Gatenbeck S (1980) The distribution of the NADPH regenerating mannitol cycle among fungal species. Arch Microbiol 128:253–255
Ikeda M (2003) Amino acid production processes. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 79:1–35
Ishii N, Nakahigashi K, Baba T, Robert M, Soga T, Kanai A, Hirasawa T, Naba M, Hirai K, Hoque A, Ho PY, Kakazu Y, Sugawara K, Igarashi S, Harada S, Masuda T, Sugiyama N, Togashi T, Hasegawa M, Takai Y, Yugi K, Arakawa K, Iwata N, Toya Y, Nakayama Y, Nishioka T, Shimizu K, Mori H, Tomita M (2007) Multiple high-throughput analyses monitor the response of E. coli to perturbations. Science 316:593–597
Iwatani S, Yamada Y, Usuda Y (2008) Metabolic flux analysis in biotechnology processes. Biotechnol Lett 30:791–799
Kelleher JK (2001) Flux estimation using isotopic tracers: common ground for metabolic physiology and metabolic engineering. Metab Eng 3:100–110
Kiefer P, Heinzle E, Zelder O, Wittmann C (2004) Comparative metabolic flux analysis of lysine-producing Corynebacterium glutamicum cultured on glucose or fructose. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:229–239
Kim HM, Heinzle E, Wittmann C (2006) Deregulation of aspartokinase by single nucleotide exchange leads to global flux rearrangement in the central metabolism of Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Microbiol Biotechnol 16:1174–1179
Kim HU, Kim TY, Lee SY (2008) Metabolic flux analysis and metabolic engineering of microorganisms. Mol Biosyst 4:113–120
Kim J, Hirasawa T, Sato Y, Nagahisa K, Furusawa C, Shimizu H (2009) Effect of odhA overexpression and odhA antisense RNA expression on Tween-40-triggered glutamate production by Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81:1097–1106
Klapa MI, Aon JC, Stephanopoulos G (2003) Systematic quantification of complex metabolic flux networks using stable isotopes and mass spectrometry. Eur J Biochem 270:3525–3542
Krömer JO, Sorgenfrei O, Klopprogge K, Heinzle E, Wittmann C (2004) In-depth profiling of lysine-producing Corynebacterium glutamicum by combined analysis of the transcriptome, metabolome, and fluxome. J Bacteriol 186:1769–1784
Krömer JO, Heinzle E, Schröder H, Wittmann C (2006) Accumulation of homolanthionine and activation of a novel pathway for isoleucine biosynthesis in Corynebacterium glutamicum McbR deletion strains. J Bacteriol 188:609–618
Krömer JO, Bolten CJ, Heinzle E, Schröder H, Wittmann C (2008) Physiological response of Corynebacterium glutamicum to oxidative stress induced by deletion of the transcriptional repressor McbR. Microbiology 154:3917–3930
Lapidot A, Nissim I (1980) Regulation of pool sizes and turnover rates of amino acids in humans: 15N-glycine and 15N-alanine single-dose experiments using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis. Metabolism 29:230–239
Lee SY, Kim HU, Park JH, Park JM, Kim TY (2009) Metabolic engineering of microorganisms: general strategies and drug production. Drug Discov Today 14:78–88
Marx A, Striegel K, de Graaf A, Sahm H, Eggeling L (1997) Response of the central metabolism of Corynebacterium glutamicum to different flux burdens. Biotechnol Bioeng 56(2):168–180
Marx A, Eikmanns BJ, Sahm H, de Graaf AA, Eggeling L (1999) Response of the central metabolism in Corynebacterium glutamicum to the use of an NADH-dependent glutamate dehydrogenase. Metab Eng 1:35–48
Marx A, Hans S, Mockel B, Bathe B, de Graaf AA (2003) Metabolic phenotype of phosphoglucose isomerase mutants of Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Biotechnol 104:185–197
Nakahigashi K, Toya Y, Ishii N, Soga T, Hasegawa M, Watanabe H, Takai Y, Honma M, Mori H, Tomita M (2009) Systematic phenome analysis of Escherichia coli multiple-knockout mutants reveals hidden reactions in central carbon metabolism. Mol Syst Biol 5:306
Nanchen A, Schicker A, Sauer U (2006) Nonlinear dependency of intracellular fluxes on growth rate in miniaturized continuous cultures of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:1164–1172
Nissim I, Lapidot A (1986) Dynamic aspects of amino acid metabolism in alloxan-induced diabetes and insulin-treated rabbits: in vivo studies with 15N and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Biochem Med Metab Biol 35:88–100
Nissim I, Yudkoff M, Yang W, Terwilliger T, Segal S (1981) Rapid gas chromatographic–mass spectrometric analysis of [15N]urea: application to human metabolic studies. Clin Chim Acta 109:295–304
Nöh K, Wahl A, Wiechert W (2006) Computational tools for isotopically instationary 13C labeling experiments under metabolic steady state conditions. Metab Eng 8:554–577
van Winden WA, Heijnen JJ, Verheijen PJ (2002) Cumulative bondomers: a new concept in flux analysis from 2D [13C, 1H] COSY NMR data. Biotechnol Bioeng 80:731–745
Nöh K, Grönke K, Luo B, Takors R, Oldiges M, Wiechert W (2007) Metabolic flux analysis at ultra short time scale: isotopically non-stationary 13C labeling experiments. J Biotechnol 129:249–267
Ohnishi J, Katahira R, Mitsuhashi S, Kakita S, Ikeda M (2005) A novel gnd mutation leading to increased L-lysine production in Corynebacterium glutamicum. FEMS Microbiol Lett 242:265–274
Park JH, Lee SY, Kim TY, Kim HU (2008) Application of systems biology for bioprocess development. Trends Biotechnol 26:404–412
Peters-Wendisch PG, Schiel B, Wendisch VF, Katsoulidis E, Mockel B, Sahm H, Eikmanns BJ (2001) Pyruvate carboxylase is a major bottleneck for glutamate and lysine production by Corynebacterium glutamicum. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 3:295–300
Peyraud R, Kiefer P, Christen P, Massou S, Portais JC, Vorholt JA (2009) Demonstration of the ethylmalonyl–CoA pathway by using 13C metabolomics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:4846–4851
Quek LE, Wittmann C, Nielsen LK, Kromer JO (2009) OpenFLUX: efficient modelling software for 13C-based metabolic flux analysis. Microb Cell Fact 8:25
Riedel C, Rittmann D, Dangel P, Mockel B, Petersen S, Sahm H, Eikmanns BJ (2001) Characterization of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene from Corynebacterium glutamicum and significance of the enzyme for growth and amino acid production. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 3:573–583
Sauer U (2006) Metabolic networks in motion: 13C-based flux analysis. Mol Syst Biol 2:62
Sauer U, Eikmanns BJ (2005) The PEP–pyruvate–oxaloacetate node as the switch point for carbon flux distribution in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:765–794
Sauer U, Heinemann M, Zamboni N (2007) Genetics. Getting closer to the whole picture. Science 316:550–551
Sawada K, Zen-In S, Wada M, Yokota A (2010) Metabolic changes in a pyruvate kinase gene deletion mutant of Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032. Metab Eng 12:401–407
Schilling O, Frick O, Herzberg C, Ehrenreich A, Heinzle E, Wittmann C, Stülke J (2007) Transcriptional and metabolic responses of Bacillus subtilis to the availability of organic acids: transcription regulation is important but not sufficient to account for metabolic adaptation. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:499–507
Schmidt K, Carlsen M, Nielsen J, Villadsen J (1997) Modeling isotopomer distributions in biochemical networks using isotopomer mapping matrices. Biotechnol Bioeng 55(6):831–840
Shimizu K (2004) Metabolic flux analysis based on 13C-labeling experiments and integration of the information with gene and protein expression patterns. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 91:1–49
Shirai T, Nakato A, Izutani N, Nagahisa K, Shioya S, Kimura E, Kawarabayasi Y, Yamagishi A, Gojobori T, Shimizu H (2005) Comparative study of flux redistribution of metabolic pathway in glutamate production by two coryneform bacteria. Metab Eng 7:59–69
Shirai T, Matsuzaki K, Kuzumoto M, Nagahisa K, Furusawa C, Shioya S, Shimizu H (2006) Precise metabolic flux analysis of coryneform bacteria by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and verification by nuclear magnetic resonance. J Biosci Bioeng 102:413–424
Shirai T, Fujimura K, Furusawa C, Nagahisa K, Shioya S, Shimizu H (2007) Study on roles of anaplerotic pathways in glutamate overproduction of Corynebacterium glutamicum by metabolic flux analysis. Microb Cell Fact 6:19
Shuichi A, Masayoshi M (1979) Identification of metabolic model: citrate production from glucose by Candida lipolytica. Biotechnol Bioeng 21:1373–1386
Sonntag K, Eggeling L, De Graaf AA, Sahm H (1993) Flux partitioning in the split pathway of lysine synthesis in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Quantification by 13C- and 1H-NMR spectroscopy. Eur J Biochem 213:1325–1331
Szyperski T (1995) Biosynthetically directed fractional 13C-labeling of proteinogenic amino acids. An efficient analytical tool to investigate intermediary metabolism. Eur J Biochem 232:433–448
Tang YJ, Hwang JS, Wemmer DE, Keasling JD (2007) Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 fluxome under various oxygen conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:718–729
Tang YJ, Martin HG, Dehal PS, Deutschbauer A, Llora X, Meadows A, Arkin A, Keasling JD (2009) Metabolic flux analysis of Shewanella spp. reveals evolutionary robustness in central carbon metabolism. Biotechnol Bioeng 102:1161–1169
Tsalikian E, Howard C, Gerich JE, Haymond MW (1984) Increased leucine flux in short-term fasted human subjects: evidence for increased proteolysis. Am J Physiol 247:E323–E327
Wendisch VF, de Graaf AA, Sahm H, Eikmanns BJ (2000) Quantitative determination of metabolic fluxes during coutilization of two carbon sources: comparative analyses with Corynebacterium glutamicum during growth on acetate and/or glucose. J Bacteriol 182:3088–3096
Wiechert W (2001) 13C metabolic flux analysis. Metab Eng 3:195–206
Wiechert W, Möllney M, Isermann N, Wurzel M, de Graaf AA (1999) Bidirectional reaction steps in metabolic networks: III. Explicit solution and analysis of isotopomer labeling systems. Biotechnol Bioeng 66:69–85
Wiechert W, Möllney M, Petersen S, de Graaf AA (2001) A universal framework for 13C metabolic flux analysis. Metab Eng 3:265–283
Wittmann C (2002) Metabolic flux analysis using mass spectrometry. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 74:39–64
Wittmann C (2007) Fluxome analysis using GC–MS. Microb Cell Fact 6:6
Wittmann C (2010) Analysis and engineering of metabolic pathway fluxes in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 120:21–49
Wittmann C, Becker J (2007) The L-lysine story: from metabolic pathways to industrial production. Microbiol Monogr 5:39–70
Wittmann C, de Graaf A (2005) Metabolic flux analysis in Corynebacterium glutamicum. In: Eggeling L, Bott M (eds) Handbook of Corynebacterium glutamicum. CRC, Boca Raton, pp 277–304
Wittmann C, Heinzle E (1999) Mass spectrometry for metabolic flux analysis. Biotechnol Bioeng 62:739–750
Wittmann C, Heinzle E (2001) Application of MALDI-TOF MS to lysine-producing Corynebacterium glutamicum: a novel approach for metabolic flux analysis. Eur J Biochem 268:2441–2455
Wittmann C, Heinzle E (2002) Genealogy profiling through strain improvement by using metabolic network analysis: metabolic flux genealogy of several generations of lysine-producing corynebacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5843–5859
Wittmann C, Kiefer P, Zelder O (2004) Metabolic fluxes in Corynebacterium glutamicum during lysine production with sucrose as carbon source. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:7277–7287
Wittmann C, Weber J, Betiku E, Kromer J, Bohm D, Rinas U (2007) Response of fluxome and metabolome to temperature-induced recombinant protein synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 132:375–384
Yang TH, Heinzle E, Wittmann C (2005) Theoretical aspects of 13C metabolic flux analysis with sole quantification of carbon dioxide labeling. Comput Biol Chem 29:121–133
Yang TH, Wittmann C, Heinzle E (2006) Respirometric 13C flux analysis, Part I: design, construction and validation of a novel multiple reactor system using on-line membrane inlet mass spectrometry. Metab Eng 8:417–431
Yuan Y, Yang TH, Heinzle E (2010) 13C metabolic flux analysis for larger scale cultivation using gas chromatography-combustion-isotope ratio mass spectrometry. Metab Eng 12:392–400
Zamboni N, Sauer U (2009) Novel biological insights through metabolomics and 13C-flux analysis. Curr Opin Microbiol 12:553–558
Zamboni N, Fischer E, Sauer U (2005) FiatFlux—a software for metabolic flux analysis from 13C-glucose experiments. BMC Bioinform 6:209
Zhang W, Li F, Nie L (2010) Integrating multiple ‘omics’ analysis for microbial biology: application and methodologies. Microbiology 156:287–301
Acknowledgments
All authors acknowledge financial support by the BMBF grant 0315784F within the research initiative “Systems biology of Microorganisms 2” as part of the research consortium BaCell-SysMo2. Christoph Wittmann and Judith Becker further acknowledge financial support by the BMBF-Grant “Biobased Polyamides through Fermentation” (No 0315239A) within the initiative Bioindustry21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kohlstedt, M., Becker, J. & Wittmann, C. Metabolic fluxes and beyond—systems biology understanding and engineering of microbial metabolism. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 88, 1065–1075 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2854-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2854-2