Abstract
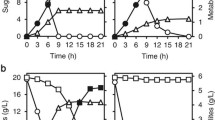
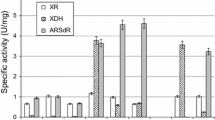
We developed a novel strategy for constructing yeast to improve levels of amylase gene expression and the practical potential of yeast by combining δ-integration and polyploidization through cell fusion. Streptococcus bovis α-amylase and Rhizopus oryzae glucoamylase/α-agglutinin fusion protein genes were integrated into haploid yeast strains. Diploid strains were constructed from these haploid strains by mating, and then a tetraploid strain was constructed by cell fusion. The α-amylase and glucoamylase activities of the tetraploid strain were increased up to 1.5- and tenfold, respectively, compared with the parental strain. The diploid and tetraploid strains proliferated faster, yielded more cells, and fermented glucose more effectively than the haploid strain. Ethanol productivity from raw starch was improved with increased ploidy; the tetraploid strain consumed 150 g/l of raw starch and produced 70 g/l of ethanol after 72 h of fermentation. Our strategy for constructing yeasts resulted in the simultaneous overexpression of genes integrated into the genome and improvements in the practical potential of yeasts.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akada R, Kaneko S, Toyonaga D, Ito S, Yamagiwa A, Kitagawa T, Kakihara Y, Hoshida H, Morimura S, Kondo A, Kida K (2006) PCR-mediated seamless gene deletion and marker recycling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 23:399–405
Birol G, Önsan I, Kirdar B, Oliver SG (1998) Ethanol production and fermentation characteristics of recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains grown on starch. Enzyme Microb Technol 22:672–677
Brigidi P, Matteuzzi D, Fava F (1988) Use of protoplast fusion to introduce methionine overproduction into Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 28:268–271
Broach JR (1983) Construction of high copy yeast vectors using 2-µm circle sequences. Methods Enzymol 101:307–325
Chen DC, Yang BC, Kuo TT (1992) One-step transformation of yeast in stationary phase. Curr Genet 21:83–84
Choi EY, Park JN, Kim HO, Shin DJ, Chun YH, Im SY, Chun SB, Bai S (2002) Construction of an industrial polyploid strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae containing Saprolegnia ferax β-amylase gene and secreting β-amylase. Biotechnol Lett 24:1785–1790
Cole GE, McCabe PC, Inlow D, Gelfand DH, BenBassat A, Innis MA (1988) Stable expression of Aspergillus awamori glucoamylase in distiller’s yeast. Biotechnology 6:417–421
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Ghang DM, Yu L, Lim MH, Ko HM, Im SY, Lee HB, Bai S (2007) Efficient one-step starch utilization by industrial strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae expressing the glucoamylase and α-amylase genes from Debaryomyces occidentalis. Biotechnol Lett 29:1203–1208
Harashima S, Takagi A, Oshima Y (1984) Transformation of protoplasted yeast cells is directly associated with cell fusion. Mol Cell Biol 4:771–778
Hashimoto S, Aritomi K, Minohara T, Nishizawa Y, Hoshida H, Kashiwagi S, Akada R (2006) Direct mating between diploid sake strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69:689–696
Hereford L, Fahrner K, Woolford J, Rosbash M, Kaback DB (1979) Isolation of yeast histone genes H2A and H2B. Cell 18:1261–1271
Higgins VJ, Bell PJL, Dawes IW, Attfield PV (2001) Generation of a novel Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain that exhibits strong maltose utilization and hyperosmotic resistance using nonrecombinant techniques. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4346–4348
Ibragimova SI, Kozlov DG, Kartasheva NN, Suntsov NI, Efremov BD, Benevolensky SV (1995) A strategy for construction of industrial strains of distiller’s yeast. Biotechnol Bioeng 46:285–290
Inlow D, McRae J, Ben-Bassat A (1988) Fermentation of corn starch to ethanol with genetically engineered yeast. Biotechnol Bioeng 32:227–234
Innis MA, Holland PC, McCabe PC, Cole GE, Wittman VP, Tal R, Watt KWK, Gelfand DH, Holland JP, Meade JH (1985) Expression, glycosylation, and secretion of an Aspergillus glucoamylase by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science 228:21–26
Khaw TS, Katakura Y, Koh J, Kondo A, Ueda M, Shioya S (2005) Evaluation of performance of different surface-engineered yeast strains for direct ethanol production from raw starch. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70:573–579
Lee FWF, Da Silva NA (1997) Sequential δ-integration for the regulated insertion of cloned genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Prog 13:368–373
Lopes TS, Hakkaart GAJ, Koerts BL, Rau HA, Planta RJ (1991) Mechanism of high-copy-number integration of pMIRY-type vectors into the ribosomal DNA of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene 105:83–90
Murray AW, Szostak JW (1983) Pedigree analysis of plasmid segregation in yeast. Cell 34:961–970
Nakamura Y, Kobayashi F, Ohnaga M, Sawada T (1997) Alcohol fermentation of starch by a genetic recombinant yeast having glucoamylase activity. Biotechnol Bioeng 53:21–25
Nieto A, Prieto JA, Sanz P (1999) Stable high-copy-number integration of Aspergillus oryzae α-amylase cDNA in an industrial baker’s yeast strain. Biotechnol Prog 15:459–466
Parekh RN, Shaw MR, Wittrup KD (1996) An integrating vector for tunable, high copy, stable integration into the dispersed Ty δ-sites of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Prog 12:16–21
Romanos MA, Scorer CA, Clare JJ (1992) Foreign gene expression in yeast: a review. Yeast 8:423–488
Sakai A, Shimizu Y, Hishinuma F (1990) Integration of heterologous genes into the chromosome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae using a delta sequence of yeast retrotransposon Ty. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 33:302–306
Shigechi H, Uyama K, Fujita Y, Matsumoto T, Ueda M, Tanaka A, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2002) Efficient ethanol production from starch through development of novel flocculent yeast strains displaying glucoamylase and co-displaying or secreting α-amylase. J Mol Catal B Enzym 17:179–187
Tajima M, Nogi Y, Fukasawa T (1985) Primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL7 gene. Yeast 1:67–77
Yamada R, Bito Y, Adachi T, Tanaka T, Ogino C, Fukuda H, Kondo A (2009) Efficient production of ethanol from raw starch by a mated diploid Saccharomyces cerevisiae with integrated α-amylase and glucoamylase genes. Enzyme Microb Technol 44:344–349
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant-in-aid from the Ministry of Environment, Japan, and was supported in part by Special Coordination Funds for Promoting Science and Technology, Creation of Innovation Centers for Advanced Interdisciplinary Research Areas (Innovative Bioproduction Kobe), MEXT, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamada, R., Tanaka, T., Ogino, C. et al. Novel strategy for yeast construction using δ-integration and cell fusion to efficiently produce ethanol from raw starch. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85, 1491–1498 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2198-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2198-y