Abstract
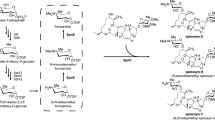
Spinosyn and its analogs, produced by Saccharopolyspora spinosa, are the active ingredients in a family of insect control agents. They are macrolides with a 21-carbon, 12-membered tetracyclic lactones that are attached to two deoxysugars, tri-O-methylrhamnose and forosamine. Labeling studies, analysis of the biosynthetically blocked mutants, and the genetic identification of the spinosyn gene cluster have provided detailed information concerning the mechanism of spinosyn biosynthesis and have enabled combinatorial biosynthesis of a large group of new spinosyns. The following developments have recently impacted the field of spinosyn biology: (1) A second-generation spinosyn called spinetoram (XDE-175) was launched in late 2007; it is a semisynthesized spinosyn derivative produced through the modification of 3′-O-methyl group of rhamnose and the double bond between C5 and C6 of spinosyn J and L. This molecule was shown to have improved insecticidal activity, enhanced duration of control, and an expanded pest spectrum. (2) A new class of spinosyns, the butenyl-spinosyns, was discovered from Saccharopolyspora pogona. The butenyl-spinosyns are similar to spinosyns, but differ in the length of the side chain at C-21. In addition to structural similarities with the spinosyns, the butenyl-spinosyns exhibit a high level of similarity in insecticidal activity to spinetoram. (3) Spinosyn analogs, 21-cyclobutyl-spinosyn A and 21-cyclobutyl-spinosyn D were generated by metabolic engineering of the spinosyn biosynthetic gene cluster. They showed better insecticidal activities against cotton aphid and tobacco budworm than that of spinosyn A and D. Future progress toward the development of more potent spinosad analogs, as well as enhancements in production yields will likely result from these recent advances in the genetics and biochemistry of spinosyns.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baltz RH (2006) Combinatorial biosynthesis of novel antibiotics. Society for Industrial Microbiology News 56:148–160
Bierman M, Logan R, O’Brien K, Seno ET, Rao RN, Schoner BE (1992) Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene 116:43–49
Brünker P, Minas W, Kallio P, Bailey J (1999) Methods and compositions for increasing production of erythromycin. US patent 5,908,764
Burns L, Graupner PR, Lewer P, Martin C, Vousden W, Waldron C, Wilkinson B (2003) Novel spinosyn-producing polyketide synthases. US patent 0,304,998
Christensen B, Nielsen J (1999) Isotopomer analysis using GC-MS. Metab Eng 1:282–290
Christensen B, Nielsen J (2000) Metabolic network analysis of Penicillium chrysogenum using 13C-labeled glucose. Biotechnol Bioeng 68:652–659
Crouse GD, Sparks TC, Schoonover J, Gifford J, Dripps J, Bruce T, Larson LL, Garlich J, Hatton C, Hill RL, Worden TV, Martynow JG (2001) Recent advances in the chemistry of spinosyns. Pest Manag Sci 57:177–185
Davies HG, Green RH (1986) Avermectins and milbemycins. Nat Prod Rep 3:87–121
Gaisser S, Lill R, Wirtz G, Grolle F, Staunton J, Leadlay PF (2001) New erythromycin derivatives from Saccharopolyspora erythraea using sugar O-methyltransferases from the spinosyn biosynthetic gene cluster. Mol Microbiol 41:1223–1231
Hahn DR, Gustafson G, Waldron C, Bullard B, Jackson JD, Mitchell J (2006) Butenyl-spinosyns, a natural example of genetic engineering of antibiotic biosynthetic genes. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 33:94–104
Hong L, Zhao Z, Liu HW (2006) Characterization of SpnQ from the spinosyn biosynthetic pathway of Saccharopolyspora spinosa: mechanistic and evolutionary implications for C-3 deoxygenation in deoxysugar biosynthesis. J Am Chem Soc 128:14262–14263
Hong L, Zhao Z, Melançon CE 3rd, Zhang H, Liu HW (2008) In vitro characterization of the enzymes involved in TDP-D-forosamine biosynthesis in the spinosyn pathway of Saccharopolyspora spinosa. J Am Chem Soc 130:4954–4967
Huang KX, Zahn J, Han L (2008) SpnH from Saccharopolyspora spinosa encodes a rhamnosyl 4′-O-methyltransferase for biosynthesis of the insecticidal macrolide, spinosyn A. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 35:1669–1676
Ito S, Hirata Y (1972) Ikarugamycin II. Structure of ikarugamycin. Tetrahedron Lett 12:1185–1188
Jakobi M, Winkelman G, Kaiser D, Kempter C, Jung G, Berg G Bahl H (1996) Maltophilin: an new antifugal compound produced by Srenotrophomonas maltophilia R 3089. J Antibiot 49:1101–1104
Jin ZH, Cheng X, Cen PL (2006a) Effect of glucose and phosphate on spinosad fermentation by Saccharopolyspora spinosa. Chin J Chem Eng 14:542–546
Jin ZH, Wu JP, Zhang Y (2006b) Improvement of spinosad producing Saccharopolyspora spinosa by rational screening. Journal of Zhejiang University 7:366–370
Kim HJ, Pongdee R, Wu Q, Hong L, Liu HW (2007) The biosynthesis of spinosyn in Saccharopolyspora spinosa: synthesis of the cross-bridging precursor and identification of the function of SpnJ. J Am Chem Soc 129:14582–14584
Kirst HA, Michel KH, Mynderse JS, Chio EH, Yao RC, Nakatsukasa WM, Boeck L, Occolowitz JL, Paschal JW, Deeter JB, Thompson GD (1992) Discovery, isolation, and structure elucidation of a family of structurally unique fermentation-derived tetracyclic macrolides. In: Baker DR, Fenyes JG, Steffens JJ (eds) Synthesis and chemistry of agrochemicals, vol. 3. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp 214–225
Kirst HA, Michel KH, Mynderse JS, Chio EH, Yao RC, Nakatsukasa WM, Boeck L, Occolowitz JL, Paschal JW, Deeter JB, Thompson GD (1993) Discovery and Identification of a novel fermentation derived insecticide. In: Brown WC (ed) Development in industrial microbiology series: microbial metabolites, vol 32. Society for Industrial Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 109–116
Liang Y, Lu WY, Wen JP (2008) Improvement of Saccharopolyspora spinosa and the kinetic analysis for spinosad production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol (in press)
Lewer P, Hahn DR, Karr LL, Graupener PR, Gilbert JR, Worden T, Yao R, Norton DW (2002) Pecticidal macrolides. US patent 6,455,504
Maaheimo H, Fiaux J, Petek J, Bailey JE, Sauer U, Szyperski T (2001) Central carbon metabolism of Saccharomyces cerevisiae explored by biosynthetic fractional 13C labeling of common amino acids. Eur J Biochem 268:2464–2479
MacNeil DJ (1995) Avermectin. Biotechnology 28:421–442
Madduri K, Waldron C, Matsushima P, Broughton MC, Crawford K, Merlo DJ, Baltz RH (2001a) Genes for the biosynthesis of spinosyns: applications for yield improvement in Saccharopolyspora spinosa. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 27:399–402
Madduri K, Waldron C, Merlo DJ (2001b) Rhamnose biosynthesis pathway supplies precursors for primary and secondary metabolism in Saccharopolyspora spinosa. J Bacteriol 183:5632–5638
Martin CJ, Timoney MC, Sheridan RM, Kendrew SG, Wilkinson B, Staunton J, Leadlay PF (2003) Heterologous expression in Saccharopolyspora erythraea of a pentaketide synthase derived from the spinosyn polyketide synthase. Org Biomol Chem 1:4144–4147
Mergott DJ, Frank SA, Roush WR (2004) Total synthesis of (−)-spinosyn A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:11955–11959
Mertz FP, Yao RC (1990) Saccharopolyspora spinosa sp. Nov. isolated from soil collected in sugar mill rum still. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:19–22
Matsushima P, Baltz RH (1994) Transformation of Saccharopolyspora spinosa protoplasts with plasmid DNA modified in vitro to avoid host restriction. Microbiology 140:139–143
Matsushima P, Broughton MC, Turner JR, Baltz RH (1994) Conjugal transfer of cosmid DNA from Escherichia coli to Saccharopolyspora spinosa: effects of chromosomal insertions on macrolide A83543 production. Gene 146:39–45
Millar NS, Denholm I (2007) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: targets for commercially important insecticides. Invert Neurosci 7:53–66
Mironov VA, Sergienko OV, Nastasyak IN, Danilenko VN (2004) Biogenesis and regulation of biosynthesis of erythomycins in Saccharopolyspora erythraea. Appl Biochem Microbiol 40:531–541
Ochi K (2007) From microbial differentiation to ribosome engineering. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71:1373–1386
Parekh S, Vinci VA, Strobel RJ (2000) Improvement of microbial strains and fermentation processes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 54:287–301
Salgado VL, Sparks TC (2005) The spinosyns: chemistry, biochemistry, mode of action, and resistance. In: Gilbert LI, Iatrou K, Gill SS (eds) Comprehensive insect molecular sciences, vol. 6. Elsevier, New York, pp 136–173
Shaw SJ (2008) The structure activity relationship of discodermolide analogues. Mini Rev Med Chem 8:276–284
Sheehan LS, Lill RE, Wilkinson B, Sheridan RM, Vousden WA, Kaja AL, Crouse GD, Gifford J, Graupner PR, Karr L, Lewer P, Sparks TC, Leadlay PF, Waldron C, Martin CJ (2006) Engineering of the spinosyn PKS: directing starter unit incorporation. J Nat Prod 69:1702–1710
Sparks TC, Crouse GD, Dripps JE, Anzeveno P, Martynow J, Deamicis CV, Gifford J (2008) Neural network-based QSAR and insecticide discovery: spinetoram. J Comput Aided Mol Des 22:393–401
Strobel RJ, Nakatsukasa WM (1993) Response surface methods for optimizing Saccharopolyspora spinosa, a novel macrolide producer. J Ind Microbiol 11:121–127
Thompson GD, Michel KH, Yao RC, Mynderse JS, Mosburg CT (1997) The discovery of Saccharopolyspora spinosa and a new class of insect control products. Down Earth 52:1–5
Vinci VA, Byng G (1999) Strain improvement by nonrecombinant methods. In: Demain AL, Davies JE (eds) Manual of industrial microbiology and biotechnology. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp 103–113
Waldron C, Madduri K, Crawford K, Merlo DJ, Treadway P, Broughton MC, Baltz RH (2000) A cluster of genes for the biosynthesis of spinosyns, novel macrolide insect control agents produced by Saccharopolyspora spinosa. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 78:385–390
Waldron C, Matsushima P, Rosteck PR Jr, Broughton MC, Turner J, Madduri K, Crawford KP, Merlo DJ, Baltz RH (2001) Cloning and analysis of the spinosad biosynthetic gene cluster of Saccharopolyspora spinosa. Chem Biol 8:487–499
Wiechert W (2001) 13C metabolic flux analysis. Metab Eng 3:195–206
Zhao Z, Hong L, Liu HW (2005) Characterization of protein encoded by spnR from the spinosyn gene cluster of Saccharopolyspora spinosa: mechanistic implications for forosamine biosynthesis. J Am Chem Soc 127:7692–7693
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 30870027) to KH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Kx., Xia, L., Zhang, Y. et al. Recent advances in the biochemistry of spinosyns. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82, 13–23 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1784-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1784-8