Summary
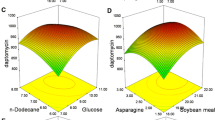
Strain A83543, recently identified asSaccharopolyspora spinosa, was cultured in a variety of media to optimize macrolide titer. Response surface methodology (RSM) was used to improve the fermentation medium and to characterize the microorganism's response to systematic variations in medium composition. Three sequential RSM studies on wild-type A83543 and two high macrolide-producing mutants showed that each strain produced maximum titers in nearly identical fermentation media. No obvious differences in nutrient requirements were evident in the three strains indicating little interaction between mutational change and medium composition through at least two cycles of mutagenesis. The overall increase in macrolide titer starting from the wild-type organism in the original fermentation medium to the second-generation mutant in the optimized medium was over 25-fold.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mertz, F.P. and R.C. Yao. 1990.Saccharopolyspora spinosa sp. nov. isolated from soil collected in a sugar mill rum still. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 40: 34–39.
Kirst, H.A., K.H. Michel, J.W. Martin, L.C. Creemer, E.H. Chio, R.C. Yao, W.M. Nakatsukasa, L.D. Boeck, J.L. Occolowitz, J.W. Paschal, J.B. Deeter, N.D. Jones and G.D. Thompson. (1991) A83543-D, Unique fermentation-derived tetracyclic macrolides. Tetrahedron Lett. 32: 4839–4842.
Nakatsukasa, W.M., J.A. Mabe, K.H. Michel, J.W. Martin, J.W. Pascal and T.K. Elsey. 1990. The use of13C-NMR spectroscopy in biosynthetic studies of the insecticide, A83543. Abstr. Second Int. Confer. Biotech. Microbial Prod., Sarasota, FL.
McDaniel, L.E., E.G. Bailey, S. Ethiraj and H.P. Andrews. 1976. Application of response surface optimization techniques to polyene macrolide fermentation studies in shake flasks. Dev. Ind. Microbiol. 17: 91–98.
Swanson, T.R., J.O. Carroll, R.A. Britto and D.J. Duhart. 1986. Development and field confirmation of a mathematical model for amyloglucosidase/pullulanase saccharification. Starch 38: 382–387.
Kautola, H. and Y.Y. Linko. 1989. Fumaric acid production from xylose by immobilizedRhizopus arrhizus cells. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 31: 448–452.
Maddox, I.S. and S.H. Richert. 1977. Production of gibberellic acid using a dairy waste as the basal medium: Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 33: 201–202.
Monaghan, R.L., E. Arcuri, E.E. Baker, B.C. Buckland, R.L. Greasham, D.R. Houck, E.D. Ihnen, E.S. Inamine, J.J. King, E. Lesniak, P.S. Masurekar, C.A. Schulman, B. Singleton and M.A. Goetz. 1989. History of yield improvements in the production of asperlicin byAspergillus alliaceus. J. Ind. Microbiol. 4: 97–104.
Miller-Wideman, M., N. Makkar, M. Tran, B. Isaac, N. Biest and R. Stonard. Herboxidiene, a new herbicidal substance fromStreptomyces chromofuscus A7847. J. Antibiot. 45: 914–921.
Box, G.E.P., W.G. Hunter and J.S. Hunter. 1978. Statistics for Experimenters, pp. 374–398. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York.
Greasham, R. and E. Inamine. 1986. Nutritional improvement of processes. In: Manual of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (Demain, A.L. and N.A. Solomon, eds.), pp. 41–48, American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC.
Box, G.E.P. and N.R. Draper. 1987. Empirical Model-Building and Response Surfaces, pp. 508–521. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strobel, R.J., Nakatsukasa, W.M. Response surface methods for optimizingSaccharopolyspora spinosa, a novel macrolide producer. Journal of Industrial Microbiology 11, 121–127 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01583684
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01583684