Abstract
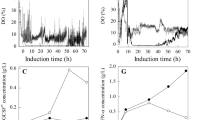
In this study, we assessed the potential of PMR1-disrupted Pichia pastoris (Pppmr1) expressing human serum albumin and interferon alpha2b fusion protein (HSA-IFN-alpha2b) in large-scale fermentation. The high osmotic pressure of standard basal salts medium (BSM) was detrimental to the growth and viability of Pppmr1. HSA-IFN-alpha2b was secreted into a supernatant with a concentration of up to 112 mg/L after 20 h of induction and then began to decline. In vitro stability tests indicated that the disappearance of HSA-IFN-alpha2b was ascribed to proteolytic degradation. Decreasing the salt concentration of BSM medium to one quarter of the original formula improved the growth and viability of Pppmr1. As a result of reduced cell lysis and protease release, HSA-IFN-alpha2b was stable in the supernatant, which enabled a longer production phase (30 h) and a higher expression level (215 mg/L). Lowering the culture temperature to 20°C increased the cell viability during carbon source transition and alleviated the oxygen and methanol limitation, which extended the production phase to 40 h and increased the expression level to 680 mg/L. The addition of 2% Soytone prolonged the production phase to 60 h and increased the expression level to 1,260 mg/L, which was more than tenfold higher than that of Pppmr1 cultured under the conditions recommended by Invitrogen.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agaphonov MO, Plotnikova TA, Fokina AV, Romanova NV, Packeiser AN, Kang HA, Ter-Avanesyan MD (2007) Inactivation of the Hansenula polymorpha PMR1 gene affects cell viability and functioning of the secretory pathway. FEMS Yeast Res 7:1145–1152
Antebi A, Fink GR (1992) The yeast Ca(2+)-ATPase homologue, PMR1, is required for normal Golgi function and localizes in a novel Golgi-like distribution. Mol Biol Cell 3:633–654
Bates S, MacCallum DM, Bertram G, Munro CA, Hughes HB, Buurman ET, Brown AJ, Odds FC, Gow NA (2005) Candida albicans Pmr1p, a secretory pathway P-type Ca2+/Mn2+-ATPase, is required for glycosylation and virulence. J Biol Chem 280:23408–23415
Cereghino JL, Cregg JM (2000) Heterologous protein expression in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. FEMS Microbiol Rev 24:45–66
Chang SW, Lee GC, Shaw JF (2006) Codon optimization of Candida rugosa lip1 gene for improving expression in Pichia pastoris and biochemical characterization of the purified recombinant LIP1 lipase. J Agric Food Chem 54:815–822
Cortés JC, Katoh-Fukui R, Moto K, Ribas JC, Ishiguro J (2004) Schizosaccharomyces pombe Pmr1p is essential for cell wall integrity and is required for polarized cell growth and cytokinesis. Eukaryot Cell 3:1124–1135
Damasceno LM, Anderson KA, Ritter G, Cregg JM, Old LJ, Batt CA (2007) Cooverexpression of chaperones for enhanced secretion of a single-chain antibody fragment in Pichia pastoris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:381–389
Dürr G, Strayle J, Plemper R, Elbs S, Klee SK, Catty P, Wolf DH, Rudolph HK (1998) The medial-Golgi ion pump Pmr1 supplies the yeast secretory pathway with Ca2+ and Mn2+ required for glycosylation, sorting, and endoplasmic reticulum-associated protein degradation. Mol Biol Cell 9:1149–1162
Dux MP, Inan M (2006) Identification and characterization of calcium and manganese transporting ATPase (PMR1) gene of Pichia pastoris. Yeast 23:613–621
Gasser B, Maurer M, Rautio J, Sauer M, Bhattacharyya A, Saloheimo M, Penttilä M, Mattanovich D (2007) Monitoring of transcriptional regulation in Pichia pastoris under protein production conditions. BMC Genomics 8:179
Jahic M, Wallberg F, Bollok M, Garcia P, Enfors SO (2003) Temperature limited fed-batch technique for control of proteolysis in Pichia pastoris bioreactor cultures. Microb Cell Fact 2:6
Ko JH, Hahm MS, Kang HA, Nam SW, Chung BH (2002) Secretory expression and purification of Aspergillus niger glucose oxidase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutant deficient in PMR1 gene. Protein Expr Purif 25:488–493
Lin H, Kim T, Xiong F, Yang X (2007) Enhancing the production of Fc fusion protein in fed-batch fermentation of Pichia pastoris by design of experiments. Biotechnol Prog 23:621–625
Melnick LM, Turner BG, Puma P, Price-Tillotson B, Salvato KA, Dumais DR, Moir DT, Broeze RJ, Avgerinos GC (1990) Characterization of a nonglycosylated single chain urinary plasminogen activator secreted from yeast. J Biol Chem 265:801–807
Murphy KP Jr, Gagne P, Pazmany C, Moody MD (1998) Expression of human interleukin-17 in Pichia pastoris: purification and characterization. Protein Expr Purif 12:208–214
Plantz BA, Sinha J, Villarete L, Nickerson KW, Schlegel VL (2006) Pichia pastoris fermentation optimization: energy state and testing a growth-associated model. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:297–305
Schenk J, Balazs K, Jungo C, Urfer J, Wegmann C, Zocchi A, Marison IW, von Stockar U (2008) Influence of specific growth rate on specific productivity and glycosylation of a recombinant avidin produced by a Pichia pastoris Mut+ strain. Biotechnol Bioeng 99:368–377
Sinclair G, Choy FY (2002) Synonymous codon usage bias and the expression of human glucocerebrosidase in the methylotrophic yeast, Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 26:96–105
Smith RA, Duncan MJ, Moir DT (1985) Heterologous protein secretion from yeast. Science 229:1219–1224
Subramanian GM, Fiscella M, Lamousé-Smith A, Zeuzem S, McHutchison JG (2007) Albinterferon alpha-2b: a genetic fusion protein for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Nat Biotechnol 25:1411–1419
Surribas A, Stahn R, Montesinos JL, Enfors SO, Valero F, Jahic M (2007) Production of a Rhizopus oryzae lipase from Pichia pastoris using alternative operational strategies. J Biotechnol 130:291–299
Uccelletti D, Farina F, Mancini P, Palleschi C (2004) KlPMR1 inactivation and calcium addition enhance secretion of non-hyperglycosylated heterologous proteins in Kluyveromyces lactis. J Biotechnol 109:93–101
Wang J, Nguyen V, Glen J, Henderson B, Saul A, Miller LH (2005) Improved yield of recombinant merozoite Surface protein 3 (MSP3) from Pichia pastoris using chemically defined media. Biotechnol Bioeng 90:838–847
Werten MW, van den Bosch TJ, Wind RD, Mooibroek H, de Wolf FA (1999) High-yield secretion of recombinant gelatins by Pichia pastoris. Yeast 15:1087–1096
Woo JH, Liu YY, Mathias A, Stavrou S, Wang Z, Thompson J, Neville DM Jr (2002) Gene optimization is necessary to express a bivalent anti-human anti-T cell immunotoxin in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expr Purif 25:270–282
Woo JH, Liu YY, Stavrou S, Neville DM Jr (2004) Increasing secretion of a bivalent anti-T-cell immunotoxin by Pichia pastoris. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:3370–3376
Woo JH, Liu JS, Kang SH, Singh R, Park SK, Su Y, Ortiz J, Neville DM Jr, Willingham MC, Frankel AE (2008) GMP production and characterization of the bivalent anti-human T cell immunotoxin, A-dmDT390-bisFv(UCHT1) for phase I/II clinical trials. Protein Expr Purif 58:1–11
Xiao AF, Zhou XS, Zhou L, Zhang YX (2006) Detection of intracellular reactive oxygen species by flow cytometry in Pichia pastoris fermentation. Chinese J Biotechnol 22:273–277
Xue C, Zhao HL, Liu ZM (2005) A simple and practical densimetric scanning protocol with computer programs. Lett Biotechnol 16:284–286
Zhang W, Zhao HL, Xue C, Xiong XH, Yao XQ, Li XY, Chen HP, Liu ZM (2006) Enhanced secretion of heterologous proteins in Pichia pastoris following overexpression of Saccharomyces cerevisiae chaperone proteins. Biotechnol Prog 22:1090–1095
Zhang W, Inan M, Meagher MM (2007) Rational design and optimization of fed-batch and continuous fermentations. Methods Mol Biol 389:43–64
Zhao HL, Xue C, Wang Y, Li XY, Xiong XH, Yao XQ, Liu ZM (2007) Circumventing the heterogeneity and instability of human serum albumin-interferon-alpha2b fusion protein by altering its orientation. J Biotechnol 131:245–252
Zhao HL, Xue C, Wang Y, Duan QF, Xiong XH, Yao XQ, Liu ZM (2008) Disruption of Pichia pastoris PMR1 gene decreases its folding capacity on human serum albumin and interferon-alpha2b fusion protein. Yeast 25:279–286
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, H.L., Xue, C., Wang, Y. et al. Increasing the cell viability and heterologous protein expression of Pichia pastoris mutant deficient in PMR1 gene by culture condition optimization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81, 235–241 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1666-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1666-0