Abstract
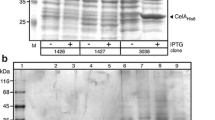
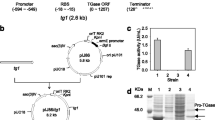
Biotechnology needs to explore the capacity of different organisms to overproduce proteins of interest at low cost. In this paper, we show that Streptomyces lividans is a suitable host for the expression of Thermus thermophilus genes and report the overproduction of the corresponding proteins. This capacity was corroborated after cloning the genes corresponding to an alkaline phosphatase (a periplasmic enzyme in T. thermophilus) and that corresponding to a beta-glycosidase (an intracellular enzyme) in Escherichia coli and in S. lividans. Comparison of the production in both hosts revealed that the expression of active protein achieved in S. lividans was much higher than in E. coli, especially in the case of the periplasmic enzyme. In fact, the native signal peptide of the T. thermophilus phosphatase was functional in S. lividans, being processed at the same peptide bond in both organisms, allowing the overproduction and secretion of this protein to the S. lividans culture supernatant. As in E. coli, the thermostability of the expressed proteins allowed a huge purification factor upon thermal denaturation and precipitation of the host proteins. We conclude that S. lividans is a very efficient and industry-friendly host for the expression of thermophilic proteins from Thermus spp.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adham SA, Honrubia P, Díaz M, Fernández-Ábalos JM, Santamaría RI, Gil JA (2001) Expression of the genes coding for the xylanase Xys1 and the cellulase Cel1 from the straw-decomposing Streptomyces halstedii JM8 cloned into the amino-acid producer Brevibacterium lactofermentum ATCC13869. Arch Microbiol 177:91–97
Angelini S, Moreno R, Gouffi K, Santini C, Yamagishi A, Berenguer J, Wu L (2001) Export of Thermus thermophilus alkaline phosphatase via the twin-arginine translocation pathway in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett 506:103–107
Brickman E, Beckwith J (1975) Analysis of the regulation of Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase synthesis using deletions and phi80 transducing phages. J Mol Biol 96:307–316
Castán P (2004) Desarrollo de cepas de interés biotecnológico mediante la manipulación de los genes recA y slpA de Thermus thermophilus. PhD thesis. Departamento de Biología Molecular. Universidad Autónoma de Madrid. Madrid
Castán P, Zafra O, Moreno R, de Pedro MA, Vallés C, Cava F, Caro E, Schwarz H, Berenguer J (2002) The periplasmic space in Thermus thermophilus: evidence from a regulation-defective S-layer mutant overexpressing an alkaline phosphatase. Extremophiles 6:225–232
Cava F, Berenguer J (2006) Biochemical and regulatory properties of a respiratory island encoded by a conjugative plasmid in the extreme thermophile Thermus thermophilus. Biochem Soc Trans 34:97–100
Cava F, de Pedro MA, Blas-Galindo E, Waldo GS, Westblade LF, Berenguer J (2008) Expression and use of superfolder green fluorescent protein at high temperatures in vivo: a tool to study extreme thermophile biology. Environ Microbiol 10:605–613
Challis GL, Hopwood DA (2003) Synergy and contingency as driving forces for the evolution of multiple secondary metabolite production by Streptomyces species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(Suppl 2):14555–14561
Dion M, Fourage L, Hallet JN, Colas B (1999) Cloning and expression of a beta-glycosidase gene from Thermus thermophilus. Sequence and biochemical characterization of the encoded enzyme. Glycoconj J 16:27–37
Díaz M, Adham SA, Ramón D, Gil JA, Santamaría RI (2004) Streptomyces lividans and Brevibacterium lactofermentum as heterologous hosts for the production of X22 xylanase from Aspergillus nidulans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65:401–406
Gong N, Chen C, Xie L, Chen H, Lin X, Zhang R (2005) Characterization of a thermostable alkaline phosphatase from a novel species Thermus yunnanensis sp. nov. and investigation of its cobalt activation at high temperature. Biochim Biophys Acta 1750:103–111
Hanahan D (1983) Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol 166:557–580
Henne A, Bruggemann H, Raasch C, Wiezer A, Hartsch T, Liesegang H, Johann A, Lienard T, Gohl O, Martinez-Arias R, Jacobi C, Starkuviene V, Schlenczeck S, Dencker S, Huber R, Klenk HP, Kramer W, Merkl R, Gottschalk G, Fritz HJ (2004) The genome sequence of the extreme thermophile Thermus thermophilus. Nat Biotechnol 22:547–553
Hidalgo A, Betancor L, Moreno R, Zafra O, Cava F, Fernández-Lafuente R, Guisán JM, Berenguer J (2004) Thermus thermophilus as a cell factory for the production of a thermophilic Mn-dependent catalase which fails to be synthesized in an active form in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:3839–3844
Katz E, Thompson CJ, Hopwood DA (1983) Cloning and expression of the tyrosinase gene from Streptomyces antibioticus in Streptomyces lividans. J Gen Microbiol 129:2703–2714
Kayser KJ, Kilbane JJ 2nd (2001) New host-vector system for Thermus spp. based on the malate dehydrogenase gene. J Bacteriol 183:1792–1795
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical streptomyces genetics. John Innes Centre, Norwich
Miller J (1972) Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Moreno R, Zafra O, Cava F, Berenguer J (2003) Development of a gene expression vector for Thermus thermophilus based on the promoter of the respiratory nitrate reductase. Plasmid 49:2–8
Moreno R, Haro A, Castellanos A, Berenguer J (2005) High-level overproduction of His-tagged Tth DNA polymerase in Thermus thermophilus. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:591–593
Pallen MJ, Chaudhuri RR, Henderson IR (2003) Genomic analysis of secretion systems. Curr Opin Microbiol 6:519–527
Pantazaki AA, Pritsa AA, Kyriakidis DA (2002) Biotechnologically relevant enzymes from Thermus thermophilus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58:1–12
Pessela BC, Vian A, Mateo C, Fernández-Lafuente R, García JL, Guisán JM, Carrascosa AV (2003) Overproduction of Thermus sp. Strain T2 beta-galactosidase in Escherichia coli and preparation by using tailor-made metal chelate supports. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1967–1972
Pessela BC, Torres R, Fuentes M, Mateo C, Filho M, Carrascosa AV, Vian A, García JL, Guisán JM, Fernández-Lafuente R (2004) A simple strategy for the purification of large thermophilic proteins overexpressed in mesophilic microorganisms: application to multimeric enzymes from Thermus sp. strain T2 expressed in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Prog 20:1507–1511
Rodríguez S, Santamaría RI, Fernández-Ábalos JM, Díaz M (2005) Identification of the sequences involved in the glucose-repressed transcription of the Streptomyces halstedii JM8 xysA promoter. Gene 351:1–9
Ruiz-Arribas A, Fernández-Ábalos JM, Sánchez P, Garda AL, Santamaría RI (1995) Overproduction, purification, and biochemical characterization of a xylanase (Xys1) from Streptomyces halstedii JM8. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:2414–2419
Santamaría R, Ruiz-Arribas A, González Holgado G, Rodríguez S, Díaz M, Fernández-Ábalos JM (2005) Secuencia de nucleótidos promotora de la expresión génica derivada de la región promotora del gen xysA. Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC) España. ES 2 235–562
Sianidis G, Pozidis C, Becker F, Vrancken K, Sjoeholm C, Karamanou S, Takamiya-Wik M, van Mellaert L, Schaefer T, Anne J, Economou A (2006) Functional large-scale production of a novel Jonesia sp. xyloglucanase by heterologous secretion from Streptomyces lividans. J Biotechnol 121:498–507
Vallín C, Ramos A, Pimienta E, Rodríguez C, Hernández T, Hernández I, Del Sol R, Rosabal G, Van Mellaert L, Anne J (2006) Streptomyces as host for recombinant production of Mycobacterium tuberculosis proteins. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 86:198–202
Van Mellaert L, Anne J (2001) Gram-positive bacteria for the heterologous production of biopharmaceutical compounds. In: Van Broekhoven A, Shapiro F, Anne J (eds) Novel frontiers in the production of compounds for biomedical use. vol. 1. Kluwer Academic, New York, pp 277–300
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by grants CSI02A05 from the Junta de Castilla y León to R. Santamaría and BIO2007-60245 and S0505/PPQ/0344 from the Ministry of Education and Science and the Comunidad Autónoma de Madrid, respectively, to J. Berenguer. Institutional grants from Fundación Ramón Areces to CBMSO and from Junta de Castilla y León are also acknowledged. We thank MJ Jimenez Rufo for her excellent technical work. Thanks are also due to N. Skinner for supervising the English version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Díaz, M., Ferreras, E., Moreno, R. et al. High-level overproduction of Thermus enzymes in Streptomyces lividans . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79, 1001–1008 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1495-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1495-1