Abstract
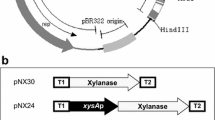
The Aspergillus nidulans gene xlnA coding for the fungal xylanase X22 has been cloned and expressed in two heterologous bacterial hosts: Streptomyces lividans and Brevibacterium lactofermentum. Streptomyces strains yielded 10 units/ml of xylanase when the protein was produced with its own signal peptide, and 19 units/ml when its signal peptide was replaced by the one for xylanase Xys1 from Streptomyces halstedii. B. lactofermentum was also able to produce xylanase X22, affording 6 units/ml upon using either the Aspergillus xlnA signal peptide or Streptomyces xysA. These production values are higher than those previously reported for the heterologous expression of the A. nidulans xlnA gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae (1 unit/ml). Moreover, the X22 enzyme produced by Streptomyces lividans showed oenological properties, indicating that this Streptomyces recombinant strain is a good candidate for the production of this enzyme at the industrial scale.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adham SA, Campelo AB, Ramos A, Gil JA (2001a) Construction of a xylanase-producing strain of Brevibacterium lactofermentum by stable integration of an engineered xysA gene from Streptomyces halstedii JM8. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:5425–5430
Adham SA, Honrubia P, Díaz M, Fernández-Ábalos JM, Santamaría RI, Gil JA (2001b) Expression of the genes coding for the xylanase Xys1 and the cellulase Cel1 from the straw-decomposing Streptomyces halstedii JM8 cloned into the amino-acid producer Brevibacterium lactofermentum ATCC13869. Arch Microbiol 177:91–97
Adham SA, Rodríguez S, Ramos A, Santamaría RI, Gil JA (2003) Improved vectors for transcriptional/translational signal screening in corynebacteria using the melC operon from Streptomyces glaucescens as reporter. Arch Microbiol 180:53–59
Anne J, Van Mellaert L (1993) Streptomyces lividans as host for heterologous protein production. FEMS Microbiol Lett 114:121–128
Beki E, Nagy I, Vanderleyden J, Jager S, Kiss L, Fulop L, Hornok L, Kukolya J (2003) Cloning and heterologous expression of a beta-d-mannosidase (EC 3.2.1.25)-encoding gene from Thermobifida fusca TM51. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1944–1952
Bernfeld P (1951) Enzymes of starch degradation and synthesis. Adv Enzymol 12:379–428
Biely P, Markovic O, Mislovicova D (1985) Sensitive detection of endo-1,4-beta-glucanases and endo-1,4-beta-xylanases in gels. Anal Biochem 144:147–151
Binnie C, Cossar JD, Stewart DI (1997) Heterologous biopharmaceutical protein expression in Streptomyces. Trends Biotechnol 15:315–320
Brawner M, Poste G, Rosenberg M, Westpheling J (1991) Streptomyces: a host for heterologous gene expression. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2:674–681
Fernández-Espinar MT, Ramón D, Piñaga F, Vallés S (1992) Xylanase production by Aspergillus nidulans. FEMS Microbiol Lett 91:91–96
Fernández-Espinar MT, Piñaga F, Sanz P, Ramón D, Valles S (1993) Purification and characterization of a neutral endoxylanase from Aspergillus nidulans. FEMS Microbiol Lett 113:223–228
Fernández-González C, Gil JA, Mateos LM, Schwarzer A, Schafer A, Kalinowski J, Puhler A, Martín JF (1996) Construction of l-lysine-overproducing strains of Brevibacterium lactofermentum by targeted disruption of the hom and thrB genes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 46:554–558
Ganga MA (1997) Producción y caracterización de enzimas implicadas en la degradación de la pared celular vegetal y su expresión en levaduras vínicas. PhD thesis, Universitat de Valencia, Valencia
Ganga MA, Querol A, Vallés S, Ramón D, MacCabe A, Piñaga F (1998) Heterologous production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae of different Aspergillus nidulans xylanases of potential interest in oenology. J Sci Food Agric 1998:78315–78320
Ganga MA, Pinaga F, Vallés S, Ramón D, Querol A (1999) Aroma improving in microvinification processes by the use of a recombinant wine yeast strain expressing the Aspergillus nidulans xlnA gene. Int J Food Microbiol 47:171–178
Geueke B, Hummel W (2003) Heterologous expression of Rhodococcus opacus l-amino acid oxidase in Streptomyces lividans. Protein Expr Purif 28:303–309
Gilbert M, Morosoli R, Shareck F, Kluepfel D (1995) Production and secretion of proteins by streptomycetes. Crit Rev Biotechnol 15:13–39
Hanahan D (1983) Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol 1983:166557–166580
Isiegas C, Parro V, Mellado RP (1999) Streptomyces lividans as a host for the production and secretion of Escherichia coli TEM beta-lactamase. Lett Appl Microbiol 28:321–326
Jager W, Schafer A, Puhler A, Labes G, Wohlleben W (1992) Expression of the Bacillus subtilis sacB gene leads to sucrose sensitivity in the gram-positive bacterium Corynebacterium glutamicum but not in Streptomyces lividans. J Bacteriol 174:5462–5465
Kaneko H, Sakaguchi K (1979) Fusion of protoplast and genetic recombination of Brevibacterium flavum. Agric Biol Chem 1979:43867–43868
Katz E, Thompson CJ, Hopwood DA (1983) Cloning and expression of the tyrosinase gene from Streptomyces antibioticus in Streptomyces lividans. J Gen Microbiol 129:2703–2714
Kieser T (1984) Factors affecting the isolation of ccc DNA from Streptomyces lividans and Escherichia coli. Plasmid 1984:1219–1236
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. John Innes Centre, Norwich
MacCabe AP, Orejas M, Pérez-González JA, Ramón D (1998) Opposite patterns of expression of two Aspergillus nidulans xylanase genes with respect to ambient pH. J Bacteriol 180:1331–1333
MacCabe AP, Orejas M, Tamayo EN, Villanueva A, Ramón D (2002) Improving extracellular production of food-use enzymes from Aspergillus nidulans. J Biotechnol 96:43–54
Mesas JM (1986) Characterization of asparaginase, aspartase and aspartokinase of Corynebacterium glutamicum. PhD thesis, Universidad de León, León
Orejas M, MacCabe AP, Pérez González JA, Kumar S, Ramón D (1999) Carbon catabolite repression of the Aspergillus nidulans xlnA gene. Mol Microbiol 31:177–184
Peterson GL (1977) A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem 83:346–356
Pérez-González JA, De Graaff LH, Visser J, Ramón D (1996) Molecular cloning and expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae of two Aspergillus nidulans xylanase genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:2179–2182
Pico Y, Fernández M, Rodríguez R, Almudever J, Manes J, Font G, Marín R, Carda C, Manzanares P, Ramón D (1999) Toxicological assessment of recombinant xylanase X(22) in wine. J Agric Food Chem 47:1597–1602
Piñaga F, Fernández-Espinar MT, Vallés S, Ramón D (1994) Xylanase production in Aspergillus nidulans: induction and carbon catabolite repression. FEMS Microbiol Lett 115:319–323
Pozidis C, Lammertyn E, Politou AS, Anne J, Tsiftsoglou AS, Sianidis G, Economou A (2001) Protein secretion biotechnology using Streptomyces lividans: large-scale production of functional trimeric tumor necrosis factor alpha. Biotechnol Bioeng 72:611–619
Ruiz-Arribas A, Fernández-Ábalos JM, Sánchez P, Garda AL, Santamaría RI (1995) Overproduction, purification, and biochemical characterization of a xylanase (Xys1) from Streptomyces halstedii JM8. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:2414–2419
Ruiz-Arribas A, Sánchez P, Calvete JJ, Raida M, Fernández-Ábalos JM, Santamaría RI (1997) Analysis of xysA, a gene from Streptomyces halstedii JM8 that encodes a 45-kilodalton modular xylanase, Xys1. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:2983–2988
Salim K, Haedens V, Content J, Leblon G, Huygen K (1997) Heterologous expression of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis gene encoding antigen 85A in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4392–4400
Sambrook J, Fristsch E, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Sanchez-Torres P, Gonzalez-Candelas L, Ramon D (1998) Heterologous expression of a Candida molischiana anthocyanin-beta-glucosidase in a wine yeast strain. J Agric Food Chem 46:354–360
Santamaría RI, Gil JA, Martín JF (1985) High-frequency transformation of Brevibacterium lactofermentum protoplasts by plasmid DNA. J Bacteriol 162:463–467
Schafer A, Kalinowski J, Simon R, Seep-Feldhaus AH, Puhler A (1990) High-frequency conjugal plasmid transfer from gram-negative Escherichia coli to various gram-positive coryneform bacteria. J Bacteriol 172:1663–1666
Smith TJ, Lloyd JS, Gallagher SC, Fosdike WL, Murrell JC, Dalton H (1999) Heterologous expression of alkene monooxygenase from Rhodococcus rhodochrous B-276. Eur J Biochem 260:446–452
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Tremblay D, Lemay J, Gilbert M, Chapdelaine Y, Dupont C, Morosoli R (2002) High-level heterologous expression and secretion in Streptomyces lividans of two major antigenic proteins from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Can J Microbiol 48:43–48
Wely KH van, Swaving J, Freudl R, Driessen AJ (2001) Translocation of proteins across the cell envelope of Gram-positive bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 25:437–454
Wu YQ, Jiang PH, Fan CS, Wang JG, Shang L, Huang WD (2003) Co-expression of five genes in E. coli for l-phenylalanine in Brevibacterium flavum. World J Gastroenterol 9:342–346
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a grant from the European Union (FD1997-1134-C03). We thank R. Valle for her excellent technical work. Drs. J.M. Férnandez-Abalos and F. Leal are thanked for their comments. Thanks are also due to N. Skinner for supervising the English version of the manuscript. These experiments comply with the current laws in Spain.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Díaz, M., Adham, S.A.I., Ramón, D. et al. Streptomyces lividans and Brevibacterium lactofermentum as heterologous hosts for the production of X22 xylanase from Aspergillus nidulans . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65, 401–406 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1633-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-004-1633-3