Abstract
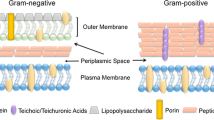
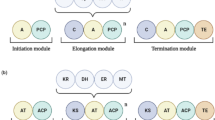
For the first time, a genome-wide transcriptional analysis was performed to elucidate the cellular response of Staphylococcus aureus to triclosan. Our results indicate that the effects of triclosan are widespread on metabolism, affecting many vital cellular processes. Triclosan downregulated the transcription of genes involved in virulence factor and energy metabolism such as amino acid, carbohydrate, lipid transport, and metabolism, while multidrug resistance genes, coenzyme transport, and metabolism and transcription genes were upregulated. Furthermore, triclosan downregulated the transcription of genes encoding major lipid metabolism enzymes such as 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase, acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase, acetyl-CoA synthetase, and acetyl-CoA carboxylase, which all play essential roles in S. aureus lipid metabolism. It is interesting to note that the expression of the enoyl-ACP reductase gene, fabI, was not changed after exposure of S. aureus with 0.05 μM triclosan at 10 and 60 min in our study. This work also implies that triclosan may kill S. aureus by interfering with its ability to form cell membranes. Another important implication of our result is that S. aureus may generate resistance factors under triclosan stress.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Affymetrix (2004) Affymetrix GeneChipÒ expression analysis technical manual. Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA
Barber LB, Keefe SH, Antweiler RC, Taylor HE, Wass RD (2006) Accumulation of contaminants in fish from wastewater treatment wetlands. Environ Sci Technol 40:603–611
Bardowski J, Ehrlich SD, Chopin A (1994) BglR protein, which belongs to the BglG family of transcriptional antiterminators, is involved in beta-glucoside utilization in Lactococcus lactis. J Bacteriol 176:5681–5685
Bayles KW (2000) The bactericidal action of penicillin: new clues to an unsolved mystery. Trends Microbiol 8:274–278
Chang W, Small DA, Toghrol F, Bentley WE (2005a) Microarray analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa reveals induction of pyocin genes in response to hydrogen peroxide. BMC Genomics 6:115
Chang W, Small DA, Toghrol F, Bentley WE (2005b) Microarray analysis of toxicogenomic effects of peracetic acid on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Environ Sci Technol 39:5893–5899
Chang W, Small DA, Toghrol F, Bentley WE (2006a) Global transcriptome analysis of Staphylococcus aureus response to hydrogen reroxide. J Bacteriol 188:1648–1659
Chang W, Toghrol F, Bentley WE (2006b) Toxicogenomic response of Staphylococcus aureus to peracetic acid. Environ Sci Technol 40:5124–5131
Cramton SE, Gerke C, Schnell NF, Nichols WW, Gotz F (1999) The intercellular adhesion (ica) locus is present in Staphylococcus aureus and is required for biofilm formation. Infect Immun 67:5427–5433
Dukan S, Levi Y, Touati D (1997) Recovery of culturability of an HOCl-stressed population of Escherichia coli after incubation in phosphate buffer: resuscitation or regrowth? Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4204–4209
Fraser KR, Harvie D, Coote PJ, O’Byrne CP (2000) Identification and characterization of an ATP binding cassette l-carnitine transporter in Listeria monocytogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:4696–4704
Fux L, Nussbaum-Shochat A, Lopian L, Amster-Choder O (2004) Modulation of monomer conformation of the BglG transcriptional antiterminator from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 186:6775–6781
Gosset G (2005) Improvement of Escherichia coli production strains by modification of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system. Microbial Cell Factories 4:14
Heath RJ, Li J, Roland GE, Rock CO (2000) Inhibition of the Staphylococcus aureus NADPH-dependent enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase by triclosan and hexachlorophene. J Biol Chem 275:4654–4659
Heath RJ, Rubin JR, Holland DR, Zhang E, Snow ME, Rock CO (1999) Mechanism of triclosan inhibition of bacterial fatty acid synthesis. J Biol Chem 274:11110–11114
Heidler J, Halden RU (2007) Mass balance assessment of triclosan removal during conventional sewage treatment. Chemosphere 66:362–369
Heidler J, Sapkota A, Halden RU (2006) Partitioning, persistence, and accumulation in digested sludge of the topical antiseptic triclocarban during wastewater treatment. Environ Sci Technol 40:3634–3639
Hoang TT, Schweizer HP (1999) Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase (FabI): a target for the antimicrobial triclosan and its role in acylated homoserine lactone synthesis. J Bacteriol 181:5489–5497
Hoshino T, Kose K, Uratani Y (1990) Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the gene braB coding for the sodium-coupled branched-chain amino acid carrier in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. Mol Gen Genet 220:461–467
Ingmer H, Vogensen FK, Hammer K, Kilstrup M (1999) Disruption and analysis of the clpB, clpC, and clpE genes in Lactococcus lactis: ClpE, a new Clp family in gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol 181:2075–2083
Kolpin DW, Furlong ET, Meyer MT, Thurman EM, Zaugg SD, Barber LB, Buxton HT (2002) Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in U.S. streams, 1999–2000: a national reconnaissance.. Environ Sci Technol 36:1202–1211
Lambert RJ (2004) Comparative analysis of antibiotic and antimicrobial biocide susceptibility data in clinical isolates of methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa between 1989 and 2000. J Appl Microbiol 97:699–711
Loraine GA, Pettigrove ME (2006) Seasonal variations in concentrations of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in drinking water and reclaimed wastewater in southern California. Environ Sci Technol 40:687–695
McMurry LM, Oethinger M, Levy SB (1998) Triclosan targets lipid synthesis. Nature 394:531–532
Mitchell WJ, Reizer J, Herring C, Hoischen C, Saier MH Jr. (1993) Identification of a phosphoenolpyruvate:fructose phosphotransferase system (fructose-1-phosphate forming) in Listeria monocytogenes. J Bacteriol 175:2758–2761
Ni Eidhin D, Perkins S, Francois P, Vaudaux P, Hook M, Foster TJ (1998) Clumping factor B (ClfB), a new surface-located fibrinogen-binding adhesin of Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Microbiol 30:245–257
Rock CO, Cronan JE (1996) Escherichia coli as a model for the regulation of dissociable (type II) fatty acid biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1302:1–16
Russell AD (2002a) Antibiotic and biocide resistance in bacteria: introduction. J Appl Microbiol 92:1S–3S Suppl
Russell AD (2002b) Introduction of biocides into clinical practice and the impact on antibiotic-resistant bacteria. J Appl Microbiol 92:121S–135S Suppl
Small DA, Chang W, Toghrol F, Bentley WE (2007a) Comparative global transcription analysis of sodium hypochlorite, peracetic acid, and hydrogen peroxide on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76:1093–1105
Small DA, Chang W, Toghrol F, Bentley WE (2007b) Toxicogenomic analysis of sodium hypochlorite antimicrobial mechanisms in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:176–185
Weber DJ, Rutala WA (2006) Use of germicides in the home and the healthcare setting: is there a relationship between germicide use and antibiotic resistance? Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 27:1107–1119
Yazdankhah SP, Scheie AA, Hoiby EA, Lunestad BT, Heir E, Fotland TO, Naterstad K, Kruse H (2006) Triclosan and antimicrobial resistance in bacteria: an overview. Microb Drug Resist 12:83–90
Zhang Y, Cronan JE Jr (1998) Transcriptional analysis of essential genes of the Escherichia coli fatty acid biosynthesis gene cluster by functional replacement with the analogous Salmonella typhimurium gene cluster. J Bacteriol 180:3295–3303
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the United States Environmental Protection Agency Grant number T-83284001-1. Although the research described in this paper has been funded wholly by the United States Environmental Protection Agency, it has not been subjected to the Agency's peer and administrative review and therefore may not necessarily reflect the views of the EPA; nor does the mention of trade names or commercial products constitute endorsement of recommendation of use.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, HJ., Chang, M.W., Toghrol, F. et al. Microarray analysis of toxicogenomic effects of triclosan on Staphylococcus aureus . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78, 695–707 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1349-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1349-x