Abstract
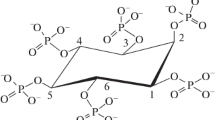
Debaryomyces castellii phytase was purified to homogeneity in a single step by hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Its molecular mass is 74 kDa with 28.8% glycosylation. Its activity was optimal at 60°C and pH 4.0. The K m value for sodium phytate was 0.532 mM. The enzyme exhibited a low specificity and hydrolyzed many phosphate esters. The phytase fully hydrolyzed myo-inositol hexakisphosphate (or phytic acid, Ins P6) to inositol and inorganic phosphate. The sequence of Ins P6 hydrolysis was determined by combining results from high-performance ionic chromatography and nuclear magnetic resonance. D. castellii phytase is a 3-phytase that sequentially releases phosphate groups through Ins (1,2,4,5,6) P5, Ins (1,2,5,6) P4, Ins (1,2,6) P3, Ins (1,2) P2, Ins (1 or 2) P1, and inositol (notation 3/4/5/6/1 or 2).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bax A, Griffey RH, Hawkins BL (1983) Correlation of proton and nitrogen-15 chemical shifts by multiple quantum RMN. J Magn Reson 55:301
Bax A, Davis GD (1985) MLEV-17-based two-dimensional homonuclear magnetization transfer spectroscopy. J Magn Reson 65:355–360
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of proteins utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Derome AE, Williamson MP (1990) Rapid-pulsing artefacts in double-quantum-filtered COSY. J Magn Reson 88:177–185
Greiner R, Konietzny U, Jany KD (1993) Purification and characterization of two phytases from E. coli. Arch Biochem Biophys 303:107–113
Greiner R, Haller E, Konietzny U, Jany KD (1997) Purification and characterization of a phytase from Klebsiella terrigena. Arch Biochem Biophys 341:201–206
Greiner R, Carlsson NG, Alminger ML (2000) Stereospecificity of myo-inositol hexakisphosphate dephosphorylation by a phytate-degrading enzyme of Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 84:53–62
Greiner R, Alminger ML, Carlsson NG (2001) Stereospecificity of myo-inositol hexakisphosphate dephosphorylation by a phytate-degrading enzyme of Baker’s yeast. J Agric Food Chem 49:2228–2233
Kerovuo J, Rouvinen J, Hatzack F (2000) Analysis of myo-inositol hexakisphosphate hydrolysis by Bacillus phytase: indication of a novel reaction mechanism. Biochemistry 352:623–628
Kim YO, Kim HK, Bae KS, Yu JH, Oh TK (1998) Purification and properties of a thermostable phytase from Bacillus sp. DS11. Enzyme Microb Technol 22:2–7
Kostrewa D, Wyss M, D’Arcy A, van Loon APGM (1999) Crystal structure of Aspergillus niger pH 2.5 acid phosphatase at 2.4 Å resolution. J Mol Biol 288:965–974
Lambrechts C, Boze H, Moulin G, Galzy P (1992) Utilization of phytase by some yeasts. Biotechnol Lett 14:61–66
Lassen SF, Bech L, Fuglsang CC, Ohmann A, Breinholt J, Østergaard PR (2000) Peniophora phytase. US Patent 6060298
Lassen SF, Breinholt J, Østergaard PR, Brugger R, Bischoff A, Wyss M, Fuglsang CC (2001) Expression, gene cloning and characterization of five novel phytases from four basidiomycete fungi: Peniophora lycii, Agrocybe pediades, a Ceriporia sp., and Trametes pubescens. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4701–4707
Nagashima T, Tange T, Anazawa H (1999) Dephosphorylation of phytase by using the Aspergillus niger phytase with a high affinity for phytate. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:4682–4684
Nakamura Y, Fukuhara H, Sano K (2000) Secreted phytase activities of yeast. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:841–844
Nayini NR, Markakis P (1984) The phytase of yeast. Lebensm Wiss Technol 17:24–26
Pandey A, Szakács G, Soccol CR, Rodriguez-Leon JA, Soccol VY (2001) Production, purification and properties of microbial phytases. Bioresour Technol 77:203–214
Rance M, Sorensen OW, Bodenhausen G, Wagner G, Ernst RR, Wüthrich K (1983) Improved spectral resolution in cosy 1H NMR spectra of proteins via double quantum filtering. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 117:479–485
Rance M (1987) Improved techniques for homonuclear rotating-frame and isotropic mixing experiments. J Magn Reson 74:557–564
Reddy NR, Sathe SK, Salunkhe DK (1982) Phytases in legumes and cereals. Adv Food Res 28:1–92
Segueilha L, Lambrechts C, Boze H, Moulin G, Galzy P (1992) Purification and properties of the phytase from Schwanniomyces castellii. J Ferm Bioeng 74:7–11
Shieh TR, Ware JH (1968) Survey of microorganisms for the production of extracellular phytase. Appl Microbiol 16:1348–1351
Skoglund E, Carlsson NG, Sandberg AS (1997) Determination of isomers of inositol mono- to hexaphophates in selected foods and intestinal contents using high-performance ion chromatography. J Agric Food Chem 45:431–436
Skoglund E, Carlsson NG, Sandberg AS (1998) High-performance chromatographic separation of inositol phosphate isomers on strong anion exchange columns. J Agric Food Chem 46:1877–1882
Türk M, Sandberg AS, Carlsson NG, Andlid T (2000) Inositol hexaphosphate hydrolysis by baker’s yeast. Capacity, kinetics, and degradation products. J Agric Food Chem 48:100–104
Ullah AHJ, Gibson DM (1987) Extracellular phytase (E.C. 3.1.3.8.) from Aspergillus ficuum NRRL 3135: purification and characterization. Prep Biochem 17:63–91
Ullah AHJ, Sethumadhavan K, Lei XG, Mullaney EJ (2000) Biochemical characterization of cloned Aspergillus fumigatus phytase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 275:279–285
Ullah AHJ, Sethumadhavan K (2003) PhyA gene product of Aspergillus ficuum and Peniophora lycii produces dissimilar phytases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 303:463–468
Vohra A, Satyanarayana T (2003) Phytases: microbial sources, production, purification and potential biotechnological applications. Crit Rev Biotechnol 23:29–60
Wodzinski RJ, Ullah AHJ (1996) Phytase. Adv Appl Microbiol 42:263–302
Wyss M, Pasamontes L, Friedlein A, Rémy R, Tessier M, Kronenberger A, Middendorf A, Lehmann M, Schnoebelen L, Röthlisberger U, Kusznir E, Wahl G, Müller F, Lahm HW, Vogel K, van Loon APGM (1999a) Biophysical characterisation of fungal phytases (myo-inositol hexakisphosphate phosphohydrolases): molecular size, glycosylation pattern, and engineering of proteolytic resistance. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:359–366
Wyss M, Brugger R, Kronenberger A, Rémy R, Fimbel R, Oesterhelt G, Lehmann M, van Loon APGM (1999b) Biochemical characterization of fungal phytases (myo-inositol hexakisphosphate phosphohydrolase): catalytic properties. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:367–373
Yamamoto M, Minoda Y, Yamada K (1972) Chemical and physico-chemical properties of phytase from Aspergillus terreus. Agric Biol Chem 36:2097–2103
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by ADISSEO France SAS society.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ragon, M., Aumelas, A., Chemardin, P. et al. Complete hydrolysis of myo-inositol hexakisphosphate by a novel phytase from Debaryomyces castellii CBS 2923. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78, 47–53 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1275-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1275-3