Abstract
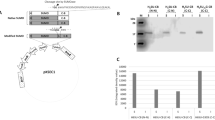
Direct expression of lactoferricin, an antimicrobial peptide, is lethal to Escherichia coli. For the efficient production of lactoferricin in E. coli, we developed an expression system in which the gene for the lysine- and arginine-rich cationic lactoferricin was fused to an anionic peptide gene to neutralize the basic property of lactoferricin, and successfully overexpressed the concatemeric fusion gene in E. coli. The lactoferricin gene was linked to a modified magainin intervening sequence gene by a recombinational polymerase chain reaction, thus producing an acidic peptide–lactoferricin fusion gene. The monomeric acidic peptide–lactoferricin fusion gene was multimerized and expressed in E. coli BL21(DE3) upon induction with isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside. The expression levels of the fusion peptide reached the maximum at the tetramer, while further increases in the copy number of the fusion gene substantially reduced the peptide expression level. The fusion peptides were isolated and cleaved to generate the separate lactoferricin and acidic peptide. About 60 mg of pure recombinant lactoferricin was obtained from 1 L of E. coli culture. The purified recombinant lactoferricin was found to have a molecular weight similar to that of chemically synthesized lactoferricin. The recombinant lactoferricin showed antimicrobial activity and disrupted bacterial membrane permeability, as the native lactoferricin peptide does.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera O, Ostolaza H, Quiros LM, Fierro JF (1999) Permeabilizing action of an antimicrobial lactoferricin-derived peptide on bacterial and artificial membranes. FEBS Lett 462(3):273–277
Ahn T, Kim H (1996) Differential effect of precursor ribose binding protein of Escherichia coli and its signal peptide on the SecA penetration of lipid bilayer. J Biol Chem 271:12372–12379
Andersons D, Engstrom A, Josephson S, Hansson L, Steiner H (1991) Biologically active and amidated cecropin produced in a baculovirus expression system from a fusion construct containing the antibody-binding part of protein A. Biochem J 280(1):219–224
Andersen JH, Jenssen H, Gutteberg TJ (2003) Lactoferrin and lactoferricin inhibit Herpes simplex 1 and 2 infection and exhibit synergy when combined with acyclovir. Antiviral Res 58(3):209–215
Bellamy W, Takase M, Yamauchi K, Wakabayashi H, Kawase K, Tomita M (1992) Identification of the bactericidal domain of lactoferrin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1121(1–2):130–136
Bellamy W, Takase M, Wakabayashi H, Kawase K, Tomita M (1992) Antibacterial spectrum of lactoferricin B, a potent bactericidal peptide derived from the N-terminal region of bovine lactoferrin. J Appl Bacteriol 73(6):472–479
Bellamy W, Wakabayashi H, Takase M, Kawase K, Shimamura S, Tomita M (1993) Killing of Candida albicans by lactoferricin B, a potent antimicrobial peptide derived from the N-terminal region of bovine lactoferrin. Med Microbiol Immunol (Berl) 182(2):97–105
Callaway JE, Lai J, Haselbeck B, Baltaian M, Bonnesen SP, Weickmann J, Wilcox G, Lei SP (1993) Modification of the C terminus of cecropin is essential for broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 37(8):1614–1619
Chevrier-Miller M, Jacques N, Raibaud O, Dreyfus M (1990) Transcription of single-copy hybrid lacZ genes by T7 RNA polymerase in Escherichia coli: mRNA synthesis and degradation can be uncoupled from translation. Nucleic Acids Res 18(19):5787–5792
Diarra MS, Petitclerc D, Lacasse P (2002) Effect of lactoferrin in combination with penicillin on the morphology and the physiology of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from bovine mastitis. J Dairy Sci 85(5):1141–1149
Dionysius DA, Milne JM (1997) Antibacterial peptides of bovine lactoferrin: purification and characterization. J Dairy Sci 80(4):667–674
Gigova L, Wishart P, Uscheva A, Ivanova M, Bardarov S, Jay E, Ivanov I (1989) Expression of repetitive human calcitonin genes in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 11(4):401–412
Goodman RE, Schanbacher FL (1991) Bovine lactoferrin mRNA: sequence, analysis, and expression in the mammary gland. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 180(1):75–84
Hara S, Yamakawa M (1996) Production in Escherichia of moricin, a novel type antibacterial peptide from the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 220(3):664–669
Haversen L, Ohlsson BG, Hahn-Zoric M, Hanson LA, Mattsby-Baltzer I (2002) Lactoferrin down-regulates the LPS-induced cytokine production in monocytic cells via NF-kappa B. Cell Immunol 220(2):83–95
Heller WT, Waring AJ, Lehrer RI, Harroun TA, Weiss TM, Yang L, Huang HW (2000) Membrane thinning effect of the beta-sheet antimicrobial protegrin. Biochemistry 39(1):139–145
Ingham AB, Sproat KW, Tizard ML, Moore RJ (2005) A versatile system for the expression of nonmodified bacteriocins in Escherichia coli. J Appl Microbiol 98(3):676–683
Iost I, Dreyfus M (1995) The stability of Escherichia colilacZ mRNA depends upon the simultaneity of its synthesis and translation. EMBO J 14(13):3252–3261
Isamida T, Tanaka T, Omata Y, Yamaguchi K, Shimazaki K, Saito A (1998) Protective effect of lactoferricin against Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice. J Vet Med Sci 60(2):241–244
Koczulla AR, Bals R (2003) Antimicrobial peptides: current status and therapeutic potential. Drugs 63(4):389–406
Laemnli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 27:680–685
LaVallie ER, McCoy JM (1995) Gene fusion expression systems in Escherichia coli. Curr Opin Biotechnol 6(5):501–506
Lee JH, Hong SS, Kim SC (1998) Expression of an antimicrobial peptide magainin by a promotor inversion system. J Microbiol Biotechnol 8(1):34–41
Lee JH, Minn I, Park CB, Kim SC (1998) Acidic peptide-mediated expression of the antimicrobial peptide buforin II as tandem repeats in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 12:53–60
Lee JH, Kim MS, Cho JH, Kim SC (2002) Enhanced expression of tandem multimers of the antimicrobial peptide buforin II in Escherichia coli by the DEAD-box protein and trxB mutant. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58(6):790–796
Matsuzaki K, Sugishita K, Ishibe N, Ueha M, Nakata S, Miyajima K, Epand RM (1998) Relationship of membrane curvature to the formation of pores by magainin 2. Biochemistry 37(34):11856–11863
Marassi FM, Opella SJ, Juvvadi P, Merrifield RB (1999) Orientation of cecropin A helices in phospholipid bilayers determined by solid-state NMR spectroscopy. Biophys J 77(6):3152–3155
McCann KB, Lee A, Wan J, Roginski H, Coventry MJ (2003) The effect of bovine lactoferrin and lactoferricin B on the ability of feline calicivirus (a norovirus surrogate) and poliovirus to infect cell cultures. J Appl Microbiol 95(5):1026–1033
Miller KW, Evans RJ, Eisenberg SP, Thompson RC (1989) Secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor binding to mRNA and DNA as a possible cause of toxicity to Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 171:2166–2172
Park CJ, Lee JH, Hong SS, Lee HS, Kim SC (1998) High-level expression of the angiotensin-converting-enzyme-inhibiting peptide, YG-1, as tandem multimers in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 50(1):71–76
Piers KL, Brown MH, Hancock RE (1993) Recombinant DNA procedures for producing small antimicrobial cationic peptides in bacteria. Gene 134(1):7–13
Rao XC, Li S, Hu JC, Jin XL, Hu XM, Huang JJ, Chen ZJ, Zhu JM, Hu FQ (2004) A novel carrier molecule for high-level expression of peptide antibiotics in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 36(1):11–18
Reddy KV, Yedery RD, Aranha C (2004) Antimicrobial peptides: premises and promises. Int J Antimicrob Agents 24(6):536–547
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Schagger H, von Jagow G (1987) Tricine sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range of 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem 166:368–397
Schibli DJ, Hwang PM, Vogel HJ (1999) The structure of the antimicrobial active center of lactoferricin B bound to sodium dodecyl sulfate micelles. FEBS Lett 446(2–3):213–217
Sharma A, Khoury-Christianson AM, White SP, Dhanjal NK, Huang W, Paulhiac C, Friedman EJ, Manjula BN, Kumar R (1994) High-efficiency synthesis of human alpha-endorphin and magainin in the erythrocytes of transgenic mice: a production system for therapeutic peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91(20):9337–9341
Shin K, Yamauchi K, Teraguchi S, Hayasawa H, Tomita M, Otsuka Y, Yamazaki S (1998) Antibacterial activity of bovine lactoferrin and its peptides against enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Lett Appl Microbiol 26(6):407–411
Swart PJ, Kuipers EM, Smit C, Van Der Strate BW, Harmsen MC, Meijer DK (1998) Lactoferrin. Antiviral activity of lactoferrin. Adv Exp Med Biol 443:205–213
Ulvatne H, Haukland HH, Olsvik O, Vorland LH (2001) Lactoferricin B causes depolarization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 and fusion of negatively charged liposomes. FEBS Lett 492(1–2):62–65
Ulvatne H, Samuelsen O, Haukland HH, Kramer M, Vorland LH (2004) Lactoferricin B inhibits bacterial macromolecular synthesis in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 237(2):377–384
Vaskovsky VE, Kostetsky EY, Vasendin IM (1975) A universal reagent for phospholipid analysis. J Chromatogr 114(1):129–141
Vorland LH, Ulvatne H, Andersen J, Haukland HH, Rekdal O, Svendsen JS, Gutteberg TJ (1999) Antibacterial effects of lactoferricin B. Scand J Infect Dis 31(2):179–184
Wakabayashi H, Abe S, Teraguchi S, Hayasawa H, Yamaguchi H (1998) Inhibition of hyphal growth of azole-resistant strains of Candida albicans by triazole antifungal agents in the presence of lactoferrin-related compounds. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 42(7):1587–1591
Wakabayashi H, Matsumoto H, Hashimoto K, Teraguchi S, Takase M, Hayasawa H (1999) Inhibition of iron/ascorbate-induced lipid peroxidation by an N-terminal peptide of bovine lactoferrin and its acylated derivatives. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 63(5):955–957
Wakabayashi H, Teraguchi S, Tamura Y (2002) Increased Staphylococcus-killing activity of an antimicrobial peptide, lactoferricin B, with minocycline and monoacylglycerol. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 66(10):2161–2167
Xu Z, Wang F, Peng L, Fang X, Cen P (2005) Expression of human beta-defensin-2 with multiple joined genes in Escherichia coli. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 120(1):1–13
Yoo YC, Watanabe S, Watanabe R, Hata K, Shimazaki K, Azuma I (1998) Bovine lactoferrin and Lactoferricin inhibit tumor metastasis in mice. Adv Exp Med Biol 443:285–291
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, HK., Chun, DS., Kim, JS. et al. Expression of the cationic antimicrobial peptide lactoferricin fused with the anionic peptide in Escherichia coli . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72, 330–338 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0266-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0266-5