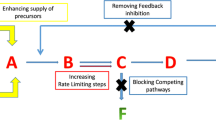
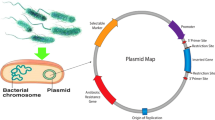
Abstract
The advent of recombinant DNA technology has revolutionized the strategies for protein production. Due to the well-characterized genome and a variety of mature tools available for genetic manipulation, Escherichia coli is still the most common workhorse for recombinant protein production. However, the culture for industrial applications often presents E. coli cells with a growth condition that is significantly different from their natural inhabiting environment in the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in deterioration in cell physiology and limitation in cell’s productivity. It has been recognized that innovative design of genetically engineered strains can highly increase the bioprocess yield with minimum investment on the capital and operating costs. Nevertheless, most of these genetic manipulations, by which traits are implanted into the workhorse through recombinant DNA technology, for enhancing recombinant protein productivity often translate into the challenges that deteriorate cell physiology or even jeopardize cell survival. An in-depth understanding of these challenges and their corresponding cellular response at the molecular level becomes crucial for developing superior strains that are more physiologically adaptive to the production environment to improve culture productivity. With the accumulated knowledge in cell physiology, whose importance to gene overexpression was to some extent undervalued previously, this review is intended to focus on the recent biotechnological advancement in engineering cell physiology to enhance recombinant protein production in E. coli.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams J (2004) Microbial evolution in laboratory environments. Res Microbiol 155:311–318
Alba BM, Gross CA (2004) Regulation of the Escherichia coli σE-dependent envelope stress response. Mol Microbiol 52:613–619
Aldor IS, Krawitz DC, Forrest W, Chen C, Nishihara JC, Joly JC, Champion KM (2005) Proteomic profiling of recombinant Escherichia coli in high-cell-density fermentations for improved production of an antibody fragment biopharmaceutical. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1717–1728
Andersen DC, Krummen L (2002) Recombinant protein expression for therapeutic applications. Curr Opin Biotechnol 13:117–123
Arneborg N, Salskoviversen AS, Mathiasen TE (1993) The effect of growth rate and other growth conditions on the lipid composition of Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 39:353–357
Arsene F, Tomoyasu T, Bukau B (2000) The heat shock response of Escherichia coli. Int J Food Microbiol 55:3–9
Aubrecht J, Caba E (2005) Gene expression profile analysis: an emerging approach to investigate mechanisms of genotoxicity. Pharmacogenomics 6:419–428
Bachinger T, Mandenius CF, Striedner G, Clementschitsch F, Durrschmid E, Cserjan-Puschmann M, Doblhoff-Dier O, Bayer K (2001) Non-invasive detection of the metabolic burden on recombinant microorganisms during fermentation processes. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 76:885–889
Baneyx F (1999) Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli. Curr Opin Biotechnol 10:411–421
Baneyx F, Mujacic M (2004) Recombinant protein folding and misfolding in Escherichia coli. Nat Biotechnol 22:1399–1408
Benhar I (2001) Biotechnological applications of phage and cell display. Biotechnol Adv 19:1–33
Bentley WE, Mirjalili N, Andersen DC, Davis RH, Kompala DS (1990) Plasmid-encoded protein: the principal factor in the “metabolic burden” associated with recombinant bacteria. Biotechnol Bioeng 35:668–681
Boor KJ (2006) Bacterial stress responses: what doesn’t kill them can make them stronger. PLoS Biol 4:18–20
Borth N, Mitterbauer R, Mattanovich D, Kramer W, Bayer K, Katinger H (1998) Flow cytometric analysis of bacterial physiology during induction of foreign protein synthesis in recombinant Escherichia coli cells. Cytometry 31:125–129
Bunin VD, Voloshin AG, Bunina ZF, Shmelev AV (1996) Electrophysical monitoring of culture process of recombinant Escherichia coli strains. Biotechnol Bioeng 51:720–724
Canonaco F, Schlattner U, Wallimann T, Sauer U (2003) Functional expression of arginine kinase improves recovery from pH stress of Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Lett 25:1013–1017
Chien LJ, Wu JM, Kuan IC, Lee CK (2004) Coexpression of Vitreoscilla hemoglobin reduces the toxic effect of expression of D-amino acid oxidase in E. coli. Biotechnol Prog 20:1359–1365
Cho SH, Shin D, Ji GE, Heu S, Ryu S (2005) High-level recombinant protein production by overexpression of Mlc in Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 119:197–203
Choi JH, Keum KC, Lee SY (2006) Production of recombinant proteins by high cell density culture of Escherichia coli. Chem Eng Sci 61:876–885
Choi JH, Lee SJ, Lee SJ, Lee SY (2003) Enhanced production of insulin-like growth factor I fusion protein in Escherichia coli by coexpression of the down-regulated genes identified by transcriptome profiling. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4737–4742
Choi JH, Lee SY (2004) Secretory and extracellular production of recombinant proteins using Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:625–635
Chou C-H, Bennett GN, San K-Y (1996) Genetic manipulation of stationary-phase genes to enhance recombinant protein production in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 50:636–642
Connolly L, De Las Penas A, Alba BM, Gross CA (1997) The response to extracytoplasmic stress in Escherichia coli is controlled by partially overlapping pathways. Genes Dev 11:2012–2021
Contiero J, Beatty C, Kumari S, DeSanti CL, Strohl WR, Wolfe A (2000) Effects of mutations in acetate metabolism on high-cell-density growth of Escherichia coli. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 24:421–430
Cornelis P (2000) Expressing genes in different Escherichia coli compartments. Curr Opin Biotechnol 11:450–454
Cserjan-Puschmann M, Kramer W, Duerrschmid E, Striedner G, Bayer K (1999) Metabolic approaches for the optimisation of recombinant fermentation processes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53:43–50
Cui SH, Meng JH, Bhagwat AA (2001) Availability of glutamate and arginine during acid challenge determines cell density-dependent survival phenotype of Escherichia coli strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4914–4918
Dartigalongue C, Missiakas D, Raina S (2001) Characterization of the Escherichia coli σE Regulon. J Biol Chem 276:20866–20875
De Anda R, Lara AR, Hernandez V, Hernandez-Montalvo V, Gosset G, Bolivar F, Ramirez OT (2006) Replacement of the glucose phosphotransferase transport system by galactose permease reduces acetate accumulation and improves process performance of Escherichia coli for recombinant protein production without impairment of growth rate. Metab Eng 8:281–290
de Marco A, De Marco V (2004) Bacteria co-transformed with recombinant proteins and chaperones cloned in independent plasmids are suitable for expression tuning. J Biotechnol 109:45–52
de Marco A, Vigh L, Diamant S, Goloubinoff P (2005) Native folding of aggregation-prone recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli by osmolytes, plasmid- or benzyl alcohol-overexpressed molecular chaperones. Cell Stress Chaperon 10:329–339
DeLisa MP, Lee P, Palmer T, Georgiou G (2004) Phage shock protein PspA of Escherichia coli relieves saturation of protein export via the Tat pathway. J Bacteriol 186:366–373
Dharmadi Y, Gonzalez R (2004) DNA microarrays: experimental issues, data analysis, and application to bacterial systems. Biotechnol Prog 20:1309–1324
Diaz-Acosta A, Sandoval ML, Delgado-Olivares L, Membrillo-Hernandez J (2006) Effect of anaerobic and stationary phase growth conditions on the heat shock and oxidative stress responses in Escherichia coli K-12. Arch Microbiol 185:429–438
Dong H, Nilsson L, Kurland CG (1995) Gratuitous overexpression of genes in Escherichia coli leads to growth inhibition and ribosome destruction. J Bacteriol 177:1497–1504
Dukan S, Nystrom T (1998) Bacterial senescence: stasis results in increased and differential oxidation of cytoplasmic proteins leading to developmental induction of the heat shock regulon. Genes Dev 12:3431–3441
Durrschmid K, Marzban G, Durrschmid E, Striedner G, Clementschitsch F, Cserjan-Puschmann L, Bayer K (2003) Monitoring of protein profiles for the optimization of recombinant fermentation processes using public domain databases. Electrophoresis 24:303–310
Farmer WR, Liao JC (1997) Reduction of aerobic acetate production by Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3205–3210
Ferenci T (1999) Regulation by nutrient limitation. Curr Opin Microbiol 2:208–213
Flores S, de Anda-Herrera R, Gosset G, Bolivar FG (2004) Growth-rate recovery of Escherichia coli cultures carrying a multicopy plasmid, by engineering of the pentose-phosphate pathway. Biotechnol Bioeng 87:485–494
Franchini AG, Egli T (2006) Global gene expression in Escherichia coli K-12 during short-term and long-term adaptation to glucose-limited continuous culture conditions. Microbiology 152:2111–2127
Frey AD, Farres J, Bollinger CJT, Kallio PT (2002) Bacterial hemoglobins and flavohemoglobins for alleviation of nitrosative stress in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:4835–4840
Georgiou G, Segatori L (2005) Preparative expression of secreted proteins in bacteria: status report and future prospects. Curr Opin Biotechnol 16:538–545
Gill RT (2003) Enabling inverse metabolic engineering through genomics. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14:484–490
Glick BR (1995) Metabolic load and heterologous gene expression. Biotechnol Adv 13:247–261
Gosset G (2005) Improvement of Escherichia coli production strains by modification of the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. Microb Cell Fact 4:14
Grabherr R, Nilsson E, Striedner G, Bayer K (2002) Stabilizing plasmid copy number to improve recombinant protein production. Biotechnol Bioeng 77:142–147
Gruber TM, Gross CA (2003) Multiple sigma subunits and the partitioning of bacterial transcription space. Annu Rev Microbiol 57:441–466
Guzman L-M, Belin D, Carson MJ, Beckwith J (1995) Tight regulation, modulation, and high-level expression by vectors containing the arabinose PBAD promoter. J Bacteriol 177:4121–4130
Haddadin FT, Harcum SW (2005) Transcriptome profiles for high-cell-density recombinant and wild-type Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 90:127–153
Han MJ, Jeong KJ, Yoo JS, Lee SY (2003) Engineering Escherichia coli for increased productivity of serine-rich proteins based on proteome profiling. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:5772–5781
Han MJ, Lee SY (2006) The Escherichia coli proteome: past, present, and future prospects. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 70:362–439
Hartley JL (2006) Cloning technologies for protein expression and purification. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:359–366
Hayhurst A, Harris WJ (1999) Escherichia coli Skp chaperone coexpression improves solubility and phage display of single-chain antibody fragments. Protein Expr Purif 15:336–343
Hazen TC, Stahl DA (2006) Using the stress response to monitor process control: pathways to more effective bioremediation. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:285–290
Hengge-Aronis R (1999) Interplay of global regulators and cell physiology in the general stress response of Escherichia coli. Curr Opin Microbiol 2:148–152
Heo MA, Kim SH, Kim SY, Kim YJ, Chung JH, Oh MK, Lee SG (2006) Functional expression of single-chain variable fragment antibody against c-Met in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 47:203–209
Hoffmann F, Rinas U (2001a) On-line estimation of the metabolic burden resulting from the synthesis of plasmid-encoded and heat-shock proteins by monitoring respiratory energy generation. Biotechnol Bioeng 76:333–340
Hoffmann F, Rinas U (2001b) Plasmid amplification in Escherichia coli after temperature upshift is impaired by induction of recombinant protein synthesis. Biotechnol Lett 23:1819–1825
Hoffmann F, Rinas U (2004a) Roles of heat-shock chaperones in the production of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 89:143–161
Hoffmann F, Rinas U (2004b) Stress induced by recombinant protein production in Escherichia coli. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 89:73–92
Hoffmann F, Schmidt M, Rinas U (2000) Simple technique for simultaneous on-line estimation of biomass and acetate from base consumption and conductivity measurements in high-cell density cultures of Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 70:358–361
Hoffmann F, Weber J, Rinas U (2002) Metabolic adaptation of Escherichia coli during temperature-induced recombinant protein production: 1. Readjustment of metabolic enzyme synthesis. Biotechnol Bioeng 80:313–319
Huisman GV, Siegele DA, Zambrano MM, Kolter R (1996) Morphological and physiological changes during stationary phase. In: Neidhardt FC, Ingraham JL, Lin ECC, Low KB, Magasanik B, Reznikoff WS, Riley M, Schaechter M, Umbarger HE (eds) Escherichia coli and Salmonella. ASM Press, Washington DC, pp 1672–1682
Ibarra RU, Edwards JS, Palsson BO (2002) Escherichia coli K-12 undergoes adaptive evolution to achieve in silico predicted optimal growth. Nature 420:186–189
Ignatova Z (2005) Monitoring protein stability in vivo. Microb Cell Fact 4:23
Ignatova Z, Mahsunah A, Georgieva M, Kasche V (2003) Improvement of posttranslational bottlenecks in the production of penicillin amidase in recombinant Escherichia coli strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1237–1245
Ihssen J, Egli T (2004) Specific growth rate and not cell density controls the general stress response in Escherichia coli. Microbiology 150:1637–1648
Imaizumi A, Takikawa R, Koseki C, Usuda Y, Yasueda H, Kojima H, Matsui K, Sugimoto S (2005) Improved production of L-lysine by disruption of stationary phase-specific rmf gene in Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 117:111–118
Imaizumi A, Koseki C, Matsui K, Kojima H (2006) Improved production of enzymes, which are expressed under the Pho regulon promoter, in the rmf gene (encoding ribosome modulation factor) disruptant of Escherichia coli. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70:949–957
Ishihama A (1997) Adaptation of gene expression in stationary phase bacteria. Curr Opin Genet Dev 7:582–588
Ishihama A (1999) Modulation of the nucleoid, the transcription apparatus, and the translation machinery in bacteria for stationary phase survival. Genes Cells 4:135–143
Jeong KJ, Choi JH, Yoo WM, Keum KC, Yoo NC, Lee SY, Sung MH (2004) Constitutive production of human leptin by fed-batch culture of recombinant rpoS −Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif 36:150–156
Jeong KJ, Lee SY (2003) Enhanced production of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli by filamentation suppression. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1295–1298
Kadokura H, Kawasaki H, Yoda K, Yamasaki M, Kitamoto K (2001) Efficient export of alkaline phosphatase overexpressed from a multicopy plasmid requires degP, a gene encoding a periplasmic protease of Escherichia coli. J Gen Appl Microbiol 47:133–141
Kemmer C, Neubauer P (2006) Antisense RNA based down-regulation of RNaseE in E. coli. Microb Cell Fact 5:38
Khmel IA (2005) Regulation of expression of bacterial genes in the absence of active cell growth. Russ J Genet 41:968–984
Khosla C, Bailey JE (1988) Heterologous expression of a bacterial hemoglobin improves the growth properties of recombinant Escherichia coli. Nature 331:633–635
Khosla C, Curtis JE, DeModena J, Rinas U, Bailey JE (1990) Expression of intracellular hemoglobin improves protein synthesis in oxygen-limited Escherichia coli. Bio/Technology 8:849–853
Kim JYH, Cha HJ (2003) Down-regulation of acetate pathway through antisense strategy in Escherichia coli: improved foreign protein production. Biotechnol Bioeng 83:841–853
Konstantinov KB (1996) Monitoring and control of the physiological state of cell cultures. Biotechnol Bioeng 52:271–289
Krojer T, Garrido-Franco M, Huber R, Ehrmann M, Clausen T (2002) Crystal structure of DegP (HtrA) reveals a new protease-chaperone machine. Nature 416:455–459
Kurland CG, Dong HJ (1996) Bacterial growth inhibition by overproduction of protein. Mol Microbiol 21:1–4
Kurokawa Y, Yanagi H, Yura T (2000) Overexpression of protein disulfide isomerase DsbC stabilizes multiple-disulfide-bonded recombinant protein produced and transported to the periplasm in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3960–3965
Lacour S, Landini P (2004) σS-Dependent gene expression at the onset of stationary phase in Escherichia coli: function of σS-dependent genes and identification of their promoter sequences. J Bacteriol 186:7186–7195
Lee HJ, Gu MB (2003) Construction of a sodA::luxCDABE fusion Escherichia coli: comparison with a katG fusion strain through their responses to oxidative stresses. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:577–580
Lee SY (1996) High cell density culture of Escherichia coli. Trends Biotechnol 14:98–105
Lee SY, Choi JH, Xu Z (2003) Microbial cell-surface display. Trends Biotechnol 21:45–52
Lee SY, Lee DY, Kim TY (2005) Systems biotechnology for strain improvement. Trends Biotechnol 23:349–358
LeThanh H, Neubauer P, Hoffmann F (2005) The small heat-shock proteins IbpA and IbpB reduce the stress load of recombinant Escherichia coli and delay degradation of inclusion bodies. Microb Cell Fact 4:6
Lewis G, Taylor IW, Nienow AW, Hewitt CJ (2004) The application of multi-parameter flow cytometry to the study of recombinant Escherichia coli batch fermentation processes. J Ind Microbiol Biot 31:311–322
Lin HY, Hoffmann F, Rozkov A, Enfors SO, Rinas U, Neubauer P (2004) Change of extracellular cAMP concentration is a sensitive reporter for bacterial fitness in high-cell-density cultures of Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 87:602–613
Looser V, Hammes F, Keller M, Berney M, Kovar K, Egli T (2005) Flow-cytometric detection of changes in the physiological state of E. coli expressing a heterologous membrane protein during carbon-limited fedbatch cultivation. Biotechnol Bioeng 92:69–78
Madan R, Kolter R, Mahadevan S (2005) Mutations that activate the silent bgl operon of Escherichia coli confer a growth advantage in stationary phase. J Bacteriol 187:7912–7917
Makinoshima H, Aizawa SI, Hayashi H, Miki T, Nishimura A, Ishihama A (2003) Growth phase-coupled alterations in cell structure and function of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 185:1338–1345
Makinoshima H, Nishimura A, Ishihama A (2002) Fractionation of Escherichia coli cell populations at different stages during growth transition to stationary phase. Mol Microbiol 43:269–279
Makrides SC (1996) Strategies for achieving high-level expression of genes in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev 60:512–538
March JC, Eiteman MA, Altman E (2002) Expression of an anaplerotic enzyme, pyruvate carboxylase, improves recombinant protein production in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5620–5624
Mogensen JE, Otzen DE (2005) Interactions between folding factors and bacterial outer membrane proteins. Mol Microbiol 57:326–346
Neubauer P, Lin HY, Mathiszik B (2003) Metabolic load of recombinant protein production: inhibition of cellular capacities for glucose uptake and respiration after induction of a heterologous gene in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 83:53–64
Narayanan N, Chou CP (2007) Physiological improvement to enhance Escherichia coli cell-surface display via reducing extracytoplasmic stress. Biotechnol Bioeng (in press)
Nishihara K, Kanemori M, Yanagi H, Yura T (2000) Overexpression of trigger factor prevents aggregation of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:884–889
Nitta T, Nagamitsu H, Murata M, Izu H, Yamada M (2000) Function of the σS regulon in dead-cell lysis in stationary-phase Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 182:5231–5237
Nystrom T (1999) Starvation, cessation of growth and bacterial aging. Curr Opin Microbiol 2:214–219
Pan K-L, Hsiao H-C, Weng C-L, Wu M-S, Chou CP (2003) Roles of DegP in prevention of protein misfolding in the periplasm upon overexpression of penicillin acylase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 185:3020–3030
Park SJ, Lee SY, Cho J, Kim TY, Lee JW, Park JH, Han MJ (2005) Global physiological understanding and metabolic engineering of microorganisms based on omics studies. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 68:567–579
Peng LF, Shimizu K (2006) Effect of fadR gene knockout on the metabolism of Escherichia coli based on analyses of protein expressions, enzyme activities and intracellular metabolite concentrations. Enzyme Microb Technol 38:512–520
Phue JN, Shiloach J (2005) Impact of dissolved oxygen concentration on acetate accumulation and physiology of E. coli BL21, evaluating transcription levels of key genes at different dissolved oxygen conditions. Metab Eng 7:353–363
Picon A, de Mattos MJT, Postma PW (2005) Reducing the glucose uptake rate in Escherichia coli affects growth rate but not protein production. Biotechnol Bioeng 90:191–200
Raman B, Nandakumar MP, Muthuvijayan V, Marten MR (2005) Proteome analysis to assess physiological changes in Escherichia coli grown under glucose-limited fed-batch conditions. Biotechnol Bioeng 92:384–392
Rhodius VA, Suh WC, Nonaka G, West J, Gross CA (2006) Conserved and variable functions of the sigma E stress response in related genomes. PLoS Biol 4:43–59
Ricci JCD, Hernandez ME (2000) Plasmid effects on Escherichia coli metabolism. Crit Rev Biotechnol 20:79–108
Richins R, Htay T, Kallio P, Chen W (1997) Elevated Fis expression enhances recombinant protein production in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 56:138–144
Riesenberg D, Guthke R (1999) High-cell-density cultivation of microorganisms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:422–430
Rinas U, Hoffmann F (2004) Selective leakage of host-cell proteins during high-cell-density cultivation of recombinant and non-recombinant Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Prog 20:679–687
Ritz D, Patel H, Doan B, Zheng M, Aslund F, Storz G, Beckwith J (2000) Thioredoxin 2 is involved in the oxidative stress response in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 275:2505–2512
Rizzitello AE, Harper JR, Silhavy TJ (2001) Genetic evidence for parallel pathways of chaperone activity in the periplasm of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 183:6794–6800
Rozkov A, Avignone-Rossa CA, Ertl PF, Jones P, O’Kennedy RD, Smith JJ, Dale JW, Bushell ME (2004) Characterization of the metabolic burden on Escherichia coli DH1 cells imposed by the presence of a plasmid containing a gene therapy sequence. Biotechnol Bioeng 88:909–915
Ruiz N, Silhavy TJ (2005) Sensing external stress: watchdogs of the Escherichia coli cell envelope. Curr Opin Microbiol 8:122–126
San KY, Bennett GN, Berrios-Rivera SJ, Vadali RV, Yang YT, Horton E, Rudolph FB, Sariyar B, Blackwood K (2002) Metabolic engineering through cofactor manipulation and its effects on metabolic flux redistribution in Escherichia coli. Metab Eng 4:182–192
Sandee D, Tungpradabkul S, Kurokawa Y, Fukui K, Takagi M (2005) Combination of Dsb coexpression and an addition of sorbitol markedly enhanced soluble expression of single-chain Fv in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 91:418–424
Schlapschy M, Grimm S, Skerra A (2006) A system for concomitant overexpression of four periplasmic folding catalysts to improve secretory protein production in Escherichia coli. Protein Eng Des Sel 19:385–390
Schmidt FR (2004) Recombinant expression systems in the pharmaceutical industry. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 65:363–372
Schultz T, Martinez L, de Marco A (2006) The evaluation of the factors that cause aggregation during recombinant expression in E. coli is simplified by the employment of an aggregation-sensitive reporter. Microb Cell Fact 5:28
Schweder T, Lin HY, Jurgen B, Breitenstein A, Riemschneider S, Khalameyzer V, Gupta A, Buttner K, Neubauer P (2002) Role of the general stress response during strong overexpression of a heterologous gene in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58:330–337
Shiloach J, Fass R (2005) Growing E. coli to high cell density—a historical perspective on method development. Biotechnol Adv 23:345–357
Shokri A, Larsson G (2004) Characterisation of the Escherichia coli membrane structure and function during fedbatch cultivation. Microb Cell Fact 3:9
Shokri A, Sanden AM, Larsson G (2002) Growth rate-dependent changes in Escherichia coli membrane structure and protein leakage. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58:386–392
Sletta H, Nedal A, Aune TEV, Hellebust H, Hakvag S, Aune R, Ellingsen TE, Valla S, Brautaset T (2004) Broad-host-range plasmid pJB658 can be used for industrial-level production of a secreted host-toxic single-chain antibody fragment in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:7033–7039
Snyder WB, Davis LJB, Danese PN, Cosma CL, Silhavy TJ (1995) Overproduction of NlpE, a new outer membrane lipoprotein, suppresses the toxicity of periplasmic LacZ by activation of the Cpx signal transduction pathway. J Bacteriol 177:4216–4223
Sonderegger M, Schumperli M, Sauer U (2005) Selection of quiescent Escherichia coli with high metabolic activity. Metab Eng 7:4–9
Sorensen H, Mortensen K (2005) Soluble expression of recombinant proteins in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli. Microb Cell Fact 4:1
Sorensen SJ, Burmolle M, Hansen LH (2006) Making bio-sense of toxicity: new developments in whole-cell biosensors. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:11–16
Soriano E, Borth N, Katinger H, Mattanovich D (2002) Optimization of recombinant protein expression level in Escherichia coli by flow cytometry and cell sorting. Biotechnol Bioeng 80:93–99
Spada S, Pembroke JT, Wall JG (2002) Isolation of a novel Thermus thermophilus metal efflux protein that improves Escherichia coli growth under stress conditions. Extremophiles 6:301–308
Storz G, Imlay JA (1999) Oxidative stress. Curr Opin Microbiol 2:188–194
Swartz JR (2001) Advances in Escherichia coli production of therapeutic proteins. Curr Opin Biotechnol 12:195–201
Tamarit J, Cabiscol E, Ros J (1998) Identification of the major oxidatively damaged proteins in Escherichia coli cells exposed to oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 273:3027–3032
Tani TH, Khodursky A, Blumenthal RM, Brown PO, Matthews RG (2002) Adaptation to famine: a family of stationary-phase genes revealed by microarray analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:13471–13476
Terpe K (2006) Overview of bacterial expression systems for heterologous protein production: from molecular and biochemical fundamentals to commercial systems. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:211–222
Thomas JG, Baneyx F (1996) Protein misfolding and inclusion body formation in recombinant Escherichia coli cells overexpressing heat-shock proteins. J Biol Chem 271:11141–11147
Tolia NH, Joshua-Tor L (2006) Strategies for protein coexpression in Escherichia coli. Nature Methods 3:55–64
Tucker DL, Tucker N, Conway T (2002) Gene expression profiling of the pH response in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 184:6551–6558
Vemuri GN, Eiteman MA, Altman E (2006) Increased recombinant protein production in Escherichia coli strains with overexpressed water-forming NADH oxidase and a deleted ArcA regulatory protein. Biotechnol Bioeng 94:538–542
Villaverde A, Carrio MM (2003) Protein aggregation in recombinant bacteria: biological role of inclusion bodies. Biotechnol Lett 25:1385–1395
Vollmer AC, Van Dyk TK (2004) Stress responsive bacteria: biosensors as environmental monitors. Adv Microb Physiol 49:131–174
Wade JT, Roa DC, Grainger DC, Hurd D, Busby SJW, Struhl K, Nudler E (2006) Extensive functional overlap between sigma factors in Escherichia coli. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13:806–814
Walsh G (2006) Biopharmaceutical benchmarks 2006. Nat Biotechnol 24:769–776
Wang Z, Xiang L, Shao J, Wegrzyn A, Wegrzyn G (2006a) Effects of the presence of ColE1 plasmid DNA in Escherichia coli on the host cell metabolism. Microb Cell Fact 5:34
Wang ZW, Chen YS, Chao YP (2006b) Enhancement of recombinant protein production in Escherichia coli by coproduction of aspartase. J Biotechnol 124:403–411
Warnecke T, Gill RT (2005) Organic acid toxicity, tolerance, and production in Escherichia coli biorefining applications. Microb Cell Fact 4
Weber H, Polen T, Heuveling J, Wendisch VF, Hengge R (2005) Genome-wide analysis of the general stress response network in Escherichia coli: σS-dependent genes, promoters, and sigma factor selectivity. J Bacteriol 187:1591–1603
Weber J, Hoffmann F, Rinas U (2002) Metabolic adaptation of Escherichia coli during temperature-induced recombinant protein production: 2. Redirection of metabolic fluxes. Biotechnol Bioeng 80:320–330
Weickert MJ, Doherty DH, Best EA, Olins PO (1996) Optimization of heterologous protein production in Escherichia coli. Curr Opin Biotechnol 7:494–499
Weikert C, Sauer U, Bailey JE (1997) Use of a glycerol-limited, long-term chemostat for isolation of Escherichia coli mutants with improved physiological properties. Microbiology-UK 143:1567–1574
Weikert C, Sauer U, Bailey JE (1998) An Escherichia coli host strain useful for efficient overproduction of secreted recombinant protein. Biotechnol Bioeng 59:386–391
Xu Y, Weng C-L, Narayanan N, Hsieh M-Y, Anderson WA, Scharer JM, Moo-Young M, Chou CP (2005) Chaperone-mediated folding and maturation of penicillin acylase precursor in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:6247–6253
Yang YT, Peredelchuk M, Bennett GN, San KY (2000) Effect of variation of Klebsiella pneumoniae acetolactate synthase expression on metabolic flux redistribution in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 69:150–159
Yoon HS, Lee IA, Lee HS, Lee BH, Jo J (2005) Overexpression of a eukaryotic glutathione reductase gene from Brassica campestris improved resistance to oxidative stress in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 326:618–623
Yoon SH, Han MJ, Lee SY, Jeong KJ, Yoo JS (2003) Combined transcriptome and proteome analysis of Escherichia coli during high cell density culture. Biotechnol Bioeng 81:753–767
Zambrano MM, Siegele DA, Almiron M, Tormo A, Kolter R (1993) Microbial competition: Escherichia coli mutants that take over stationary phase cultures. Science 259:1757–1760
Zheng M, Wang X, Templeton LJ, Smulski DR, LaRossa RA, Storz G (2001) DNA microarray-mediated transcriptional profiling of the Escherichia coli response to hydrogen peroxide. J Bacteriol 183:4562–4570
Zhu T, Phalakornkule C, Koepsel RR, Domach MM, Ataai MM (2001) Cell growth and by-product formation in a pyruvate kinase mutant of E. coli. Biotechnol Prog 17:624–628
Zinser ER, Kolter R (1999) Mutations enhancing amino acid catabolism confer a growth advantage in stationary phase. J Bacteriol 181:5800–5807
Zinser ER, Kolter R (2004) Escherichia coli evolution during stationary phase. Res Microbiol 155:328–336
Acknowledgments
Research activities in the author’s lab are supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council and the Canada Research Chair program of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chou, C.P. Engineering cell physiology to enhance recombinant protein production in Escherichia coli . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 76, 521–532 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1039-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1039-0