Abstract
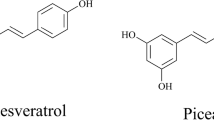
Biotransformation of piceid in Polygonum cuspidatum to resveratrol by Aspergillus oryzae was investigated in this study. Resveratrol is widely used in medicine, food, and cosmetic because of its pharmacological properties. However, it has a much lower content in plants compared with its glucoside piceid, which has a much lower bioavailability. Traditionally, the aglycone is acquired by acid or enzymatic hydrolysis of its glucoside, but the violent condition and the acid pollution in hydrolytic reaction and the high cost of the enzyme limit their industrial development. In this paper, fermentation of P. cuspidatum by A. oryzae was successfully performed, during which, piceid was converted to resveratrol with the highest yield of trans-resveratrol 1.35%, 3.6 times higher than that obtained from raw herb by microwave-assisted extraction. Scale-up production was also performed and the yield of trans-resveratrol was 3.1 times higher after 24 h incubation. Therefore, biotransformation is a better method to increase the yield of resveratrol because of its high yield and mild conditions.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrus MB, Liu J, Meredith EL, Nartey E (2003) Synthesis of resveratrol using a direct decarbonylative Heck approach from resorcylic acid. Tetrahedron Lett 44:4819–4822
Becker JVW, Armstrong GO, Merwe MJ, Lambrechts MG, Vivier MA, Pretorius IS (2003) Metabolic engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the synthesis of the wine-related antioxidant resveratrol. FEMS Yeast Res 4:79–85
Bertelli AA, Ferrara F, Diana G, Fulgenzi A, Corsi M, Ponti W, Ferrero ME, Bertelli A (1999) Resveratrol, a natural stilbene in grapes and wine, enhances intraphagocytosis in human promonocytes: a co-factor in antiinflammatory and anticancer chemopreventive activity. Int J Tissue React 21:93–104
Cao Y (2004) Techniques for the extraction of high purity resveratrol from Polygonum cuspidatum. Chinese Patent CN 1513822A
Chi H, Ji GE (2005) Transformation of ginsenosides Rb1 and Re from Panax ginseng by food microorganisms. Biotechnol Lett 27:765–771
Decker CH, Visser J, Schreier P (2001) β-glucosidase multiplicity from Aspergillus tubingensis CBS 643.92: purification and characterization of four β-glucosidases and their differentiation with respect to substrate specificity, glucose inhibition and acid tolerance. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 55:157–163
Esen A (1993) Glucosidases: overview. Chemtracts Biochem Mol Biol 1–14
James L, Neil S, Feng X (2006) Substrate specificity of Aspergillus oryzae family 3 β-glucosidase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1764:972–978
Jiang H-W (2000) A technique for the extraction of resveratrol from Polygonum cuspidatum. Chinese Patent CN 1251361A
Luo H-S, Tong W-Y (2005) A method for the preparation of resveratrol from Polygonum cuspidatum. Chinese Patent CN 1566349A
Mandeds M, Andreotti R, Roche C (1976) Measurement of saccharifying cellulose. Biotechnol Bioeng Symp 6:21–33
Meng X-F, Maliakal P, Lu H, Lee M-J, Yang C-S (2004) Urinary and plasma levels of resveratrol and quercetin in humans, mice, and rats after ingestion of pure compounds and grape juice. J Agric Food Chem 52:935–942
Ning L-L, Zhan J-X, Qu G-Q, Zhong L, Guo H-Z, Bi K-S, Guo D-A (2003) Biotransformation of triptolide by Cunninghamella blakesleana. Tetrahedron 59:4209–4213
Pace-Asciak CR, Hahn S, Diamandis EP, Soleas G, Goldberg DM (1995) The red wine phenolics trans-resveratrol and quercetin block human platelet aggregation and eicosanoid synthesis: Implications for protection against coronary heart disease. Clin Chim Acta 235:207–219
Parshikov IA, Miriyala B, Avery MA, Williamson JS (2004a) Hydroxylation of 10-deoxoartemisinin to 15-hydroxy-10-deoxoartemisinin by Aspergillus niger. Biotechnol Lett 26:607–610
Parshikov IA, Muraleedharan KM, Avery MA, Williamson JS (2004b) Transformation of artemisinin by Cunninghamella elegans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:782–786
Riou C, Salmon JM, Vallier MJ, Günata Z, Barre P (1998) Purification, characterization, and substrate specificity of a novel highly glucose-tolerantβ-glucosidase from Aspergillus oryzae. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3607–3614
Wendy AL (2000) Biotransformations in organic synthesis. Bioresour Technol 74:49–62
Yan TR, Lin CL (1997) Purification and characterization of a glucose-tolerant beta-glucosidase from Aspergillus niger CCRC 31494. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 61:965–970
Zhang C-Z, Li D, Yu H-S, Zhang B, Jin F-X (2007) Purification and characterization of piceid-β-d-glucosidase from Aspergillus oryzae. Process Biochem 42:83–88
Zhou J-J, Zhang H-J, Yang P-J, Li H-N (2002) Determination of resveratrol glucoside and resveratrol in radix and rhizome of Polygonum cuspidatum yielded in Hanzhong Region (in Chinese). Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs (Zhong Cao Yao) 33:414–416
Zou X-D, Shu X (2002) Method to improve content of resveratrol in Polygonum cuspidatum. Chinese Patent CN 1385535A
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Chinese “973” plan project (2003CB716000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Liu, L., Guo, YX. et al. Biotransformation of piceid in Polygonum cuspidatum to resveratrol by Aspergillus oryzae . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75, 763–768 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-0874-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-0874-3