Abstract
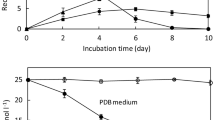
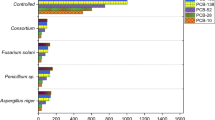
Toxic coplanar polychlorinated biphenyls (Co-PCBs) were used as substrates for a degradation experiment with white-rot fungus, Phlebia brevispora TMIC33929, which is capable of degrading polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins. Eleven PCB congener mixtures (7 mono-ortho- and 4 non-ortho-PCBs) were added to the cultures of P. brevispora and monitored by high resolution gas chromatography and mass spectrometry (HRGC/HRMS). Five PCB congeners, 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl, 2,3,3′,4,4′-pentachlorobiphenyl, 2,3′,4,4′,5-pentachlorobiphenyl, 3,3′,4,4′,5-pentachlorobiphenyl, and 2,3′,4,4′,5,5′-hexachlorobiphenyl were degraded by P. brevispora. To investigate the fungal metabolism of PCB, each Co-PCB was treated separately by P. brevispora and the metabolites were analyzed by gas chromatography and mass spectrometry (GC/MS) and identified on the basis of the GC/MS comparison with the authentic compound. Meta-methoxylated metabolite was detected from the culture containing each compound. Additionally, para-dechlorinated and -methoxylated metabolite was also detected from the culture with 2,3,3′,4,4′-pentachlorobiphenyl, 2,3′,4,4′,5-pentachlorobiphenyl, and 2,3′,4,4′,5,5′-hexachlorobiphenyl, which are mono-ortho-PCBs. In this paper, we identified the congener specific degradation of coplanar PCBs by P. brevispora, and clearly proved for the first time by identifying the metabolites that the white-rot fungus, P. brevispora, transformed recalcitrant coplanar PCBs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramowicz DA (1990) Aerobic and anaerobic biodegradation of PCBs: a review. Crit Rev Biotechnol 10:241–251
Arora DS, Gill PK (2001) Effects of various media and supplements on laccase production by some white rot fungi. Bioresour Technol 77:89–91
Aust SD (1990) Degradation of environmental pollutants by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Microb Ecol 20:197–209
Beaudette LE, Davies S, Fedorak PM, Ward OP, Pickard MA (1998) Comparison of gas chromatography and mineralization experiment for measuring loss of selected polychlorinated biphenyl congeners in cultures of white rot fungi. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2020–2025
Bedard DL, Haberl ML (1990) Influence of chlorine substitution pattern on the degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls by eight bacterial strains. Microb Ecol 20:87–102
Bedard DL, Wagner RE, Brennan MJ, Haberl ML, Brown JF Jr (1987) Extensive degradation of Aroclors and environmentally transformed polychlorinated biphenyls by Alcaligenes eutropus H850. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:1094–1102
Bergman Å, Klasson WE, Kuroki H, Nilsson A (1995) Synthesis and mass spectrometry of some methoxylated PCB. Chemosphere 30:1921–1938
Bopp LH (1986) Degradation of highly chlorinated PCBs by Pseudomonas strain LB400. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 1:23–29
Boyle AW, Silvin CJ, Hassett JP, Nakas JP, Tanenbaum SW (1992) Bacterial PCB degradation. Biodegradation 3:285–298
Bumpus JA, Tien M, Wright D, Aust SD (1985) Oxidation of persistent environmental pollutants by a white rot fungus. Science 228:1434–1436
de Voogt P, Wells DE, Reutergårdh L, Brinkman UATh (1990) Biological activity, determination and occurrence of planar, mono- and di-ortho PCBs. Int J Environ Anal Chem 40:1–46
Dietrich D, Hickey WJ, Lamar R (1995) Degradation of 4,4’-dichlorobiphenyl, 3,3’,4,4’-tetrachlorobiphenyl, and 2,2’,4,4’,5,5’-hexachlorobiphenyl by the white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3904–3909
Eaton DC (1985) Mineralization of polychlorinated biphenyls by Phanerochaete chrysosporium: a ligninolitic fungus. Enzyme Microb Technol 7:194–196
Furukawa K, Miyazaki T (1986) Cloning of a gene cluster encoding biphenyl and chlorobiphenyl degradation in Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes. J Bacteriol 166:392–398
Haraguchi K, Kato Y, Kimura R, Masuda Y (1998) Hydroxylation and methylthiolation of mono-ortho-substituted polychlorinated biphenyls in rats: identification of metabolites with tissue affinity. Chem Res Toxicol 11:1508–1515
Haraguchi K, Kato Y, Koga N, Degawa M (2004) Metabolism of Polychlorinated biphenyls by Gunn Rats: identification and serum retention of catechol metabolites. Chem Res Toxicol 17:1684–1691
Haraguchi K, Koga N, Kato Y (2005) Comparative metabolism of polychlorinated biphenyls and tissue distribution of persistent metabolites in rats, hamsters, and guinea pigs. Drug Metab Dispos 33:373–380
Kamei I, Kondo R (2005) Biotransformation of dichloro-, trichloro-, and tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin by the white-rot fungus Phlebia lindtneri. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 68:560–566
Kamei I, Suhara H, Kondo R (2005) Phylogenetical approach to isolation of white-rot fungi capable of degrading polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69: 358–366
Kondo R, Kurashiki K, Sakai K (1994) In vitro bleaching of hardwood kraft pulp by extracellular enzyme excreted from white rot fungi in cultivation system using membrane filter. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:921–926
Lamar RT, Dietrich DM (1990) In situ depletion of pentachlorophenol from contaminated soil by Phanerochaete spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:3093–3100
Mori T, Kondo R (2002) Degradation of 2,7-dichlorodibenzo-p-dioxin by wood-rotting fungi, screened by dioxin degrading ability. FEMS Microbiol Lett 213:127–132
Reddy GVB, Gold MH (2000) Degradation of pentachlorophenol by Phanerochaete chrysosporium: intermediates and reactions involved. Microbiology 146:405–413
Safe S (1992) Toxicology, structure–function relationship, and human and environmental health impacts of polychlorinated biphenyls: progress and problems. Environ Health Perspect 100:259–268
Safe SH (1994) Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs): Environmental impact, biochemical and toxic responses, and implications for risk assessment. Crit Rev Toxicol 24:87–149
Sasek V, Volfova O, Erbanova P, Vyas BRM, Matucha M (1993) Degradation of PCBs by white rot fungi, methylotrophic and hydrocarbon utilizing yeasts and bacteria. Biotechnol Lett 15:521–526
Schultz A, Jonas U, Hammer E, Schauer F (2001) Dehalogenation of chlorinated hydroxybiphenyls by fungal laccase. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4377–4381
Seto M, Kimbara K, Shimura M, Hatta T, Fukuda M, Yano K (1995) A novel transformation of polychlorinated biphenyls by Rhodococcus sp. strain RHA1. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3353–3358
Sundström G, Hutzinger O, Safe S (1976) The metabolism of chlorobiphenyls—a review. Chemosphere 5:267–298
Takada S, Nakamura M, Matsueda T, Kondo R, Sakai K (1996) Degradation of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans by the white rot fungus Phanerochaete sordida YK624. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:4323–4328
Thomas DR, Carlswell K, Georgiou G (1992) Mineralization of biphenyl and PCBs by the white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Biotechnol Bioeng 40:1395–1402
Tien M, Kirk TK (1988) Lignin peroxidase of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Methods Enzymol 161:238–249
Tsutsumi T, Amakura Y, Sasaki K, Toyoda M, Maitani T (2003) Evaluation of an aqueous KOH digestion followed by hexane extraction for analysis of PCDD/Fs and dioxin-like PCBs in retailed fish. Anal Bioanal Chem 375:792–798
Valli K, Wariishi H, Gold MH (1992) Degradation of 2,7-dichlorodibenzo-p-dioxin by the lignin-degrading basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. J Bacteriol 174:2131–2137
Viney I, Bewley RJF (1990) Preliminary studies on the development of a microbiological treatment for polychlorinated biphenyls. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 19:189–786
Vyas BRM, Sasek V, Matucha M, Bubner M (1994) Degradation of 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl by selected white rot fungi. Chemosphere 28:1127–1134
Yadav JS, Quensen JF III, Tiedje JM, Reddy CA (1995) Degradation of polychlorinated biphenyl mixtures (aroclors 1242, 1254, and 1260) by the white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium as evidenced by congener-specific analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:2560–2565
Acknowledgements
We thank Shigeyuki Takagi and Ryusuke Higuchi (Azabu University, Kanagawa, Japan) for the technical assistance. This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-aid (hazardous chemicals) from the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries of Japan (HC-06-2444-1) and by a Grant-in-aid for scientific research from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Japan (16380121).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamei, I., Sonoki, S., Haraguchi, K. et al. Fungal bioconversion of toxic polychlorinated biphenyls by white-rot fungus, Phlebia brevispora . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73, 932–940 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0529-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0529-9