Abstract
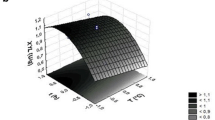
The production of a battery of arabinoxylan-degrading enzymes by the fungus Penicillium brasilianum grown on brewer’s spent grain (BSG) under solid-state fermentation was investigated. Initial moisture content, initial pH, temperature, and nitrogen source content were optimized to achieve maximum production of feruloyl esterase, xylanase, and α-l-arabinofuranosidase. Under the optimum growth conditions (80% moisture, pH 6, 26.5°C, and 5 g/l nitrogen source), the maximum level of feruloyl esterase (1,542 mU/g BSG) was found after 196 h, whereas xylanase (709 U/g BSG) and ArabF activity (3,567 mU/g BSG) were maximal after 108 h and 96 h, respectively. Based on substrate utilization data, the feruloyl esterases produced by P. brasilianum was anticipated to subclass B. A crude enzyme (CE) preparation from P. brasilianum culture grown on BSG was tested for the release of hydroxycinnamic acids and pentoses from BSG. The P. brasilianum CE produced in this work contains a balance of cell wall-modifying enzymes capable of degrading arabinoxylan of BSG by more than 40%.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asther M, Haon M, Roussos S, Record E, Delattre M, Lesage-Meessen L, Labat M, Asther M (2002) Feruloyl esterase from Aspergillus niger a comparison of the production in solid state and submerged fermentation. Proc Biochem 38:685–691
Bartolome B, Faulds CB, Williamson G (1997) Enzymic release of ferulic acid from barley spent grain. J Cereal Sci 25:285–288
Bartolome B, Santos M, Jimenez JJ, del Nozal MJ, Gomez-Cordoves C (2002) Pentoses and hydroxycinnamic acids in brewer’s spent grain. J Cereal Sci 36:51–58
Bartolome B, Gomez-Cordoves C, Sancho AI, Diez N, Ferreira P, Solivery J, Copa-Patino JL (2003) Growth and release of hydroxycinnamic acids from brewer’s spent grain by Streptomyces avermitilis CECT 3339. Enzyme Microb Technol 32:140–144
Berto D (2003) Panorama do Mercado de bebidas. Cerveja, a bebida alcoolica mais consumida no pais. Food Ingred 23:36–39
Christov LP, Prior BA (1993) Esterases of xylan-degrading microorganisms. Production, properties, and significance. Enzyme Microb Technol 15:460–475
Crepin VF, Faulds CB, Connerton IF (2003) A non-modular type-B feruloyl esterase from Neurospora crassa exhibits concentration dependent substrate inhibition. Biochem J 370:417–427
Crepin VF, Faulds CB, Connerton IF (2004) Functional classification of the microbial feruloyl esterases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63:647–652
De Vries RP, Jansen J, Aguilar G, Parenicova I, Joosten V, Wulfert F, Benen JAE, Visser J (2002) Expression profiling of pectinolytic genes from Aspergillus niger. FEBS Lett 530:41–47
Donaghy JA, Mckay AM (1995) Production of feruloyl/p-coumaroyl esterase activity by Penicillium expansum, Penicillium brevicompactum and Aspergillus niger. J Appl Bacteriol 79:657–682
Durand A, Chereau DA (1988) A new pilot reactor for solid state fermentation: application to the protein enrichment of sugar beet pulp. Biotechnol Bioeng 31:466–476
Faulds CB, de Vries RP, Kroon PA, Visser J, Williamson G (1997) Influence of ferulic acid on the production of feruloyl esterases by Aspergillus niger. FEMS Microbiol Lett 157:239–244
Faulds CB, Mandalari G, LoCurto R, Bisignano G, Waldrom KW (2004) Arabinoxylan and mono- and dimeric ferulic acid release from brewer’s spent grain and wheat bran by feruloyl esterases and glycosyl hydrolases from Humicola insolens. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:644–650
Garcia BL, Ball AS, Rodriguez J, Perez-Leblic MI, Arias ME, Copa-Patino JL (1998a) Induction of feruloyl esterase and xylanase activities in Streptomyces avermitilis UAH30. FEMS Microbiol Lett 158:95–99
Garcia BL, Ball AS, Rodriguez J, Perez-Leblic MI, Arias ME, Copa-Patino JL (1998b) Production and characterization of feruloyl esterase activity in crude extracts by Streptomyces avermitilis CECT 3339. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 50:213–218
Gowthaman MK, Krishna C, Moo-Young M (2001) Fungal solid state fermentation—an overview. In: Agriculture and food productions. Appl Mycol Biotechnol 1:305–352
Haltrich D, Nidetzky B, Kulbe KD, Steiner W, Zupancic S (1996) Production of fungal xylanases. Biores Technol 58:137–161
Jørgensen H, Eriksson T, Börjesson J, Tjerneld F, Olsson L (2003) Purification and characterization of five cellulases and one xylanase from Penicillium brasilianum IBT 20888. Enzyme Microb Technol 32:851–861
Kormelink FJM, Voragen AGJ (1992) Combined action of xylan-degrading and accessory enzymes on different {[glucurono]arabino}xylans. In: Visser J et al (eds) Xylans and xylanases. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, pp 415–418
Krishna C (2005) Solid state fermentation systems—an overview. Crit Rev Biotechnol 25:1–30
Krogh KBR, Mørkeberg A, Jørgensen H, Frisvad JC, Olsson L (2004) Screening genus Penicillium for producers of cellulolytic and xylanolytic enzymes. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 113–116:389–401
Kroon PA, Garcia-Conesa MT, Fillingham IJ, Hazlewood GP, Williamson G (1999) Release of ferulic acid dehydrodimers from plant cell walls by feruloyl esterases. J Sci Food Agric 79:428–434
Kroon PA, Williamson G, Fish NM, Archer DB, Belshaw NJ (2000) A modular esterase from Penicillium funiculosum which releases ferulic acid from plant cell walls and binds crystalline cellulose contains a carbohydrate binding module. Eur J Biochem 267:6740–6752
Mackenzie CR, Bilous D, Schneider H, Johnson KG (1987) Induction of cellulolytic and xylanolytic enzyme systems in Streptomyces. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:2835–2839
Panagiotou G, Kekos M, Macris BJ, Christakopoulos P (2003a) Production of cellulolytic and xylanolytic enzymes by Fusarium oxysporum grown on corn stover in solid state fermentation. Ind Crops Prod 18:37–45
Panagiotou G, Topakas E, Economou L, Kekos D, Macris BJ, Christakopoulos P (2003b) Induction, purification and characterization of two extracellular α-L-arabinofuranosidases from Fusarium oxysporum. Can J Microbiol 49:639–644
Puls J, Schuseil J (1993) Chemistry of hemicelluloses: relationship between hemicellulose structure and enzymes required for hydrolysis. In: Coughlan MP, Hazlewood GP (eds) Hemicellulose and hemicellulases. Portland Press, London, pp 1–27
Raimbault M (1998) General and microbiological aspects of solid substrate fermentation. EJB Elect J Biotech 1:1–15
Saha CB (2000) α-L-arabinofuranosidases: biochemistry, molecular biology and application in biotechnology. Biotechnol Adv 18:403–423
Saha CB, Bothast RJ (1998) Effect of carbon source on production of α-L-arabinofuranosidase by Aureobasidium pullulans. Curr Microbiol 37:337–340
Sato K, Sudo S (1999) Small scale solid state fermentations. In: Demain AL, Davies JE (eds) Manual of industrial microbiology and biotechnology, 2nd edn. ASM Press, Washington, DC, pp 61–79
Singh S, du Preez CJ, Pillay B, Prior BA (2000) The production of hemicellulases by Thermomyces lanuginosus strain SSBP: influence of agitation and dissolved oxygen tension. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 54:698–704
Sonia KG, Chadha BS, Badhan AK, Saini HS (2004) Diversity of hemicellulases in thermophilic fungi. Conference on microbiology of the tropical seas, National Institute of Oceanography, Dona Paula, Goa 403 004 India, 13–15 December 2004, Marine Biotechnology Poster, MB (P) 01
Sørensen HR, Meyer AS, Pedersen S (2003) Enzymatic hydrolysis of water soluble wheat arabinoxylan. 1. Synergy between α-L-arabinofuranosidases, endo-1,4-β-xylanases, and β-xylosidase activities. Biotechnol Bioeng 81:726–731
Thibault JF, Asther M, Colonna-Ceccaldi B, Couteau D, Delattre M, Cardoso Duarte J, Faulds C, Heldt-Hansen HP, Kroon P, Lesage-Meesen L, Micard V, Renard MGC, Tuhohy M, Van Hulle S, Williamson G (1998) Fungal bioconversion of agricultural by-products to vanillin. Lebensm-Wiss Technol 31:530–536
Topakas E, Christakopoulos P (2004) Production and partial characterization of alkaline feruloyl esterases by Fusarium oxysporum during submerged batch cultivation. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 20:245–250
Topakas E, Kalogeris E, Kekos D, Macris BJ, Christakopoulos P (2003) Production and partial characterization of feruloyl esterase by Sporotrichum thermophile in solid-state fermentation. Proc Biochem 38:1539–1543
Valverde P (1994) Barley spent grain and its future. Cerveza y Malta 122:7–26
Vardakou M, Katapodis P, Topakas E, Kekos D, Macris BJ, Christakopoulos P (2004) Synergy between enzymes involved in the degradation of insoluble wheat flour arabinoxylan. Innov Food Sci Technol 5:107–112
Wood TM (1985) Properties of cellulolytic enzyme systems. Biochem Soc Trans 10:341–346
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. J. Smedsgaard for the useful advises on the detection of the hydroxycinnamic acids and Carlsberg A/S for providing us with the brewer’s spent grain. G. Panagiotou acknowledges financial support from Villum Kann Rasmussen foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panagiotou, G., Granouillet, P. & Olsson, L. Production and partial characterization of arabinoxylan-degrading enzymes by Penicillium brasilianum under solid-state fermentation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72, 1117–1124 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0394-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0394-6