Abstract
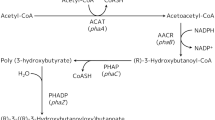
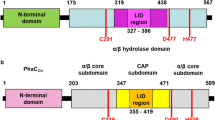
Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) synthase is the central enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of PHA, a family of bacterial biodegradable polyesters. Due to its high variability, the N-terminal fragment of this enzyme was previously considered as unnecessary for a functionally active enzyme. In this study, polyhydroxybutyrate synthase from Ralstonia eutropha (PhbCRe) with a deletion on N-terminal 88 amino acid residues showed a significant reduced activity, as reflected by only 1.5% PHB accumulation compared with the wild type which produced 58.4% PHB of the cell dry weight. Whilst several site-specific mutagenesis results revealed the amphiphilic α-helix assembled by the amino acid region, D70–E88 played an important role in both maintaining the PHB synthase activity and regulating molecular weight and polydispersity of accumulated PHB homopolymer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amara AA, Rehm BHA (2003) Replacement of the catalytic nucleophile cysteine-296 by serine in class II polyhydroxyalkanoates synthase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa-mediated synthesis of new polyester: identification of catalytic residues. Biochem J 374:413–421
Anderson AJ, Dawes EA (1990) Occurrence, metabolism, metabolic role, and industrial uses of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoates. Microbiol Rev 54:450–472
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brandl H, Gross RA, Lenz RW, Fuller RC (1988) Pseudomonas oleovorans as a source of poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates) for potential applications as biodegradable polyesters. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:1977–1982
Chou PY, Fasman GD (1978) Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol 47:45–457
Combet C, Blanchet C, Geourjon C, Deléage G (2000) Network protein sequence analysis. Trends Biochem Sci 291:147–150
Creighton TE (1982) Proteins. Freeman, New York
Geourjon C, Deléage G (1995) SOPMA: significant improvement in protein secondary structures prediction by consensus prediction from multiple alignments. Comput Appl Biosci 11:681–684
Jendrossek D, Schirmer A, Schlegel HG (1996) Biodegradation of polyhydroxyalkanoic acids. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 46:451–463
Jia Y, Kappock J, Frick T, Sinskey A, Stubbe J (2000) Lipases provide a new mechanistic model for polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) synthase: characterization of the functional residues in Chromatium vinosum PHB synthase. Biochemistry 39:3927–3936
Jia Y, Yuan W, Wodzinska J, Park C, Sinskey A, Stubbe J (2001) Mechanistic studies on class I polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) synthase from Ralstonia eutropha: class I and III synthases share a similar catalytic mechanism. Biochemistry 40:1011–1019
Kalousek S, Dennis D, Lubitz W (1992) Genetic engineering of PHB synthase from Alcaligenes eutrophus H16. FEMS Microbiol Rev 103:426–427
Kawaguchi Y, Doi Y (1992) Kinetics and mechanism of synthesis and degradation of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) in Alcaligenes eutrophus. Macromolecules 25:2324–2329
Klinke S, De Roo G, Witholt B, Kessler B (2000) Role of phaD in accumulation of medium-chain-length poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates) in Pseudomonas oleovorans. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3705–3710
Kneller DG, Cohen FE, Langridge R (1990) Improvements in protein secondary structure prediction by an enhanced neural network. J Mol Biol 214:171–182
Kovach ME, Elzer PH, Hill DS, Robertson GT, Farris MA, Roop RM II, Peterson KM (1995) Four new derivatives of the broad-host-range cloning vector pBBRMCS carrying different antibiotic-resistance cassettes. Gene 166:175–176
Lee SY, Park SH, Lee Y, Lee SH (2003) Production of chiral and other valuable compounds from microbial polyesters. In: Steinbüchel A (ed) Biopolymers, vol 4. Wiley-VCH Verkag GmbH, Weinheim, Germany pp 375–387
Lemoigne M (1926) Produits de deshydration et depolymerisation de l’acide β-oxybytyrique. Bull Soc Chim Biol 8:770–781
Madison LL, Huisman GM (1999) Metabolic engineering of poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates): from DNA to plastic. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:21–53
Normi YM, Hiraishi T, Taguchi S, Abe H, Sudesh K, Najimudin N, Doi Y (2005a) Characterization and properties of G4X mutants of Ralstonia eutropha PHA synthase for poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Macromol Biosci 5:197–206
Normi YM, Hiraishi T, Taguchi S, Sudesh K, Najimudin N, Doi Y (2005b) Site-directed saturation mutagenesis at residue F420 and recombination with another beneficial mutation of Ralstonia eutropha polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase. Biotechnol Lett 27:705–712
Ollis DL, Cheah E, Cygler M, Dijkstra B, Frolow F, Franken SM, Harel M, Remington SJ, Silman I, Schrag J, Sussman JL, Verschueren KGG, Goldman A (1992) The α/β hydrolase fold. Protein Eng 5:197–211
Peoples OP, Sinskey AJ (1989) Poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) biosynthesis in Alcaligenes eutrophus H16. Identification and characterization of the PHB polymerase gene (phbC). J Biol Chem 264:15298–15303
Pötter M, Madkour MH, Mayer F, Steinbüchel A (2002) Regulation of phasin expression and polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) granule formation in Ralstonia eutropha H16. Microbiology 148:2413–2426
Pries A, Priefert H, Krüger N, Sternbüchel A (1991) Identification and characterization of two Alcaligenes eutrophus gene loci relevant to poly(β-hydroxybutyric acid)-leaky phenotype which exhibit homology to ptsH and ptsI of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 173:5843–5853
Prieto MA, Bühler B, Jung K, Witholt B, Kessler B (1999) PhaF, a polyhydroxyalkanoate-granule-associated protein of Pseudomonas oleovorans GPo1 involved in the regulatory expression system for pha genes. J Bacteriol 181:858–868
Ramsay BA, Lomaliza K, Chavarie C, Bubé B, Bataille P, Ramsay JAB (1990) Production of poly-(β-hydroxybutyric-co-β-hydroxyvaleric) acids. Appl Environ Microbiol 56:2093–2098
Rehm BHA (2003) Polyester synthases: natural catalysts for plastics. Biochem J 376:15–33
Rehm BHA, Antonio RV, Spiekermann P, Amara AA, Steinbüchel A (2002) Molecular characterization of the poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) synthase from Ralstonia eutropha: in vitro evolution, site-specific mutagenesis and development of a PHB synthase protein model. Biochim Biophys Acta 1594:178–190
Rehm BHA, Steinbüchel A (1999) Biochemical and genetic analysis of PHA synthases and other proteins required for PHA synthesis. Int J Biol Macromol 25:3–19
Sambrook J, Russel DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Schubert P, Krüger N, Steinbüchel A (1991) Molecular analysis of the Alcaligenes erutropha poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) biosynthetic operon: identification of the N-terminus of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) synthase and identification of the promoter. J Bacteriol 173:168–175
Schubert P, Steinbüchel A, Schlegel HG (1988) Cloning of the Alcaligenes eutrophus genes for synthesis of poly-beta-hydroxybutyric acid (PHB) and synthesis of PHB in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 170:5837–5847
Segrest JP, De Loof H, Dohlman JG, Brouillette CG, Anantharamaiah GM (1990) Amphipathic helix motif: classes and properties. Proteins 8:103–117
Sim SJ, Snell KD, Hogan SA, Stubbe J, Rha CK, Sinskey A (1997) PHA synthase activity controls the molecular weight and polydispersity of polyhydroxybutyrate in vivo. Nat Biotechnol 15:63–67
Simon R, Priefer U, Pühler A (1983) A broad host range mobilization system for in vivo genetic engineering: transposon mutagenesis in Gram-negative bacteria. Biotechnology 1:784–791
Spiekermann P, Rehm BHA, Kalscheuer R, Baumeister D, Steinbüchel A (1999) A sensitive, viable-colony staining method using Nile red for direct screening of bacteria that accumulate polyhydroxyalkanoic acids and other lipid storage compounds. Arch Microbiol 171:73–80
Steinbüchel A, Lütke-Eversloh T (2003) Metabolic engineering and pathway construction for biotechnological production of relevant polyhydroxyalkanoates in microorganisms. Biochem Eng J 16:81–96
Taguchi S, Nakamura H, Hiraishi T, Yamato I, Doi Y (2002) In vitro evolution of a polyhydroxybutyrate synthase by intragenic suppression-type mutagenesis. J Biochem (Tokyo) 131:801–806
Tian SJ, Lai WJ, Zheng Z, Wang HX, Chen GQ (2005) Effect of over-expression of phasin gene from Aeromonas hydrophila on biosynthesis of copolyesters of 3-hydroxybutyrate and 3-hydroxyhexanoate. FEMS Microbiol Lett 244:19–25
Valentin HE, Steinbüchel A (1994) Application of enzymatically synthesized short-chain-length hydroxyl fatty acid coenzyme A thioesters for assay of polyhydroxyalkanoic acid synthases. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 40:699–709
Williams SF, Martin DP, Horowitz DH, Peoples OP (1999) PHA applications: addressing the price performance issue. I. Tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol 25:111–121
York GM, Stubbe J, Sinskey AJ (2001) New insight into the role of the PhaP phasin of Ralstonia eutropha in promoting synthesis of polyhydroxybutyrate. J Bacteriol 183:2394–2397
Zheng Z, Bei FF, Tian HL, Chen GQ (2005) Effects of crystallization of polyhydroxyalkanoate blend on surface physiochemical properties and interactions with rabbit articular cartilage chondrocytes. Biomaterials 26:3537–3548
Zheng Z, Deng Y, Lin XS, Zhang LX, Chen GQ (2003) Induced production of rabbit articular cartilage-derived chondrocytes collagen II on polyhydroxyalkanoates blends. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 14:615–624
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholar (grant no. 30225001). The State 863 Funds (no. 2002A213051) also contributed financially to this study. We are also in debt to Professor S. Taguchi of Hokkaido University/Japan and Professor B. Rehm of Massey University/New Zealand for their critical comments and suggestions to improve this paper. Their expert views have contributed to the quality of this paper. The plasmid pBHR68 and the host strain R.eutropha PHB−4 were kindly provided by Dr. B. Rehm and Professor A. Steinbüchel of the Westfälische Wilhelm-Univerität Münster, Münster, Germany. We also thank Jing-Yu Chen and Andrew R. Chang for their assistance in the manuscript preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Zhong Zheng and Ming Li contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Z., Li, M., Xue, XJ. et al. Mutation on N-terminus of polyhydroxybutyrate synthase of Ralstonia eutropha enhanced PHB accumulation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72, 896–905 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0371-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0371-0