Abstract
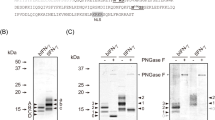
Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus (BmNPV) baculovirus expression system (BES) has a lot of advantages such as high expression efficiency, convenience, and low feeding cost. In this report, we used a recently developed BmNPV bacmid, which could infect both B. mori cell lines and silkworm larvae. The results showed it takes only 7 to 10 days to generate recombinant baculovirus and permit the rapid isolation from small-scale cultures and then use it to transfect B. mori cell lines, compared to traditional homologous recombination method, which needs at least 40 days for multiple rounds of purification and amplification of viruses. Using this BES, we expressed a recombinant spider flagelliform protein in BmN cell line, which was around 37 kDa in sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and western blot analysis. The BmNPV bacmid system using silkworm would be very attractive for expression of target proteins.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arcidiacono S, Mello C, Kaplan D, Cheley S, Bayley H (1998) Purification and characterization of recombinant spider silk expressed in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 49:31–38
Catherine LC, Christian R (2002) Comparative architecture of silks, fibrous proteins and their encoding genes in insects and spiders. Comp Biochem Physiol, B 133:493–507
Ciccarone VC, Polayes D, Luckow VA (1997) In: U Reischt (ed) Generation of recombinant baculovirus DNA in using baculovirus shuttle vector, vol 13. Humana Press Inc., pp 38–96
Daniel H, Christopher WH, Susanne Q, Jan O, Rainer R, Thomas S (2004a) Primary structure elements of spider dragline silks and their contribution to protein solubility. Biochemistry 43:13604–13612
Daniel H, Thomas S, Fritz V, Shulamit C, Uri G, Shmulik I (2004b) Novel assembly properties of recombinant spider dragline silk proteins. Curr Biol 14:2070–2074
Elisabetta B, David PK, David LK (2004) Mapping domain structures in silks from insects and spiders related to protein assembly. J Mol Biol 335:27–40
Fritz V (1999) Biology of spider silk. Biol Macromol 24:81–88
Fukushima Y (1998) Genetically engineered syntheses of tandem repetitive polypeptides consisting of glycine-rich sequence of spider dragline silk. Biopolymers 45(4):269–279
Gatesy J, Hayashi C, Dagmara M, Justin W, Lewis RV (2001) Extreme diversity,conservation, and convergence of spider silk fibroin sequences. Science 291:2603–2605
Hayashi CY, Lewis RV (1998) Evidence from flagelliform silk cDNA for the structure basis of elasticity and modular nature of spider silks. J Mol Biol 275:773–784
Hayashi CY, Lewis RV (2000) Molecular architecture and evolution of a modular spider silk protein gene. Science 287(5457):1477–1479
Jeefrey LC, Charles SC (1996) Insect cell expression technology. In: Protein engineering. Wiley-Liss Press, Chapter 7, pp 183–218
Lazaris A, Arcidiacono S, Huang Y et al (2002) Spider silk fibers spun from soluble recombinant silk produced in mammalian cells. Science 295:472–476
Lewis RV, Hinman M, Kothakota S, Fournier MJ (1996) Expression and purification of a spider silk protein: a new strategy of production repetitive proteins. Protein Expr Purif 7:400–405
Maeda S (1994) Expression of foreign genes in insect cells using baculovirus vectors. In: Maramorosch K, McIntosh AH (eds) Insect cell biotechnology. CRC Press, pp 1–31
Motohashi T, Shimojima T, Fukagawa T, Maenaka K, Park EY (2005) Efficient large-scale protein production of larvae and pupae of silkworm by Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus bacmid system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 326:564–569
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T et al (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Scheller J, Guhrs KH, Grosse F, Conrad U (2001) Production of spider silk proteins in tobacco and potato. Nat Biotechnol 19:573–577
Shimizu K, Shiomi K, Kajiura Z, Nakagaki M (2004) Nephila clavata flagelliform silk protein expressed in insect cell. J Seric Sci Jpn 73(1):23–29
Sommons A, Michal C, Jelinski L (1996) Molecular orientation and two-component nature of the crystalline fraction of spider dragline silk. Science 271:84–87
Stefan W, David LK (2000) Molecular biology of spider silk. Rev Mol Biotechnol 74:85–93
Xia Q, Zhou Z, Lu C et al (2004) A draft sequence for the genome of the domesticated silkworm (Bombyx mori). Science 306:1937–1940
Xu M, Lewis RV (1990) Structure of a protein superfiber: spider dragline silk. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87:7120–7124
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by an exchange program between China Scholarship Council (CSC) and Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan (No. 2003833041).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, Y., Zhang, Y., Nakagaki, K. et al. Expression of spider flagelliform silk protein in Bombyx mori cell line by a novel Bac-to-Bac/BmNPV baculovirus expression system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71, 192–199 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0127-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-005-0127-2