Abstract
Since the cytoskeleton is known to regulate many cell functions, an increasing amount of effort to characterize cells by their mechanical properties has occured. Despite the structural complexity and dynamics of the multicomponent cytoskeleton, mechanical measurements on single cells are often fit to simple models with two to three parameters, and those parameters are recorded and reported. However, different simple models are likely needed to capture the distinct mechanical cell states, and additional parameters may be needed to capture the ability of cells to actively deform. Our new approach is to capture a much larger set of possibly redundant parameters from cells’ mechanical measurement using multiple rheological models as well as dynamic deformation and image data. Principal component analysis and network-based approaches are used to group parameters to reduce redundancies and develop robust biomechanical phenotyping. Network representation of parameters allows for visual exploration of cells’ complex mechanical system, and highlights unexpected connections between parameters. To demonstrate that our biomechanical phenotyping approach can detect subtle mechanical differences, we used a Microfluidic Optical Cell Stretcher to mechanically stretch circulating human breast tumor cells bearing genetically-engineered alterations in c-src tyrosine kinase activation, which is known to influence reattachment and invasion during metastasis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert R, Barabàsi A (2002) Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Rev Mod Phys 74(1):47–97
Balland M, Desprat N, Icard D, Féréol S, Asnacios A, Browaeys J, Hénon S, Gallet F (2006) Power laws in microrheology experiments on living cells: comparative analysis and modeling. Phys Rev E 74(2):021911–1–17
Balzer E, Whipple R, Thompson K, Boggs A, Slovic J, Cho E, Matrone M, Yoneda T, Mueller S, Martin S (2010) c-src differentially regulates the functions of microtentacles and invadopodia. Oncogene 29(48):6402–6408
Barrat A, Barthèlemy M, Pastor-Satorras R, Vespignani A (2004) The architecture of complex weighted networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(11):3747–3752
Boyde L, Chalut K, Guck J (2009) Interaction of gaussian beam with near-spherical particle: an analytic-numerical approach for assessing scattering and stresses. J Opt Soc Am A 26(8):1814–1826
Brangwynne C, MacKintosh F, Kumar S, Geisse N, Talbot J, Mahadevan L, Parker K, Ingber D, Weitz D (2006) Microtubules can bear enhanced compressive loads in living cells because of lateral reinforcement. J Cell Biol 173(5):733–741
Clauset A, Moore C, Newman M (2008) Hierarchical structure and the prediction of missing links in networks. Nature 453(7191):98–101
Desprat N, Richert A, Simeon J, Asnacios A (2005) Creep function of a single living cell. Biophys J 88(3):2224–2233
Elson E (1988) Cellular mechanics as an indicator of cytoskeletal structure and function. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem 17:397–430
Fabry B, Maksym G, Butler J, Glogauer M, Navajas D, Fredberg J (2001) Scaling the microrheology of living cells. Phys Rev Lett 87(14):148102–1–4
Faith JJ, Hayete B, Thaden JT, Mogno I, Wierzbowski J, Cottarel G, Kasif S, Collins JJ, Gardner TS (2007) Large-scale mapping and validation of escherichia coli transcriptional regulation from a compendium of expression profiles. PLoS Biol 5(1):e8
Fritsch A, Höckel M, Kiessling T, Nnetu KD, Wetzel F, Zink M, Käs JA (2010) Are biomechanical changes necessary for tumour progression. Nat Phys 6(10):730–732
Fuchs E, Cleveland DW (1998) A structural scaffolding of intermediate filaments in health and disease. Science 279(5350):514–519
Girvan M, Newman MEJ (2002) Community structure in social and biological networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(12):7821–7826
Glotzbach J, Januszyk M, Vial I, Wong V, Gelbard A, Kalisky T, Thangarajah H, Longaker MT, Quake SR, Chu G, Gurtner GC (2011) An information theoretic, microfluidic-based single cell analysis permits identification of subpopulations among putatively homogeneous stem cells. PloS ONE 6(6):e21,211
Guck J, Ananthakrishnan R, Mahmood H, Moon T, Cunningham C, Käs J (2001) The optical stretcher: a novel laser tool to micromanipulate cells. Biophys J 81(2):767–784
Guck J, Schinkinger S, Lincoln B, Wottawah F, Ebert S, Romeyke M, Lenz D, Erickson HM, Ananthakrishnan R, Mitchell D, Käs J, Ulvick S, Bilby C (2005) Optical deformability as an inherent cell marker for testing malignant transformation and metastatic competence. Biophys J 88(5):3689–3698
Huang H, Kamm R, Lee R (2004) Cell mechanics and mechanotransduction: pathways, probes, and physiology. Am J Physiol-Cell Physiol 287(1):C1
Jain A, Murty M, Flynn P (1999) Data clustering: a review. ACM Comput Surv (CSUR) 31(3):264–323
Jolliffe T (2002) Principal component analysis. Springer, Heidelberg
Jonas O, Mierke C, Käs J (2011) Invasive cancer cell lines exhibit biomechanical properties that are distinct from their noninvasive counterparts. Soft Matter 87:669–676
Lautenschläger F, Paschke S, Schinkinger S, Bruel A, Beil M, Guck J (2009) The regulatory role of cell mechanics for migration of differentiating myeloid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(37):15,696
Lim C, Zhou E, Quek S (2006) Mechanical models for living cells—a review. J Biomech 39(2):195–216
Lincoln B, Schinkinger S, Travis K, Wottawah F, Ebert S, Sauer F, Guck J (2007) Reconfigurable microfluidic integration of a dual-beam laser trap with biomedical applications. Biomed Microdevices 9(5):703–710
Maloney J, Nikova D, Lautenschläger F, Clarke E, Langer R, Guck J, Van Vliet K (2010) Mesenchymal stem cell mechanics from the attached to the suspended state. Biophys J 99(8):2479–2487
Matrone M, Whipple R, Balzer E, Martin S (2010) Microtentacles tip the balance of cytoskeletal forces in circulating tumor cells. Cancer Res 70(20):7737–7741
Mauritz J, Tiffert T, Seear R, Lautenschläger F, Esposito A, Lew V, Guck J, Kaminski C (2010) Detection of plasmodium falciparum-infected red blood cells by optical stretching. J Biomed 15(3):0305171–0305173
Mierke C, Rösel D, Fabry B, Brábek J (2008) Contractile forces in tumor cell migration. Eur J Cell Biol 87(8-9):669–676
Mofrad M (2009) Rheology of the cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 41:433–453
Mogilner A, Keren K (2009) The shape of motile cells. Curr Biol 19(17):R762–R771
Montell DJ (2008) Morphogenetic cell movements: diversity from modular mechanical properties. Science 322(5907):1502–1505
Newman M (2006) Modularity and community structure in networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(23):8577–8582
Ramaekers F, Bosman F (2004) The cytoskeleton and disease. J Pathol 204(4):351–354
Strogatz S (2001) Exploring complex networks. Nature 410(6825):268–276
Suresh S (2007) Biomechanics and biophysics of cancer cells. Acta Mater 3(4):413–438
Vogel V, Sheetz M (2009) Cell fate regulation by coupling mechanical cycles to biochemical signaling pathways. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21:38–46
Wang Y, Botvinick EL, Zhao Y, Berns MW, Usami S, Tsien RY, Chien S (2005) Visualizing the mechanical activation of src. Nature 434(7036):1040–1045
Weaver V (2009) Mechanics, malignancy, and metastasis: the force journey of a tumor cell. Cancer Metastasis Rev 28(1–2):113–127
Acknowledgements
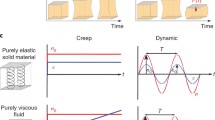
Support from a DOD Era of Hope Scholar award (BC100675) is gratefully acknowledged. M.H. was supported by the Department of Defense (DoD) through the National Defense Science & Engineering Graduate Fellowship (NDSEG) Program. T.K. was financially supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft within the Graduate School BuildMoNa. We are grateful to S. Pawlizak and T. Händler for providing Fig. 1a. Funded in parts by the European Union and the Free State of Saxony within the research program "Theranostik", and by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) under the project "Agescreen", grant identifier 13N1093.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kießling, T.R., Herrera, M., Nnetu, K.D. et al. Analysis of multiple physical parameters for mechanical phenotyping of living cells. Eur Biophys J 42, 383–394 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-013-0888-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-013-0888-y