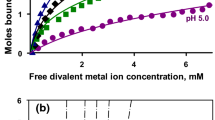
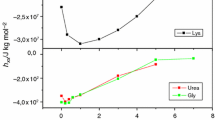
Abstract
An equilibrium thermodynamic model of the interaction of calcium, phosphate and casein in milk is described in which the micellar calcium phosphate is assumed to be in the form of calcium phosphate nanoclusters. A generalized empirical formula for the nanocluster is used to define the molar ratios of small ions (Ca, Mg, Pi and citrate) to a casein phosphorylated sequence (phosphate centre, PC). From this model, a method of calculating the partition of milk salts into diffusible and non-diffusible fractions is obtained. No arbitrary assumptions are made, no fitting of adjustable parameters is done and the PCs in the caseins are defined by inspection of their primary structures. In addition to the salt partition, the mole fractions of the individual caseins not complexed to the calcium phosphate through one or more of their PCs are computed and a generic stability rule for milks is derived. The use of the model is illustrated by calculations of the partition of salts in a standard milk and by comparison with experimental data on the partition of salts in the milk of individual cows. The generic stability rule is applied to the individual milks to determine whether the micellar calcium phosphate is thermodynamically stable. According to the calculations, compositions that might lead to pathological calcification in the lumen of the mammary gland were seldom found in primiparous healthy cows in early or mid lactation but occurred more often in multiparous animals, in late lactation and during mastitic infection.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACP:
-
amorphous calcium phosphate
- Cit:
-
citrate
- CN:
-
casein
- CPN:
-
calcium phosphate nanocluster
- DCPD:
-
dicalcium phosphate dihydrate
- HA:
-
hydroxyapatite
- IAP:
-
ion activity product
- MCP:
-
micellar calcium phosphate
- MWCO:
-
molecular weight cut-off
- OCP:
-
octacalcium phosphate
- PC:
-
phosphate centre
- TCC:
-
tricalcium citrate
References
Ailamo MH, Kumosinski TF, Farrell HM Jr (1996) High resolution solid state NMR of milk products. J Magn Reson Anal 2:267–274
Andrews AT, Alichanidis E (1983) Proteolysis of caseins and the proteose-peptone fraction of bovine milk. J Dairy Res 50:275–290
Aoki T, Umeda T, Kako Y (1992) The least number of phosphate groups for crosslinking of casein by non-diffusible calcium phosphate. J Dairy Sci 75:971–975
Bak M, Rasmussen LK, Petersen TE, Nielsen NC (2001). Non-diffusible calcium phosphate in casein micelles studied by slow-speed spinning 31P magic angle spinning solid state nuclear magnetic resonance, J Dairy Sci 84:1310–1319
Chaplin LC (1984) Studies of micellar calcium phosphate: composition and apparent solubility product in milk over a wide pH range. J Dairy Res 51:251–257
Chaplin LC, Lyster RLJ (1988) Effect of temperature on the pH of skim milk. J Dairy Res 55:277–280
Creamer LK, Berry GP, Mills OE (1977) A study of the dissociation of β-casein from the bovine casein micelle at low temperature. NZ J Dairy Sci Technol 12:58–66
Dalgleish DG, Law AJR (1988) pH-induced dissociation of bovine casein micelles. I. Analysis of liberated caseins. J Dairy Res 55:529–538
Dalgleish DG, Law AJR (1989) pH-induced dissociation of bovine casein micelles. II. Mineral solubilization and its relation to casein release. J Dairy Res 56:727–735
Davies DT, Law AJR (1977) The composition of whole casein from the milk of Ayrshire cows. J Dairy Res 44:447–454
Davies DT, Law AJR (1983) Variation in the protein composition of bovine casein micelles and serum casein in relation to micellar size and milk temperature. J Dairy Res 50:67–75
Davies DT, Law AJR (1987) Quantitative fractionation of casein mixtures by fast protein liquid chromatography. J Dairy Res 54:369–376
Davies DT, White JCD (1960). The use of ultrafiltration and dialysis in isolating the aqueous phase of milk and in determining the partition of milk constituents between the aqueous and disperse phases. J Dairy Res 27:171–190
De Kruif CG, Holt C (2003) Structure, functions and interactions of casein micelles. In: Fox PF, McSweeney P (eds) Advanced dairy chemistry, vol 1: proteins, 3rd edn. Kluwer/Plenum, New York, pp 233–276
Fox PF (1992) Indigenous enzymes of milk. 3. Proteinases. In: Fox PF (ed) Advanced dairy chemistry, vol 1: proteins. Elsevier, Barking, UK
Hansen S, Bauer R, Lomholt SB, Bruun Qvist K, Pedersen JS, Mortensen K (1996) Structure of casein micelles studied by small-angle neutron scattering. Eur Biophys J 24:143–147
Holt C (1982) The inorganic constituents of milk. III. The non-diffusible calcium phosphate of cow milk. J Dairy Res 49:29–38
Holt C (1993) Interrelationships of the concentrations of some ionic constituents of human milk and comparison with cow and goat milks. Comp Biochem Physiol A 104:5–41
Holt C (1997) The milk salts and their interaction with casein. In: Fox PF (ed) Advanced dairy chemistry, vol 3: lactose, water, salts and vitamins. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 233–254
Holt C (1998) Casein micelle substructure and calcium phosphate interactions studied by sephacryl column chromatography. J Dairy Sci 81:2994–3003
Holt C (2001) Calcium phosphate nanoclusters and their applications. UK Pat Appl 0030634.0; PCT Appl PCT/GB00/04827
Holt C, Hukins DWL (1991) Structural analysis of the environment of Ca ions in crystalline and amorphous calcium phosphates by X-ray absorption spectroscopy and a hypothesis concerning the biological function of the casein micelle. Int Dairy J 1:151–165
Holt C, Dalgleish DG, Jenness R (1981) Calculation of the ion equilibria in milk diffusate and comparison with experiment. Anal Biochem 113:154–163
Holt C, Hasnain SS, Hukins DWL (1982) Structure of bovine milk calcium phosphate determined by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta 719:299–303
Holt C, Davies DT, Law AJR (1986) The effects of non-diffusible calcium phosphate content and milk serum free Ca ion concentration on the dissociation of bovine casein micelles. J Dairy Res 53:557–572
Holt C, van Kemenade MJJM, Nelson LS Jr, Sawyer L, Harries JE, Bailey RT, Hukins DWL (1989) Composition and structure of micellar calcium phosphate. J Dairy Res 56:411–416
Holt C, Wahlgren NM, Drakenberg T (1996) Ability of a β-casein phosphopeptide to modulate the precipitation of calcium phosphate by forming amorphous dicalcium phosphate nanoclusters. Biochem J 314:1035–1039
Holt C, Timmins PA, Errington N, Leaver J (1998) A core-shell model of calcium phosphate nanoclusters derived from sedimentation equilibrium and small angle X-ray and neutron scattering measurements. Eur J Biochem 252:73–78
Holt C, de Kruif CG, Tuinier R, Timmins PE (2003) Substructure of bovine casein micelles by small-angle X-ray and neutron scattering. Colloids Surf 213:275–284
Kent JC, Arthur PG, Hartmann PE (1998) Citrate, calcium, phosphate and magnesium in sow’s milk at initiation of lactation. J Dairy Res 65:55–68
Knoop A-M, Knoop E, Wiechen A (1979) Sub-structure of synthetic casein micelles. J Dairy Res 46:347–350
Kolar ZI, Verburga TG, van Dijk HJM (2002) Three kinetically different inorganic phosphate entities in bovine casein micelles revealed by isotopic exchange method and compartmental analysis. J Inorg Biochem 90:61–66
Le Bars D, Gripon JC (1989) Specificity of plasmin towards αs2-casein. J Dairy Res 56:817–821
Little EM, Holt C (2004) An equilibrium thermodynamic model of the sequestration of calcium phosphate by casein phosphopeptides. Eur Biophys J (in press)
Lyster RLJ, Mann S, Parker SB, Williams RJP (1984) Nature of micellar calcium phosphate in cow’s milk as studied by high resolution electron microscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta 801:315–317
Mayer JL, Eanes ED (1978) A thermodynamic analysis of the amorphous to crystalline calcium phosphate transformation. Calcif Tiss Int 25:59–68
McGann TCA, Pyne GT (1960) The non-diffusible phosphate of milk. III. Nature of its association with casein. J Dairy Res 27: 403–417
McGann TCA, Buchheim W, Kearney RD, Richardson T (1983a) Composition and ultrastructure of calcium phosphate–citrate complexes in bovine milk systems. Biochim Biophys Acta 760:415–420
McGann TCA, Kearney RD, Buchheim W, Posner AS, Betts F, Blumenthal NC (1983b) Amorphous calcium phosphate in casein micelles of bovine milk. Calcif Tiss Int 35:821–823
McMahon DJ, McManus WR (1998) Rethinking casein micelle structure using electron microscopy. J Dairy Sci 81:2985–2993
Niewold TA, Murphy CL, Hulskamp-Koch CAM, Tooten CJ, Gruys E (1999) Casein related amyloid, characterisation of a new and unique amyloid protein isolated from bovine corpora amylacea. Int J Exp Clin Invest 6:244–249
Ono T, Ohotawa T, Takagi Y (1994) Complexes of casein phosphopeptide and calcium phosphate prepared from casein micelles by tryptic digestion. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 58:1376–1380
Pierre A, Brulé G, Fauquant J (1983) Etude de la mobilité du Ca dans le lait à l’aide du Ca 45. Lait 63:473–489
Pyne GT (1934) The non-diffusible phosphate of milk. Biochem J 28:940–948
Pyne GT (1962) Some aspects of the physical chemistry of the salts in milk. J Dairy Res 29:101–130
Pyne GT, McGann TCA (1960) The non-diffusible phosphate of milk. II. Influence of citrate. J Dairy Res 27:9–17
Pyne GT, Ryan JJ (1932) Non-diffusible calcium phosphate of milk. Sci Proc R Dublin Soc 20:471–476
Rasmussen LK, Sørensen ES, Petersen TE, Nielsen NC, Thomsen JK (1997) Characterization of phosphate sites in native ovine, caprine and bovine casein micelles and their caseinomacropeptides: a solid-state phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance and sequence and mass spectrometric study. J Dairy Sci 80:607–614
Schmidt DG (1982) Association of caseins and casein micelle structure. In: Fox PF (ed) Developments in dairy chemistry. Applied Science, Barking, UK, pp 61–86
Shennan DB, Peaker M (2000) Transport of milk constituents by the mammary gland. Physiol Rev 80:925–951
Stothart PH (1989) Subunit structure of casein micelles from small-angle neutron scattering. J Mol Biol 208:635–638
Stothart PH, Cebula DJ (1982) Small-angle neutron scattering study of bovine casein micelles and sub-micelles. J Mol Biol 160:391–395
Thomsen JK, Jakobsen HJ, Nielsen NC, Petersen TE, Rasmussen LK (1995) Solid state magic angle spinning 31P NMR studies of native casein micelles. Eur J Biochem 230:454–459
van Dijk HJM (1990a) The properties of casein micelles. 1. Formation and degradation of the micellar calcium phosphate. Neth Milk Dairy J 44:111–124
van Dijk HJM (1990b) The properties of casein micelles. 2. The nature of the micellar calcium phosphate. Neth Milk Dairy J 44:65–81
van Dijk HJM (1991) The properties of casein micelles. 4. The effect of the addition of NaCl, MgCl2, or NaOH on the partition of Ca, Mg and PO4 in cows’ milk. Neth Milk Dairy J 45:241–251
van Dijk HJM, Hersevoort A (1992) The properties of casein micelles. 5. The determination of heat-induced calcium phosphate precipitations in milk. Neth Milk Dairy J 46:69–76
van Kemenade MJJM, de Bruyn PL (1989a) The influence of casein on the kinetics of hydroxyapatite precipitation. J Colloid Interface Sci 129:1-14
van Kemenade MJJM, de Bruyn PL (1989b) The influence of casein on the precipitation of brushite and octacalcium phosphate. Colloids Surf 36:359–368
Wahlgren M, Dejmek P, Drakenberg T (1990) A 43Ca and 31P NMR study of the Ca and phosphate equilibria in heated milk solutions. J Dairy Res 57:355–364
Walstra P (1999) Casein sub-micelles: do they exist? Int Dairy J 9:189–192
White JCD, Davies DT (1958) The relation between the chemical composition of milk and the stability of the caseinate complex. 1. General introduction, description of samples, methods and chemical composition of samples. J Dairy Res 25:236–255
White JCD, Davies DT (1963) The determination of citric acid in milk and milk sera. J Dairy Res 30:171–189
Yamauchi K, Yoneda Y (1977) Effect of some treatments of milk on the exchangeability of non-diffusible Ca in milk with soluble calcium. Agric Biol Chem 41:2395–2399
Yamauchi K, Yoneda Y, Koga Y, Tsugo T (1969) Exchangeability of non-diffusible Ca in milk with soluble calcium. Agric Biol Chem 33:907–914
Zhang PZ, Aoki T (1996) Behaviour of Ca and phosphate in bovine casein micelles. Int Dairy J 6:769–78
Acknowledgements
The author is grateful to Drs. D.T. Davies, A.J.R. Law and J.C.D. White for allowing use of their original compositional data on cows’ milk.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holt, C. An equilibrium thermodynamic model of the sequestration of calcium phosphate by casein micelles and its application to the calculation of the partition of salts in milk. Eur Biophys J 33, 421–434 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-003-0377-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-003-0377-9