Abstract
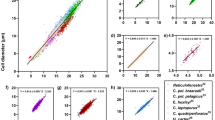
We recently published a new method based on determining cyanobacterial biomass by confocal laser scanning microscopy image analysis (CLSM-IA) (Solé et al., Ultramicrosc 107:669–673, 2007). CLSM-IA allows biomass calculation for microorganisms of a small size, since the limit of the technique’s resolution is that generated by a voxel, the smallest unit of a three-dimensional digital image, equivalent to 1.183 × 10−3 mgC/cm3 of sediment. This method is especially suitable for the quantitative analysis of a large number of CLSM images generated from benthic sediments in which complex populations of cyanobacteria are abundant, such as microbial mats. In order to validate the new CLSM approach, mats with varying structural characteristics were studied. We have grouped them into three types: Microcoleus mats (laminated), sandy mats (nonlaminated and composed of well-sorted quartz sands), and oil-polluted mats. In this work, we applied CLSM-IA in natural [the Ebro delta and Sant Jordi colony (Spain), Salins-de-Giraud and Etang de Berre (France), and Orkney Islands (Scotland)] and artificial [mesocosms (Israel)] microbial mats. A total of 4,103 confocal images were obtained in order to determine total and individual cyanobacteria biomass profiles, at microscale level. The data presented in this paper show the efficacy of the method, as it can be applied to highly diverse mat samples.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abed RM, Garcia-Pichel F, Hernández-Mariné M (2002) Polyphasic characterization of benthic, moderately halophilic, moderately thermophilic cyanobacteria with very thin trichomes and the proposal of Halomicronema excentricum gen. nov., sp. nov. Arch Microbiol 177:361–370
Al-Hasan RH, Khanafer M, Eliyas M, Radwan SS (2001) Hydrocarbon accumulation by picocyanobacteria from the Arabian gulf. J Appl Microbiol 91:533–540
Barranguet C, van Beusekom SAM, Veuger B, Neu TR, Manders EMM, Sinke JJ, Admiraal W (2004) Studying undisturbed autotrophic biofilms: still a technical challenge. Aquat Microbiol Ecol 34:1–9
Becker JM, Parkin T, Nakatsu CH, Wilbur JD, Konopka A (2006) Bacterial activity, community structure, and centimeter-scale spatial heterogeneity in contaminated soil. Microb Ecol 51:220–231
Bloem J, Veninga M, Shepherd J (1995) Fully automatic determination of soil bacterium numbers, cell volumes, and frequencies of dividing cells by confocal laser scanning microscopy and image analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:926–936
Boivin ME, Massieux B, Breure AM, Greve GD, Rutgers M, Admiraal W (2006) Functional recovery of biofilm bacterial communities after copper exposure. Environ Pollut 140:239–246
Castenholz RW (2001) Phylum BX Cyanobacteria. Oxygenic Photosynthetic Bacteria. In: Boone DR, Castenholz RW, Garrity GM (eds) Bergey’s Manual Systematic Bacteriology, vol. 1, The Archea and deeply branching and phototrophic bacteria. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 473–599
Caumette P, Matheron R, Raymond N, Relexans JC (1994) Microbial mats in the hypersaline ponds of Mediterranean salterns (Salins-de-Giraud, France). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 13:273–286
Chapman MJ, Margulis L (1998) Morphogenesis by symbiogenesis. Internat Microbiol 1:319–373
Cohen Y, Rosenberg E (1989) Photosynthesis in cyanobacterial mats and its relation to the sulfur cycle. In: Microbial mats, physiological ecology of benthic microbial communities. A model for microbial sulfur interactions. American Society Microbiology, Washington, D. C., pp. 22–36
Cornée A (1982) Bactéries des saumures et sédiments des marais salants de Salin-de-Giraud (Sud de la France). Géologie Méditerranéenne 9:369–390
de los Ríos A, Ascaso C, Wierzchos J, Fernández-Valiente E, Quesada A (2004) Microstructural characterization of cyanobacterial mats from the McMurdo ice shelf, Antarctica. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:569–580
Esteve I, Martínez-Alonso M, Mir J, Guerrero R (1992) Distribution, typology and structure of microbial mat communities in Spain. Preliminary studies. Limnetica 8:185–195
Esteve I, Ceballos, D, Martínez-Alonso M, Gaju N, Guerrero R (1994) Development of versicolored microbial mats: succession of microbial communities. In: Stal L, Caumette P (eds) Microbial Mats: Structure, Development and Environmental Significance. NATO ASI Series G-35, pp. 415–420
Fourçans A, García de Oteyza T, Wieland A, Solé A, Diestra E, van Bleijswijk J, Grimalt JO, Kühl M, Esteve I, Muyzer G, Caumette P, Duran R (2004) Characterization of functional bacterial groups in a hypersaline microbial mat community (Saline-de-Giraud, Camargue, France). FEMS Microbial Ecol 51:55–70
Fry JC (1990) Direct methods and biomass estimation. Meth Microbiol 22:411–485
García de Oteyza T, Grimalt JO, Diestra E, Solé A, Esteve I (2004) Changes in the composition of polar and apolar crude oil fractions under the action of Microcoleus consortia. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66:226–232
Guerrero R, Urmeneta J, Rampone G (1993) Distribution of types of microbial mats at the Ebro Delta, Spain. Biosystems 31:135–144
Herbert R (1985) Fully automatic determination of soil bacterium numbers, cell volumes, and frequencies of dividing cells by confocal laser scanning microscopy and image analysis. Proc. Roy. Soc. Edinburgh 87:15–25
Hernandez-Raquet G, Budzinski H, Caumette P, Dabert P, Le Ménach K, Muyzer G, Duran R (2006) Molecular diversity studies of bacterial communities of oil polluted microbial mats from the Etang de Berre (France). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 58:550–562
Joynt J, Bischoff M, Turco R, Konopka A, Nakatsu CH (2006) Microbial community analysis of soils contaminated with lead, chromium and petroleum hydrocarbons. Microb Ecol 51:209–219
Konopka A, Zakharova T, Bischoff M, Oliver L, Nakatsu C, Turco RF (1999) Microbial biomass and activity in lead-contaminated soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2256–2259
Krumbein WE, Cohen Y, Shiko M (1977) Solar Lake (Sinai). 4. Stromatolitic cyanobacterial mats. Limnol Oceanogr 22:635–656
Ley RE, Harris JK, Wilcox J, Spear JR, Miller SR, Bebout BM, Maresca JA, Bryant DA, Sogin ML, Pace NR (2006) Unexpected diversity and complexity of the Guerrero Negro hypersaline microbial mat. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:3685–3695
Lorenzen M, Batley G (1988) Chemical speciation and trace element toxicity. Chem Aust 55:363–366
Martínez-Alonso M, Mir J, Caumette P, Guerrero R, Esteve I (2004) Distribution of phototrophic populations and primary production in a microbial mat from the Ebro Delta, Spain. Int Microbiol 7:19–25
Massieux B, Boivin ME, Van Den Ende FP, Langenskiold J, Marvan P, Barranguet C, Admiraal W, Laanbroek HJ, Zwart G (2004) Analysis of structural and physiological profiles to assess the effects of Cu on biofilm microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4512–4521
Neu TR, Woelfl S, Lawrence JR (2004) Three-dimensional differentiation of photo-autotrophic biofilm constituents by multi-channel laser scanning microscopy (single-photon and two-photon excitation). J Microbiol Methods 56:161–172
Pierson BK, Oesterle A, Castenholz RW (1984) Pigments, light penetration and photosynthetic activity in the multi-layered microbial mats of Great Sippewisset Salt Marsh, Massachussetts. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 45:365–376
Rasband WS (1997–2007). ImageJ, US National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA, http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/
Rasmussen LD, Sorensen SJ (2001) Effects of mercury contamination on the culturable heterotrophic, functional and genetic diversity of the bacterial community in soil. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 36:1–9
Revsbech NP, Jørgensen BB, Blackburn TH, Cohen Y (1983) Microelectrode studies of the photosynthesis and O2, H2S and pH profiles in a microbial mat. Limnol Oceanogr 28:1062–1074
Solé A, Gaju N, Méndez-Álvarez S, Esteve I (2001) Confocal laser scanning microscopy as a tool to determine cyanobacteria biomass in microbial mats. J Microscopy 204:258–262
Solé A, Gaju N, Esteve I (2003) The biomass dynamics of cyanobacteria in an annual cycle determined by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Scanning 25:1–7
Solé A, Mas J, Esteve I (2007) A new method based on image analysis for determining cyanobacterial biomass by CLSM in stratified benthic sediments. Ultramicrosc 107:669–673
van Gemerden H, Tughan CS, de Wit R, Herbert RA (1989) Laminated microbial ecosystems on sheltered beaches in Scapa Flow, Orkney Islands. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 62:87–102
Wieland A, Kühl M, Mc Gowan L, Solé A, Diestra E, Esteve I, Garcia de Oteyza T, Grimalt JO, Duran R, Fourçans A, Caumette P, Herbert R (2003) Microbial Mats on the Orkney Islands Revisited: Microenvironment and Microbial Community Composition. Microb Ecol 46:371–390
Wieland A, Zopfi J, Benthien M, Kühl M (2005) Biogeochemistry of an iron-rich hypersaline microbial mat (Camargue, France). Microb Ecol 49:34–49
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge financial support from the EC (MATBIOPOL project, grant EVK3-CT-1999-00010) and by Spanish Grant DGICYT CGL2005-03792/BOS to I.E. The authors express their thanks to all of the staff of the Servei de Microscòpia at the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona for their valuable technical assistance. We are also grateful to Marc Alamany and Francesc Fornells from Ecologia Portuaria S.L. for comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solé, A., Diestra, E. & Esteve, I. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Image Analysis for Cyanobacterial Biomass Determined at Microscale Level in Different Microbial Mats. Microb Ecol 57, 649–656 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-008-9463-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-008-9463-y