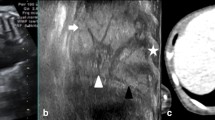
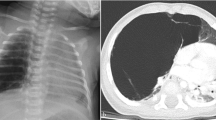
Abstract
Congenital lung malformations represent a spectrum of abnormalities that can overlap in imaging appearance and frequently coexist in the same child. Imaging diagnosis in the neonatal period can be challenging; however, the recognition of several archetypal radiographic patterns can aid in narrowing the differential diagnosis. Major radiographic archetypes include (1) hyperlucent lung, (2) pulmonary cysts, (3) focal opacity and (4) normal radiograph. Here we review the multimodality imaging appearances of the most commonly seen congenital lung malformations, categorized by their primary imaging archetypes. Along with the congenital lung malformations, we present several important imaging mimickers.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Langston C (2003) New concepts in the pathology of congenital lung malformations. Semin Pediatr Surg 12:17–37
Riedlinger WFJ, Vargas SO, Jennings RW et al (2006) Bronchial atresia is common to extralobar sequestration, intralobar sequestration, congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation, and lobar emphysema. Pediatr Dev Pathol 9:361–373
Criss CN, Musili N, Matusko N et al (2018) Asymptomatic congenital lung malformations: is nonoperative management a viable alternative? J Pediatr Surg 53:1092–1097
Laberge JM, Flageole H, Pugash D et al (2001) Outcome of the prenatally diagnosed congenital cystic adenomatoid lung malformation: a Canadian experience. Fetal Diagn Ther 16:178–186
Newman B (2006) Congenital bronchopulmonary foregut malformations: concepts and controversies. Pediatr Radiol 36:773–791
Cleveland RH, Weber B (1993) Retained fetal lung liquid in congenital lobar emphysema: a possible predictor of polyalveolar lobe. Pediatr Radiol 23:291–295
Biyyam DR, Chapman T, Ferguson MR et al (2010) Congenital lung abnormalities: embryologic features, prenatal diagnosis, and postnatal radiologic pathologic correlation. Radiographics 30:1721–1738
Style CC, Mehollin-Ray AR, Verla MA et al (2020) Accuracy of prenatal and postnatal imaging for management of congenital lung malformations. J Pediatr Surg 55:844–847
Lee EY (2012) Congenital lung masses. In: Imaging in pediatric pulmonology. Springer, New York, pp 31–38
Berrocal T, Madrid C, Novo S et al (2004) Congenital anomalies of the tracheobronchial tree, lung, and mediastinum: embryology, radiology, and pathology. Radiographics 24:e17
Oliver ER, DeBari SE, Horii SC et al (2019) Congenital lobar overinflation: a rare enigmatic lung lesion on prenatal ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging. J Ultrasound Med 38:1229–1239
Kunisaki SM, Saito JM, Fallat ME et al (2019) Current operative management of congenital lobar emphysema in children: a report from the Midwest pediatric surgery consortium. J Pediatr Surg 54:1138–1142
Alamo L, Vial Y, Gengler C, Meuli R (2016) Imaging findings of bronchial atresia in fetuses, neonates and infants. Pediatr Radiol 46:383–390
Berdon WE (2000) Rings, slings, and other things: vascular compression of the infant trachea updated from the midcentury to the millennium — the legacy of Robert E. Gross, MD, and Edward B. D. Neuhauser, MD. Radiology 216:624–632
Rosenberg BF, Tantiwongse T, Wittenborg MH (1956) Anomalous course of left pulmonary artery with respiratory obstruction. Radiology 67:339–345
Ramaswamy M, Rudrappa S, Beeman A et al (2021) Lung hypoplasia associated with ring-sling complex is usually right-sided. Ann Thorac Surg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2021.01.059
Yong MS, D’Udekem Y, Brizard CP et al (2013) Surgical management of pulmonary artery sling in children. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 145:1033–1039
Riggs KW, Zafar F, Jacobs ML et al (2021) Tracheal surgery for airway anomalies associated with increased mortality in pediatric patients undergoing heart surgery: Society of Thoracic Surgeons database analysis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 161:1112–1121.e7
Brunner S, Nissen E (1963) Agenesis of the lung. Am Rev Respir Dis 87:103–106
Osborne J, Masel J, Mccredie J (1989) A spectrum of skeletal anomalies associated with pulmonary agenesis: possible neural crest injuries. Pediatr Radiol 19:425–432
Wang H, Kalfa D, Rosenbaum MS et al (2018) Scimitar syndrome in children and adults: natural history, outcomes, and risk analysis. Ann Thorac Surg 105:592–598
Lee EY, Greenberg SB, Boiselle PM (2011) Multidetector computed tomography of pediatric large airway diseases: state-of-the-art. Radiol Clin N Am 49:869–893
Mata JM, Castellote A (2008) Pulmonary malformations beyond the neonatal period. Springer, Berlin, pp 123–146
Jones J, Almond C, Snyder H et al (1965) Lobar emphysema and congenital heart disease in infancy. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 49:1–10
Hishitani T, Ogawa K, Hoshino K et al (2003) Lobar emphysema due to ductus arteriosus compressing right upper bronchus in an infant with congenital heart disease. Ann Thorac Surg 75:1308–1310
Doğan ÖF, Duman Ü, Yorgancıoğlu C, Böke E (2006) Spontaneous regression of left upper lobe emphysema after division of large ductus arteriosus in an infant. Turk J Pediatr 48:269–271
DiGeorge NW, El-Ali AM, White AM et al (2020) Pediatric cardiac CT and MRI: considerations for the general radiologist. AJR Am J Roentgenol 215:1464–1473
Shelmerdine SC, Semple T, Wallis C et al (2017) Filamin A (FLNA) mutation — a newcomer to the childhood interstitial lung disease (ChILD) classification. Pediatr Pulmonol 52:1306–1315
Burrage LC, Guillerman RP, Das S et al (2017) Lung transplantation for FLNA-associated progressive lung disease. J Pediatr 186:118–123.e6
Loo DT, Kanner SB, Aruffo A (1998) Filamin binds to the cytoplasmic domain of the β1-integrin: identification of amino acids responsible for this interaction. J Biol Chem 273:23304–23312
Playford MP, Nurminen E, Pentikäinen OT et al (2010) Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator interacts with multiple immunoglobulin domains of filamin A. J Biol Chem 285:17156–17165
Pelizzo G, Collura M, Puglisi A et al (2019) Congenital emphysematous lung disease associated with a novel filamin A mutation. Case report and literature review. BMC Pediatr 19:1–10
Shah AS, Black ED, Simon DM et al (2021) Heterogeneous pulmonary phenotypes in filamin A mutation-related lung disease. Pediatr Allergy Immunol Pulmonol 34:7–14
Lange M, Kasper B, Bohring A et al (2015) 47 patients with FLNA associated periventricular nodular heterotopia. Orphanet J Rare Dis 10:1–11
Woodward PJ, Kennedy A, Sohaey R et al (2005) Diagnostic imaging: obstetrics, 1st edn. Amirsys, Salt Lake City
Lee EY, Dorkin H, Vargas SO (2011) Congenital pulmonary malformations in pediatric patients: review and update on etiology, classification, and imaging findings. Radiol Clin N Am 49:921–948
Stocker JT (2009) Cystic lung disease in infants and children. Fetal Pediatr Pathol 28:155–184
Stocker JT (2002) Congenital pulmonary airway malformation: a new name for and an expanded classification of congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation of the lung. Histopathology 41:424–430
MacSweeney F, Papagiannopoulos K, Goldstraw P et al (2003) An assessment of the expanded classification of congenital cystic adenomatoid malformations and their relationship to malignant transformation. Am J Surg Pathol 27:1139–1146
Priest JR, Williams GM, Hill DA et al (2009) Pulmonary cysts in early childhood and the risk of malignancy. Pediatr Pulmonol 44:14–30
Cass DL, Quinn TM, Yang EY et al (1998) Increased cell proliferation and decreased apoptosis characterize congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation of the lung. J Pediatr Surg 33:1043–1046
Vu L, Tsao KJ, Lee H et al (2007) Characteristics of congenital cystic adenomatoid malformations associated with nonimmune hydrops and outcome. J Pediatr Surg 42:1351–1356
Epelman M, Kreiger PA, Servaes S et al (2010) Current imaging of prenatally diagnosed congenital lung lesions. Semin Ultrasound CT MRI 31:141–157
Ng C, Stanwell J, Burge DM, Stanton MP (2014) Conservative management of antenatally diagnosed cystic lung malformations. Arch Dis Child 99:432–437
Wong A, Vieten D, Singh S et al (2009) Long-term outcome of asymptomatic patients with congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation. Pediatr Surg Int 25:479–485
Singh R, Davenport M (2015) The argument for operative approach to asymptomatic lung lesions. Semin Pediatr Surg 24:187–195
Hill DA, Jarzembowski JA, Priest JR et al (2008) Type I pleuropulmonary blastoma: pathology and biology study of 51 cases from the International Pleuropulmonary Blastoma Registry. Am J Surg Pathol 32:282–295
Schultz KAP, Rednam SP, Kamihara J et al (2017) PTEN, DICER1, FH, and their associated tumor susceptibility syndromes: clinical features, genetics, and surveillance recommendations in childhood. Clin Cancer Res 23:e76–e82
Stewart D, Best A, Williams GM et al (2019) Neoplasm risk among individuals with a pathogenic germline variant in DICER1. J Clin Oncol 37:668–676
Schultz KAP, Williams GM, Kamihara J et al (2018) DICER1 and associated conditions: identification of at-risk individuals and recommended surveillance strategies. Clin Cancer Res 24:2251–2261
Messinger YH, Stewart DR, Priest JR et al (2015) Pleuropulmonary blastoma: a report on 350 central pathology-confirmed pleuropulmonary blastoma cases by the International Pleuropulmonary Blastoma Registry. Cancer 121:276–285
Guillerman RP, Foulkes WD, Priest JR (2019) Imaging of DICER1 syndrome. Pediatr Radiol 49:1488–1505
Lima JS, Camargos PAM, Aguiar RALP et al (2014) Pre and perinatal aspects of congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation of the lung. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 27:228–232
Feinberg A, Hall NJ, Williams GM et al (2016) Can congenital pulmonary airway malformation be distinguished from type I pleuropulmonary blastoma based on clinical and radiological features? J Pediatr Surg 51:33–37
Waelti SL, Garel L, Soglio DD et al (2017) Neonatal congenital lung tumors — the importance of mid-second-trimester ultrasound as a diagnostic clue. Pediatr Radiol 47:1766–1775
Macklin MT, Macklin CC (1944) Malignant interstitial emphysema of the lungs and mediastinum as an important occult complication in many respiratory diseases and other conditions: an interpretation of the clinical literature in the light of laboratory experiment. Medicine 23:281–358
Carey B (1999) Neonatal air leaks: pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, pulmonary interstitial emphysema, pneumopericardium. Neonatal Netw 18:81–84
Greenough A, Dixon AK, Roberton NRC (1984) Pulmonary interstitial emphysema. Arch Dis Child 59:1046–1051
Li S, Still GG, Abdelbaki A et al (2018) Diffuse pulmonary interstitial emphysema in a late preterm neonate without mechanical ventilation. Case Reports Perinat Med. https://doi.org/10.1515/crpm-2017-0066
Gürakan B, Tarcan A, Arda IS, Coşkun M (2002) Persistent pulmonary interstitial emphysema in an unventilated neonate. Pediatr Pulmonol 34:409–411
Gronbach J, Ehrhardt H, Zimmer K-P, Waitz M (2018) Early pulmonary interstitial emphysema in preterm neonates — respiratory management and case report in nonventilated very low birth weight twins. Am J Perinatol Reports 08:e99–e105
Agrons GA, Courtney SE, Stocker JT, Markowitz RI (2005) Lung disease in premature neonates: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics 25:1047–1073
Donnelly LF, Frush DP (1999) Localized radiolucent chest lesions in neonates: causes and differentiation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 172:1651–1658
Jabra AA, Fishman EK, Shehata BM, Perlman EJ (1997) Case report. Localized persistent pulmonary interstitial emphysema: CT findings with radiographic-pathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 169:1381–1384
Hansell DM, Bankier AA, MacMahon H et al (2008) Fleischner Society: glossary of terms for thoracic imaging. Radiology 246:697–722
Quigley MJ, Fraser RS (1988) Pulmonary pneumatocele: pathology and pathogenesis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 150:1275–1277
Armstrong LB, Mooney DP (2018) Pneumatoceles in pediatric blunt trauma: common and benign. J Pediatr Surg 53:1310–1312
Gerdung CA, Ross BC, Dicken BJ, Bjornson CL (2019) Pneumonectomy in a child with multilobar pneumatocele secondary to necrotizing pneumonia: case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Pediatr 2019:1–5
Harris VJ, Brown R (1975) Pneumatoceles as a complication of chemical pneumonia after hydrocarbon ingestion. AJR Am J Roentgenol 125:531–537
Clarke TA, Edwards DK (1979) Pulmonary pseudocysts in newborn infants with respiratory distress syndrome. AJR Am J Roentgenol 133:417–421
Victoria MS, Steiner P, Rao M (1981) Persistent postpneumonic pneumatoceles in children. Chest 79:359–361
Amitai I, Mogle P, Godfrey S, Aviad I (1983) Pneumatocele in infants and children: report of 12 cases. Clin Pediatr 22:420–422
Chow JS, Chung EM, Colin AA, Cleveland RH (2012) Focal lung disease. In: Imaging in pediatric pulmonology. Springer, New York, pp 193–248
Imamoǧlu M, Çay A, Koşucu P et al (2005) Pneumatoceles in postpneumonic empyema: an algorithmic approach. J Pediatr Surg 40:1111–1117
Puligandla PS, Laberge JM (2012) Infections and diseases of the lungs, pleura, and mediastinum. In: Pediatric surgery. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 855–880
Burgos CM, Frenckner B, Luco M et al (2019) Prenatally versus postnatally diagnosed congenital diaphragmatic hernia — side, stage, and outcome. J Pediatr Surg 54:651–655
Coren ME, Rosenthal M, Bush A (1997) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia misdiagnosed as tension pneumothorax. Pediatr Pulmonol 24:119–121
Tsui KP, Chan KW, Lee KH (2010) Acute complications of late-presenting congenital diaphragmatic hernia in children: report of 2 cases and review of literature. Hong Kong J Paediatr 15:157–160
Juwarkar CS, Kamble DS, Sawant V (2010) A late presenting congenital diaphragmatic hernia misdiagnosed as spontaneous pneumothorax. Indian J Anaesth 54:464–466
Stolar CJH, Dillon PW (2012) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia and eventration. In: Pediatric surgery. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 809–824
Baerg J, Kanthimathinathan V, Gollin G (2012) Late-presenting congenital diaphragmatic hernia: diagnostic pitfalls and outcome. Hernia 16:461–466
Taber P, Gyepes MT, Lackey DA (1973) Malposition of umbilical vascular catheters in the diagnosis of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Radiology 109:413–415
Sakural M, Donnelly LF, Klosterman LA, Strîfe JL (2000) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia in neonates: variations in umbilical catheter and enteric tube position. Radiology 216:112–116
Winters WD, Effmann EL (2001) Congenital masses of the lung: prenatal and postnatal imaging evaluation. J Thorac Imaging 16:196–206
Zhang H, Tian J, Chen Z et al (2014) Retrospective study of prenatal diagnosed pulmonary sequestration. Pediatr Surg Int 30:47–53
Lager DJ, Kuper KA, Haake GK (1991) Subdiaphragmatic extralobar pulmonary sequestration. Arch Pathol Lab Med 115:536–538
Adzick NS, Harrison MR, Crombleholme TM et al (1998) Fetal lung lesions: management and outcome. Am J Obstet Gynecol 179:884–889
Riley JS, Urwin JW, Oliver ER et al (2018) Prenatal growth characteristics and pre/postnatal management of bronchopulmonary sequestrations. J Pediatr Surg 53:265–269
Brown SC, De Laat M, Proesmans M et al (2012) Treatment strategies for pulmonary sequestration in childhood: resection, embolization, observation? Acta Cardiol 67:629–634
Fagan CJ, Swischuk LE (1972) The opaque lung in lobar emphysema. AJR Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 114:300–304
Epelman M, Lee EY (2013) Congenital lung anomalies. In: Coley B (ed) Caffey’s pediatric diagnostic imaging, 12th edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, p 551
Bellini C, Ergaz Z, Radicioni M et al (2012) Congenital fetal and neonatal visceral chylous effusions: neonatal chylothorax and chylous ascites revisited. A multicenter retrospective study. Lymphology 45:91–102
Groom KR, Murphey MD, Howard LM et al (2002) Mesenchymal hamartoma of the chest wall: radiologic manifestations with emphasis on cross-sectional imaging and histopathologic comparison. Radiology 222:205–211
Dishop MK, McKay EM, Kreiger PA et al (2010) Fetal lung interstitial tumor (FLIT): a proposed newly recognized lung tumor of infancy to be differentiated from cystic pleuropulmonary blastoma and other developmental pulmonary lesions. Am J Surg Pathol 34:1762–1772
Orman G, Masand P, Hicks J et al (2020) Pediatric thoracic mass lesions: beyond the common. Eur J Radiol Open 7:100240
Guillerman PR, Vogelius E, Pinto-Rojas A, Parham DM (2015) Malignancies of the pediatric lower respiratory tract. In: Pediatric malignancies: pathology and imaging. Springer, New York, pp 227–243
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Ali, A.M., Strubel, N.A. & Lala, S.V. Congenital lung lesions: a radiographic pattern approach. Pediatr Radiol 52, 622–636 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-021-05210-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-021-05210-9