Abstract
Background
The transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) is effective for treating complications of portal hypertension in cirrhotic adults but the experience in children is limited.
Objective
To retrospectively review the safety and efficacy of expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE)-covered TIPS in children with acute or recurrent gastrointestinal bleeding.
Materials and methods
We reviewed the medical records of children who received implants of 10-mm-diameter PTFE-covered endoprostheses for acute or recurring upper gastrointestinal bleeding caused by medically or endoscopically uncontrollable varices. The recurrence of upper gastrointestinal bleeding, associated complications and permeability were assessed with Doppler sonography sequentially or up to transplantation.
Results
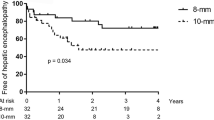
In all children (n = 12; mean age 9 years; mean weight 30 kg) a single endoprosthesis was implanted with no associated mortality. The mean initial transhepatic gradient was 15 mmHg (range 3–21 mmHg), dropping to 7 mmHg (range 1–12 mmHg) after TIPS. Immediate complications were mild encephalopathy (n = 1) and acute occlusion of the TIPS (n = 1). Stenosis of the TIPS was observed in two children, at 9 months and 54 months follow-up, and thrombosis was observed in two children, at 7 months and 12 months follow-up. All four stenoses/occlusions were resolved with coaxial endoprostheses.
Conclusion
The safety profile and efficacy of expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE)-covered TIPS were satisfactory in this small series of children with acute or recurrent gastrointestinal bleeding.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garcia-Pagan JC, Caca K, Bureau C et al (2010) Early use of TIPS in patients with cirrhosis and variceal bleeding. N Engl J Med 362:2370–2379
Rossle M, Ochs A, Gulberg V et al (2000) A comparison of paracentesis and transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting in patients with ascites. N Engl J Med 342:1701–1707
Hackworth CA, Leef JA, Rosenblum JD et al (1998) Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt creation in children: initial clinical experience. Radiology 206:109–114
Lorenz J (2008) Placement of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts in children. Technol Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 11:235–240
Bureau C, Garcia-Pagan JC, Layrargues GP et al (2007) Patency of stents covered with polytetrafluorethylene in patients treated by transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts: long-term results of a randomised multicentre study. Liver Int 27:742–747
Huppert PE, Goffette P, Astfal W et al (2002) Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemsic shunt in children with biliary atresia. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 25:484–493
Vo NJ, Shivariam GM, Andrews RT et al (2012) Midterm follow-up of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts using polytetrafluoroethylene endografts in children. J Vasc Interv Radiol 23:919–924
Di Giorgio A, Agazzi R, Alberti D et al (2012) Feasibility and efficacy of transjugular intrahepatic porto-systemic shunt (TIPS) in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 54:594–600
Shneider BL, Bosch J, de Franchis R et al (2012) Portal hypertension in children: expert pediatric opinion on the report of the Baveno v Consensus workshop on methodology of diagnosis and therapy in portal hypertension. Pediatr Transplant 16:426–437
Eesa M, Clark T (2011) Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: state of the art. Semin Roentgenol 46:125–132
Kalva SP, Salazar GM, Walker G (2009) Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt of acute variceal hemorrhage. Technol Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 12:92–101
Pozler O, Krajina A, Vanicek H et al (2003) Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in five children with cystic fibrosis: long term results. Hepatogastroenterology 50:1111–1114
Heyman M, LaBerge J, Sombely K et al (1997) Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in children. J Pediatr 131:914–919
Mileti E, Rosenthal P (2011) Management of portal hypertension in children. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 13:10–16
Chlapoutaki CE, Franchi-Abella S, Habes D et al (2009) Custom-made covered transjugular intrahepatic portosytemic shunt (TIPS) in an infant with trisomy 22 and biliary atresia. Pediatr Radiol 39:739–742
Maleux G, Perez-Gutierrez NA, Evrard S et al (2010) Covered stents are better than uncovered stents for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts in cirrhotic patients with refractory ascites: a retrospective cohort study. Acta Gastroenterol Belg 73:336–341
Mermuys K, Maleux G, Heye S et al (2008) Use of the Viatorr expanded polytetrafluoroethylene-covered stent-graft for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt creation in children: initial clinical experience. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 31:S192–S196
Van Ha TG, Funaki BS, Ehrhardt J et al (2005) Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt placement in liver transplant recipients: experiences with pediatric and adult patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 184:920–925
Rössle M (2013) TIPS: 25 years later. J Hepatol 59:1081–1093
Schweizer P, Brambs HJ, Schweizer M et al (1995) TIPS: a new therapy for esophageal variceal bleeding caused by EHBA. Eur J Pediatr Surg 5:211–215
Miller DL, Balter S, Schueler BA et al (2010) Clinical radiation management for fluoroscopically guided interventional procedures. Radiology 257:321–332
Hernanz-Schulman M, Goske MJ, Bercha IH et al (2011) Pause and pulse: ten steps that help manage radiation dose during pediatric fluoroscopy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 197:475–481
Acknowledgements
The authors thank J.A. Miñano for supporting the estimation of fluoroscopic radiation doses.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zurera, L.J., Espejo, J.J., Lombardo, S. et al. Safety and efficacy of expanded polytetrafluoroethylene-covered transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts in children with acute or recurring upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Pediatr Radiol 45, 422–429 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-014-3181-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-014-3181-z