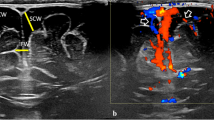
Abstract
Sonographic patterns of brain injury in the term and near-term infant are quite different from those in the premature infant. Although periventricular leukomalacia and germinal matrix hemorrhage are rarely seen in term infants, selective neuronal injury, parasagittal infarction, focal stroke, diffuse hypoxic-ischemic injury, and deep parenchymal hemorrhages are more common lesions. In addition, congenital brain tumors, hamartomatous lesions, such as hemimegalencephaly, and tuberous sclerosis can mimic ischemic and hemorrhagic injury. Sonography remains an important tool in the initial evaluation of intracranial abnormalities in critically ill term and near-term infants. An understanding of the differences in etiology, sonographic patterns, and limitations of sonography in the term infant is essential for accurate and effective diagnoses in this age group.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daneman A, Epelman M, Blaser S et al (2006) Imaging of the brain in full-term neonates: does sonography still play a role? Pediatr Radiol 36:636–646
Volpe JJ (1989) Current concepts of brain injury in the premature infant. AJR 153:243–251
Ghazi-Birry HS, Brown WR, Moody DM et al (1997) Human germinal matrix: venous origin of hemorrhage and vascular characteristics. AJNR 18:219–229
Boylan GB, Young K, Panerai RB et al (2000) Dynamic cerebral autoregulation in sick newborn infants. Pediatr Res 48:12–17
Back SA, Luo NL, Borenstein NS et al (2001) Late oligodendrocyte progenitors coincide with the developmental window of vulnerability for human perinatal white matter injury. J Neurosci 21:1302–1312
Back SA, Han BH, Luo NL et al (2002) Selective vulnerability of late oligodendrocyte progenitors to hypoxia-ischemia. J Neurosci 22:455–463
Shalak L, Perlman JM (2002) Hemorrhagic-ischemic cerebral injury in the preterm infant: current concepts. Clin Perinatol 29:745–763
Grow J, Barks JD (2002) Pathogenesis of hypoxic-ischemic cerebral injury in the term infant: current concepts. Clin Perinatol 29:585–602
Lorek A, Takei Y, Cady EB et al (1994) Delayed ("secondary") cerebral energy failure after acute hypoxia-ischemia in the newborn piglet: continuous 48-hour studies by phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Pediatr Res 36:699–706
McDonald JW, Johnston MV (1990) Physiological and pathophysiological roles of excitatory amino acids during central nervous system development. Brain Res Rev 15:41–70
Wright LL, Merenstein GB, Hirtz D (1996) Report of the workshop on acute perinatal asphyxia in term infants. National Institute of Child Health & Human Development http://www.nichd.nih.gov/publications/pubs/acute/acute.cfm. Cited 19 September 2007
Barkovich AJ (2005) Pediatric neuroimaging, 4th edn. Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 195–245
Volpe JJ (2001) Neurology of the newborn, 4th edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 296–330
Fawer CL, Calame A, Perentes E et al (1985) Periventricular leukomalacia: a correlation study between real-time ultrasound and autopsy findings. Periventricular leukomalacia in the neonate. Neuroradiology 27:292–300
Rodriguez MJ, Ursu G, Bernal F et al (2001) Perinatal human hypoxia-ischemia vulnerability correlates with brain calcification. Neurobiol Dis 8:59–68
Grant EG, Williams AL, Schellinger D et al (1985) Intracranial calcification in the infant and neonate: evaluation by sonography and CT. Radiology 157:63–68
Friede RL, Schachenmayr W (1977) Early stages of status marmoratus. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 38:123–127
Folkerth RD (2005) Neuropathologic substrate of cerebral palsy. J Child Neurol 20:940–949
Yoshioka H, Iino S, Sato N et al (1989) New model of hemorrhagic hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in newborn mice. Pediatr Neurol 5:221–225
Rivkin MJ (1997) Hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in the term newborn. Neuropathology, clinical aspects, and neuroimaging. Clin Perinatol 24:607–625
Raju TN, Nelson KB, Ferreiro D et al (2007) Ischemic perinatal stroke: summary of a workshop sponsored by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development and the National Institute of Neurological Disorder and Stroke. Pediatrics 120:609–616
Govaert P, Matthys E, Zecic A et al (2000) Perinatal cortical infarction within middle cerebral artery trunks. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 82:59–63
Carvalho KS, Bodensteiner JB, Connolly PJ et al (2001) Cerebral venous thrombosis in children. J Child Neurol 16:574–580
Kinney HC, Amstrong DD (2002) Perinatal neuropathology. In: Graham DI, Lantos PL (eds) Greenfield’s neuropathology, 7th edn. Oxford University Press, New York, p 551
Nelson KB, Lynch JK (2004) Stroke in newborn infants. Lancet Neurol 3:150–158
Golomb MR, MacGregor DL, Domi T et al (2001) Presumed pre- or perinatal arterial ischemic stroke: risk factors and outcomes. Ann Neurol 50:163–168
Roodhooft AM, Parizel PM, Van Acker KJ et al (1987) Idiopathic cerebral arterial infarction with paucity of symptoms in the full-term neonate. Pediatrics 80:381–385
Mannino FL, Trauner DA (1983) Stroke in neonates. J Pediatr 102:605–610
Filipek PA, Krishnamoorthy KS, Davis KR et al (1987) Focal cerebral infarction in the newborn: a distinct entity. Pediatr Neurol 3:141–147
Cowan F, Mercuri E, Groenendaal F et al (2005) Does cranial ultrasound imaging identify arterial cerebral infarction in term neonates? Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 90:252–256
Hernanz-Schulman M, Cohen W, Genieser NB (1988) Sonography of cerebral infarction in infancy. AJR 150:897–902
Taylor GA (1997) Recent advances in neonatal cranial ultrasound and Doppler techniques. Clin Perinatol 24:677–691
Siegel MJ, Shackelford GD, Perlman JM et al (1984) Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in term infants: diagnosis and prognosis evaluated by ultrasound. Radiology 152:395–399
Siegel MJ, Patel J, Gado MH et al (1983) Cranial computed tomography and real-time sonography in full-term neonates and infants. Radiology 149:111–116
Hertzberg BS, Pasto ME, Needleman L et al (1987) Postasphyxial encephalopathy in term infants. Sonographic demonstration of increased echogenicity of the thalamus and basal ganglia. J Ultrasound Med 6:197–202
Han BK, Towbin RB, De Courten-Myers G et al (1989) Reversal sign on CT: effect of anoxic/ischemic cerebral injury in children. AJNR 10:1191–1198
Ilves P, Talvik R, Talvik T (1998) Changes in Doppler ultrasonography in asphyxiated term infants with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy. Acta Paediatr 87:680–684
Taylor GA (1992) Effect of scanning pressure on intracranial hemodynamics during transfontanellar duplex US. Radiology 185:763–766
Brunelle F (1997) Arteriovenous malformation of the vein of Galen in children. Pediatr Radiol 27:501–513
Hanigan WC, Powell FC, Miller TC (1995) Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage in full-term infants. Childs Nerv Syst 11:698–707
Hanigan WC, Powell FC, Palagallo G et al (1995) Lobar hemorrhages in full-term neonates. Childs Nerv Syst 11:276–280
Looney CB, Smith JK, Merck LH et al (2007) Intracranial hemorrhage in asymptomatic neonates: prevalence on MR images and relationship to obstetric and neonatal risk factors. Radiology 242:535–541
Grant EG, Kerner M, Schellinger D et al (1982) Evolution of porencephalic cysts from intraparenchymal hemorrhage in neonates: sonographic evidence. AJR 138:467–470
Hayashi N, Endo S, Oka N et al (1994) Intracranial hemorrhage due to rupture of an arteriovenous malformation in a full-term neonate. Childs Nerv Syst 10:344–346
Sandberg DI, Lamberti-Pasculli M, Drake JM et al (2001) Spontaneous intraparenchymal hemorrhage in full-term neonates. Neurosurgery 48:1042–1048
Tekkok IH, Ventureyra EC (1997) Spontaneous intracranial hemorrhage of structural origin during the first year of life. Childs Nerv Syst 13:154–165
Mehwald PS, Dittrich S, Grohmann J (2005) Coarctation of the aorta presenting as cerebral hemorrhage. J Pediatr 146:293
Perlman JM (2004) Brain injury in the term infant. Semin Perinatol 28:415–424
Heibel M, Heber R, Bechinger D et al (1993) Early diagnosis of perinatal cerebral lesions in apparently normal full-term newborns by ultrasound of the brain. Neuroradiology 35:85–91
Reeder JD, Kaude JV, Setzer ES (1982) Choroid plexus hemorrhage in premature neonates: recognition by sonography. AJNR 3:619–622
Bosman C, Boldrini R, Dimitri L et al (1996) Hemimegalencephaly. Histological, immunohistochemical, ultrastructural and cytofluorimetric study of six patients. Childs Nerv Syst 12:765–775
Lam AH, Villanueva AC, de Silva M (1992) Hemimegalencephaly. Cranial sonographic findings. J Ultrasound Med 11:241–244
Hung PC, Wang HS (2005) Hemimegalencephaly: cranial sonographic findings in neonates. J Clin Ultrasound 33:243–247
Wakai S, Arai T, Nagai M (1984) Congenital brain tumors. Surg Neurol 21:597–609
Buetow PC, Smirniotopoulos JG, Done S (1990) Congenital brain tumors: a review of 45 cases. AJNR 11:793–799
Shimamura N, Asano K, Ogane K et al (2003) A case of definitely congenital glioblastoma manifested by intratumoral hemorrhage. Childs Nerv Syst 19:778–781
Sell M, Huber-Schumacher S, van Landeghem FK (2006) Congenital glioblastoma multiforme with abnormal vascularity presenting as intracranial hemorrhage in prenatal ultrasound. Childs Nerv Syst 22:729–733
Baron Y, Barkovich AJ (1999) MR imaging of tuberous sclerosis in neonates and young infants. AJNR 20:907–916
Ramenghi LA, Verrotti A, Domizio S et al (1996) Neonatal diagnosis of tuberous sclerosis. Childs Nerv Syst 12:121–123
Sgro M, Barozzino T, Toi A et al (1999) Prenatal detection of cerebral lesions in a fetus with tuberous sclerosis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 14:356–359
Frank LM, Chaves-Carballo E, Earley LM (1984) Early diagnosis of tuberous sclerosis by cranial ultrasonography. Arch Neurol 41:1302–1303
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yikilmaz, A., Taylor, G.A. Cranial sonography in term and near-term infants. Pediatr Radiol 38, 605–616 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-007-0692-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-007-0692-x