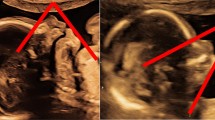
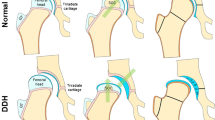
Abstract
Babies are ideal subjects for investigation by sonography. They are small and easily examined with the use of high-frequency transducers. Their unique status in US imaging tends to get lost amid the array of other available modalities, such as MRI and CT imaging. Some of the questions posed in pediatric musculoskeletal imaging that are routinely directed to other imaging modalities can be solved quickly at a lower cost by sonography in neonates and infants without sedation or any known clinical risk. These small children not only have thinner soft tissues but they have long bones and midline spine structures whose ends are largely composed of cartilage, which provides an early opportunity to examine these regions by US. And we cannot overestimate the value of new parents being able to stay next to their baby during imaging in a warm, friendly and non-threatening environment.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bedi DG, John SD, Swischuk LE (1998) Fibromatosis colli of infancy: variability of sonographic appearance. J Clin Ultrasound 267:345–348
Vazquez E, Enriquez G, Castellote A, et al (1995) US, CT, and MR imaging of neck lesions in children. Radiographics 15:105–122
Hernandez RJ (1984) Concentric reduction of the dislocated hip: computed-tomographic evaluation. Radiology 150:266–268
Graf R (1987) Sonographic diagnosis of hip dysplasia: principles, sources of error and consequences. Ultraschall Med 8:2–8
Harcke HT, Grissom LE (1990) Performing dynamic sonography of the infant hip. AJR 155:837–844
Keller MS, Weltin GG, Rattner Z, et al (1988) Normal instability of the hip in the neonate: US standards. Radiology 169:733–736
Riboni G, Bellini A, Serantoni S, et al (2003) Ultrasound screening for developmental dysplasia of the hip. Pediatr Radiol 33:475–481
Rosendahl K, Markestad T, Lie RT (1992) Ultrasound in the early diagnosis of congenital dislocation of the hip: the significance of hip stability versus acetabular morphology. Pediatr Radiol 22:430–433
Taylor GR, Clarke NM (1997) Monitoring the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip with the Pavlik harness. The role of ultrasound. J Bone Joint Surg Br 79:719–723
Babcock DS, Hernandez RJ, Kushner DC, et al (2000) Developmental dysplasia of the hip. American College of Radiology. ACR appropriateness criteria. Radiology [Suppl] 215:819–827
Gillespie R, Torode IP (1983) Classification and management of congenital abnormality of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Br 65:557–568
Strouse PJ, DiPietro MA, Adler RS (1998) Pediatric hip effusions: evaluation with power Doppler sonography. Radiology 206:731–735
Gigante C, Talenti E, Turra S (2004) Sonographic assessment of clubfoot. J Clin Ultrasound 32:235–242
Aurell Y, Johansson A, Hansson G, et al (2002) Ultrasound anatomy in the normal neonatal and infant foot: an anatomic introduction to ultrasound assessment of foot deformities. Eur Radiol 12:2306–2312
Markowitz RI, Hubbard AM, Harty MP, et al (1993) Sonography of the knee in normal and abused infants. Pediatr Radiol 23:264–267
Davidson RS, Markowitz RI, Dormans J, et al (1994) Ultrasonographic evaluation of the elbow in infants and young children after suspected trauma. J Bone Joint Surg Am 76:1804–1813
Grissom LE, Harcke HT (2001) Infant shoulder sonography: technique, anatomy, and pathology. Pediatr Radiol 12:863–868
Abiri MM, Kirpekar M, Ablow RC (1989) Osteomyelitis: detection with US. Radiology 172:509–511
Acknowledgements
Many thanks to my colleagues Drs. Ted Harcke and Leslie Grissom for allowing me to use some of their illustrative materials.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keller, M.S. Musculoskeletal sonography in the neonate and infant. Pediatr Radiol 35, 1167–1173 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-005-1550-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-005-1550-3