Abstract.
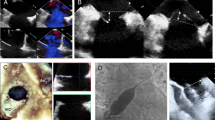
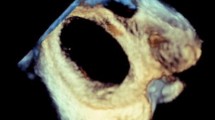
Atrial septal defect (ASD) size measurement is of paramount importance for the successful deployment of a transcatheter septal occluder. The stretched balloon diameter (SBD) has long been regarded as the gold standard for selection of the size of any device. Three-dimensional (3-D) transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) can visualize the overall structure of the atrial septum, therefore rendering an accurate size of the ASD. In this study we aimed to validate the accuracy of ASD size measurement by 3-D TEE and to elucidate the reason for the difference between balloon sizing and 3-D measurement. Forty-one consecutive patients were enrolled in this protocol for ASD device closure using the Amplatzer septal occluder. Thirty-nine patients were diagnosed by 2-D transthoracic echocardiography as secundum ASD and 2 patients were diagnosed as patent foramen ovale. Two measurements of the balloon size were sequentially obtained by 2-D TEE after the balloon was fully inflated in the left atrium. First, no residual shunt across the septum could be seen while the balloon was pulled back against the septum. This measurement was called the balloon occlusive diameter (BOD). Second, with balloon deflation, a slight deformity of the balloon was seen just prior to its popping through the septum. This measurement was called the stretched balloon diameter (SBD). Three-dimensional TEE was performed in all patients at the beginning of the procedure before device deployment and within 15 minutes after device release. Three-dimensional TEE provided superior views of the ASDs, showing the spatial relationship between the ASD and the neighboring structures. For maximal ASD size measurement, balloon sizing was larger than 3-D TEE examination, whereas 2-D was smaller than the other two methods. The best correlation was found between 3-D TEE measurements and the BOD (r= 0.98, p < 0.0001). Three-dimensional TEE provides en face view of ASD; thus, it can accurately measure the size of ASD. Three-dimensional TEE measurement of ASD can be used instead of balloon sizing for the selection of transcatheter ASD occluder size.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, W., Cao, QL., Rhodes, J. et al. Measurement of Atrial Septal Defect Size: A Comparative Study Between Three-Dimensional Transesophageal Echocardiography and the Standard Balloon Sizing Methods. Pediatr Cardiol 21, 465–469 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002460010111
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002460010111