Abstract
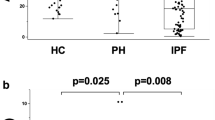
In this study, we aimed to assess levels of serum B cell lymphoma 2 (sBcl-2) in children, which has been implicated in the etiopathogenesis of pulmonary hypertension (PH), as well its association with tissue Doppler echocardiographic imaging (TDI) data and parameters used in the follow-up of PH. The sBcl-2 level was assessed in 35 children with PH (24 had eisenmenger syndrome, and 11 had idiopathic PH) and in 38 healthy children as controls. TDI was performed on 25 patients whose cardiac anatomy allowed the test. The respective sBcl-2 values in patients and controls were 35.69 ± 18.83 and 2.66 ± 7.95 ng/ml (p < 0.001). The sBcl-2 levels were significantly greater in the New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class 3 patients than those in the NYHA class 2 patients (p = 0.033). The sBcl-2 value in patients who walked <475 m in the 6-min walk distance (6MWD) test was significantly greater than in those who walked ≥475 m (p = 0.038). The sBcl-2 level showed a negative correlation with ejection time measured at the septal anulus (p = 0.026) and a positive correlation with interventricular septum-Tei (p = 0.018). The results of this study showed for the first time that there is an increase in the levels of sBcl-2 as an inflammatory marker and that the sBcl-2 levels are associated with prognostic parameters in children with PH. Because sBcl-2 levels were greater in patients who walked <475 meters during the 6MWD test, we suggest 475 ms as the cut-off value for the 6MWD test to differentiate between a good and a bad prognosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang SM, Lin CC, Hsiao SH, Lee CY, Yang SH, Lin SK et al (2007) Pulmonary hypertension and left heart function: insights from tissue Doppler imaging and myocardial performance index. Echocardiography 24(4):366–373
Colombel M, Symmans F, Gil S, O’Toole KM, Chopin D, Benson M et al (1993) Detection of the apoptosis-suppressing oncoprotein bc1-2 in hormone-refractory human prostate cancers. Am J Pathol 143(2):390–400
Cowan KN, Jones PL, Rabinovitch M (1999) Regression of hypertrophied rat pulmonary arteries in organ culture is associated with suppression of proteolytic activity, inhibition of tenascin-C, and smooth muscle cell apoptosis. Circ Res 84(10):1223–1233
Cowan KN, Heilbut A, Humpl T, Lam C, Ito S, Rabinovitch M (2000) Complete reversal of fatal pulmonary hypertension in rats by a serine elastase inhibitor. Nat Med 6(6):698–702
de Jong D, Prins FA, Mason DY, Reed JC, van Ommen GB, Kluin PM (1994) Subcellular localization of the bcl-2 protein in malignant and normal lymphoid cells. Cancer Res 54(1):256–260
Ecarnot-Laubriet A, Assem M, Poirson-Bichat F, Moisant M, Bernard C, Lecour S et al (2002) Stage-dependent activation of cell cycle and apoptosis mechanisms in the right ventricle by pressure overload. Biochim Biophys Acta 1586(3):233–242
Fontanini G, Vignati S, Bigini D, Mussi A, Lucchi M, Angeletti CA et al (1995) Bcl-2 protein: a prognostic factor inversely correlated to p53 in non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 71(5):1003–1007
Galie N, Hoeper MM, Humbert M, Torbicki A, Vachiery JL, Barbera JA et al (2009) Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS), endorsed by the International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Heart J 30(20):2493–2537
Gibbons GH, Dzau VJ (1994) The emerging concept of vascular remodeling. New Engl J Med 330(20):1431–1438
Goldstein JC, Waterhouse NJ, Juin P, Evan GI, Green DR (2000) The coordinate release of cytochrome c during apoptosis is rapid, complete and kinetically invariant. Nat Cell Biol 2(3):156–162
Gurbanov E, Shiliang X (2006) The key role of apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 30(3):499–507
Hassoun PM, Mouthon L, Barbera JA, Eddahibi S, Flores SC, Grimminger F et al (2009) Inflammation, growth factors, and pulmonary vascular remodeling. J Am Coll Cardiol 54(1 Suppl):S10–S19
Huang JB, Liu YL, Sun PW, Lv XD, Bo K, Fan XM (2010) Novel strategy for treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension: enhancement of apoptosis. Lung 188(3):179–189
Levy M, Maurey C, Celermajer DS, Vouhe PR, Danel C, Bonnet D et al (2007) Impaired apoptosis of pulmonary endothelial cells is associated with intimal proliferation and irreversibility of pulmonary hypertension in congenital heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 49(7):803–810
Martin B, Paesmans M, Berghmans T, Branle F, Ghisdal L, Mascaux C et al (2003) Role of Bcl-2 as a prognostic factor for survival in lung cancer: a systematic review of the literature with meta-analysis. Br J Cancer 89(1):55–64
Miyamoto S, Nagaya N, Satoh T, Kyotani S, Sakamaki F, Fujita M et al (2000) Clinical correlates and prognostic significance of six-minute walk test in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Comparison with cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 161(2 Pt 1):487–492
Paciocco G, Martinez FJ, Bossone E, Pielsticker E, Gillespie B, Rubenfire M (2001) Oxygen desaturation on the six-minute walk test and mortality in untreated primary pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J 17(4):647–652
Silvestrini R, Veneroni S, Daidone MG, Benini E, Boracchi P, Mezzetti M et al (1994) The Bcl-2 protein: a prognostic indicator strongly related to p53 protein in lymph node-negative breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst 86(7):499–504
Simonneau G, Gatzoulis MA, Adatia I, Celermajer D, Denton C, Ghofrani A et al (2013) Updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 24(62(25 Suppl)):D34–D41
Sitbon O, Humbert M, Nunes H, Parent F, Garcia G, Herve P et al (2002) Long-term intravenous epoprostenol infusion in primary pulmonary hypertension: prognostic factors and survival. J Am Coll Cardiol 40(4):780–788
Stenmark KR, Fagan KA, Frid MG (2006) Hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Circ Res 99(7):675–691
Tanaka K, Iwamoto S, Gon G, Nohara T, Iwamoto M, Tanigawa N (2000) Expression of survivin and its relationship to loss of apoptosis in breast carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 6(1):127–134
Yeo TC, Dujardin KS, Tei C, Mahoney DW, McGoon MD, Seward JB (1998) Value of a Doppler-derived index combining systolic and diastolic time intervals in predicting outcome in primary pulmonary hypertension. Am J Cardiol 81(9):1157–1161
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Hacettepe University Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit Ankara/Turkey. The project number is FON 12/02-29. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akın, A., Alehan, D., Aykan, H.H. et al. Serum Bcl-2 Values in Children with Pulmonary Hypertension. Pediatr Cardiol 36, 579–583 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-014-1052-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-014-1052-x