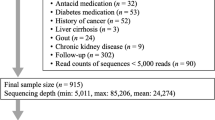
Abstract
Nephrolithiasis is a common urological disease with high prevalence and recurrence rates. Characterizing gut microbiome profiles of nephrolithiasis patients may provide valuable insights and potential biomarkers for the disease. Therefore, we explored the relation between gut microbiome and nephrolithiasis using 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) gene sequencing. 13 patients with multiple kidney stones and 13 matched healthy controls were recruited. A decreasing trend in number of observed species in nephrolithiasis patients was detected, although statistical significance was not reached (p = 0.086). The inter-group variability in community structure by beta diversity analysis showed a clear separation between nephrolithiasis patients and healthy controls. Twenty genera differentiated significantly in relative abundance between nephrolithiasis patients and healthy controls (all p < 0.05). Among the 20 genera, Phascolarctobacterium, Parasutterella, Ruminiclostridium_5, Erysipelatoclostridium, Fusicatenibacter and Dorea were correlated with the concentration of the trace elements in blood, including potassium, sodium, calcium and chlorinum. Characteristic microbiome in nephrolithiasis patients was also identified by linear discriminant analysis effect size (LEfSe). These findings may provide novel and non-invasive potential diagnostic biomarkers for nephrolithiasis, and contribute to prevention and treatment of nephrolithiasis from the perspective of maintaining micro-ecological equilibrium in gut.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang W, Fan J, Huang G, Li J, Zhu X, Tian Y, Su L (2017) Prevalence of kidney stones in mainland China: a systematic review. Sci Rep 7:41630
Attanasio M (2011) The genetic components of idiopathic nephrolithiasis. Pediatr Nephrol 26(3):337–346
Curhan GC (2007) Epidemiology of stone disease. Urol Clin N. Am 34(3):287–293
Nouvenne A, Meschi T, Prati B, Guerra A, Allegri F, Vezzoli G, Soldati L, Gambaro G, Maggiore U, Borghi L (2010) Effects of a low-salt diet on idiopathic hypercalciuria in calcium-oxalate stone formers: a 3-mo randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr 91(3):565
Taylor EN, Curhan GC (2008) Fructose consumption and the risk of kidney stones. Kidney Int 73(2):207–212
Leone V, Chang EB, Devkota S (2013) Diet, microbes, and host genetics: the perfect storm in inflammatory bowel diseases. J Gastroenterol 48(3):315–321
Tan J, Mckenzie C, Potamitis M, Thorburn AN, Mackay CR, Macia L (2014) The role of short-chain fatty acids in health and disease. Adv Immunol 121:91–119
Taylor EN, Stampfer MJ, Curhan GC (2005) Obesity, weight gain, and the risk of kidney stones. Jama 293(4):455–462
Taylor EN, Stampfer MJ, Curhan GC (2005) Diabetes mellitus and the risk of nephrolithiasis. Kidney Int 68(3):1230–1235
Obligado SH, Goldfarb DS (2008) The association of nephrolithiasis with hypertension and obesity: a review. Am J Hypertens 21(3):257–264
Saucier NA, Sinha MK, Liang KV, Krambeck AE, Weaver AL, Bergstralh EJ, Li X, Rule AD, Lieske JC (2010) Risk factors for CKD in persons with kidney stones: a case-control study in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Am J Kidney Dis 55(1):61–68
Stern JM, Moazami S, Qiu Y, Kurland I, Chen Z, Agalliu I, Burk R, Davies KP (2016) Evidence for a distinct gut microbiome in kidney stone formers compared to non-stone formers. Urolithiasis 44(5):399–407
Suryavanshi MV, Bhute SS, Jadhav SD, Bhatia MS, Gune RP, Shouche YS (2016) Hyperoxaluria leads to dysbiosis and drives selective enrichment of oxalate metabolizing bacterial species in recurrent kidney stone endures. Sci Rep 6:34712
Hatch M (2017) Gut microbiota and oxalate homeostasis. Ann Transl Med 5(2):36
Siener R, Bangen U, Sidhu H, Honow R, von Unruh G, Hesse A (2013) The role of Oxalobacter formigenes colonization in calcium oxalate stone disease. Kidney Int 83(6):1144–1149
Magwira CA, Kullin B, Lewandowski S, Rodgers A, Reid SJ, Abratt VR (2012) Diversity of faecal oxalate-degrading bacteria in black and white South African study groups: insights into understanding the rarity of urolithiasis in the black group. J Appl Microbiol 113(2):418–428
Tang Z, Jiang S, Li J, Li X, Zhong M, Huang R, Li P, Zou A (2014) Correlation analysis between renal calculus and dietary factors in Gongcheng Yao ethnic group. J Clin Urology (China) 29(11):1018–1021 (In Chinese)
Tang Z, Jiang S, Li J, Li X, Zhong M, Huang R, Li P, Zou A (2015) Epidemiological survey of renal calculi in adult Yao population in Guangxi. Chin Gen Pract 18(14):1691–1694 (In Chinese)
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Turnbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7(5):335–336
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J, Glockner FO (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 41 (Database issue):D590–D596
Segata N, Izard J, Waldron L, Gevers D, Miropolsky L, Garrett WS, Huttenhower C (2011) Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol 12(6):R60
Langille MG, Zaneveld J, Caporaso JG, Mcdonald D, Knights D, Reyes JA, Clemente JC, Burkepile DE, Vega Thurber RL, Knight R (2013) Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat Biotechnol 31(9):814–821
Kelly JP, Curhan GC, Cave DR, Anderson TE, Kaufman DW (2011) Factors related to colonization with Oxalobacter formigenes in U.S. adults. J Endourol 25(4):673–679
Batislam E, Yilmaz E, Yuvanc E, Kisa O, Kisa U (2012) Quantitative analysis of colonization with real-time PCR to identify the role of Oxalobacter formigenes in calcium oxalate urolithiasis. Urol Res 40(5):455–460
Xian X, Xie Y, Ye J, Tang R, Jiang Y, Yao Z (2016) Quantification of oxalate-degrading bacteria in the gut of kidney stone patients using real-time PCR. Genom Appl Biol 35(9):2222–2228 (In Chinese)
Barrbeare E, Saxena V, Hilt EE, Thomaswhite K, Schober M, Li B, Becknell B, Hains DS, Wolfe AJ, Schwaderer AL (2015) The interaction between Enterobacteriaceae and calcium oxalate deposits. PloS One 10(10):e0139575
Benakis C, Brea D, Caballero S, Faraco G, Moore J, Murphy M, Sita G, Racchumi G, Ling L, Pamer EG, Iadecola C, Anrather J (2016) Commensal microbiota affects ischemic stroke outcome by regulating intestinal gammadelta T cells. Nat Med 22(5):516–523
Russell SL, Gold MJ, Hartmann M, Willing BP, Thorson L, Wlodarska M, Gill N, Blanchet MR, Mohn WW, McNagny KM, Finlay BB (2012) Early life antibiotic-driven changes in microbiota enhance susceptibility to allergic asthma. EMBO Rep 13(5):440–447
Bashiardes S, Shapiro H, Rozin S, Shibolet O, Elinav E (2016) Non-alcoholic fatty liver and the gut microbiota. Mol Metab 5(9):782–794
Huang W, Guo HL, Deng X, Zhu TT, Xiong JF, Xu YH, Xu Y (2017) Short-chain fatty acids inhibit oxidative stress and inflammation in mesangial cells induced by high glucose and lipopolysaccharide. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 125(2):98–105
Cattaneo A, Cattane N, Galluzzi S, Provasi S, Lopizzo N, Festari C, Ferrari C, Guerra UP, Paghera B, Muscio C, Bianchetti A, Volta GD, Turla M, Cotelli MS, Gennuso M, Prelle A, Zanetti O, Lussignoli G, Mirabile D, Bellandi D, Gentile S, Belotti G, Villani D, Harach T, Bolmont T, Padovani A, Boccardi M, Frisoni GB (2017) Association of brain amyloidosis with pro-inflammatory gut bacterial taxa and peripheral inflammation markers in cognitively impaired elderly. Neurobiol Aging 49:60–68
Lim MY, You HJ, Yoon HS, Kwon B, Lee JY, Lee S, Song YM, Lee K, Sung J, Ko G (2016) The effect of heritability and host genetics on the gut microbiota and metabolic syndrome. Gut 66(6):1031–1038
Ling Z, Jin C, Xie T, Cheng Y, Li L, Wu N (2016) Alterations in the fecal microbiota of patients with HIV-1 infection: an observational study in a Chinese population. Sci Rep 6:30673
Funding
This study was funded by Guangxi Natural Science Foundation under Grant no. 2016GXNSFBA380193, Guangxi Natural Science Fund for Innovation Research Team (2013GXNSFFA019002), Guangxi Collaborative Innovation Center for genomic and personalized medicine (201319), the Science and technology research project of Guangxi Higher Education (KY2015YB051), and Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant no. 81501284.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Figure S1: Rarefaction curves
. A Rarefaction curves of Shannon index for the microbiota of KS group and HC group. B Rarefaction curves of observed species of KS group (blue lines) and HC group (red lines) (TIF 459 KB)
Figure S2: Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of the species with LDA score > 4 from the LEfSe results
. ROC for Pseudomonas aeruginosa, AUC = 0.947; ROC for Escherichia coli, AUC = 0.870 (TIF 142 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, R., Jiang, Y., Tan, A. et al. 16S rRNA gene sequencing reveals altered composition of gut microbiota in individuals with kidney stones. Urolithiasis 46, 503–514 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-018-1037-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-018-1037-y