Abstract
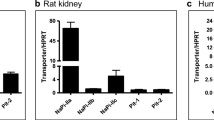
Little is known about oxalate transport in renal epithelia under basal conditions, let alone in hyperoxaluria when the capacity for renal oxalate excretion is increased. Sulfate anion transporter 1 (SAT1, Slc26a1) is considered to be a major basolateral anion-oxalate exchanger in the proximal tubule and we hypothesized its expression may correlate with urinary oxalate excretion. We quantified changes in the renal expression of SAT1 mRNA and protein in two rat models, one with hyperoxaluria (HYP) and one with renal insufficiency (HRF) induced by hyperoxaluria. The hyperoxaluria observed in the HYP group could not simply be ascribed to changes in SAT1 mRNA or protein abundance. However, when hyperoxaluria was accompanied by renal insufficiency, significant reductions in SAT1 mRNA and protein were detected in medullary and papillary tissue. Together, the results indicate that transcriptional modulation of the SAT1 gene is not a significant component of the hyperoxaluria observed in these rat models.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hatch M (1993) Oxalate status in stone-formers. Two distinct hyperoxaluric entities. Urol Res 21:55–59
Danpure CJ (2005) Molecular etiology of primary hyperoxaluria type 1: new directions for treatment. Am J Nephrol 25:303–310
Hatch M, Freel RW (2005) Intestinal transport of an obdurate anion: oxalate. Urol Res 33:1–16
Knight TF, Sansom SC, Senekjian HO, Weinman EJ (1981) Oxalate secretion in the rat proximal tubule. Am J Physiol 240:F295–F298
Senekjian HO, Weinman EJ (1982) Oxalate transport by proximal tubule of the rabbit kidney. Am J Physiol 243:F271–F275
Hatch M, Freel RW (2008) The roles and mechanisms of intestinal oxalate transport in oxalate homeostasis. Semin Nephrol 28:143–151
Hatch M, Freel RW (2003) Renal and intestinal handling of oxalate following oxalate loading in rats. Am J Nephrol 23:18–26
Kuo SM, Aronson PS (1988) Oxalate transport via the sulfate/HCO3 exchanger in rabbit renal basolateral membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem 263:9710–9717
Greger R, Lang F, Oberleithner H, Deetjen P (1978) Handling of oxalate by the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch 374:243–248
Weinman EJ, Frankfurt SJ, Ince A, Sansom S (1978) Renal tubular transport of organic acids. Studies with oxalate and para-aminohippurate in the rat. J Clin Invest 61:801–806
Krick W, Schnedler N, Burckhardt G, Burckhardt BC (2009) Ability of SAT-1 to transport sulfate, bicarbonate, or oxalate under physiological conditions. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 297:F145–F154
Brandle E, Bernt U, Hautmann RE (1998) In situ characterization of oxalate transport across the basolateral membrane of the proximal tubule. Pflugers Arch 435:840–849
Dawson PA, Russell CS, Lee S, McLeay SC, van Dongen JM, Cowley DM, Clarke LA, Markovich D (2010) Urolithiasis and hepatotoxicity are linked to the anion transporter SAT1 in mice. J Clin Invest 120:706–712
Karniski LP, Lotscher M, Fucentese M, Hilfiker H, Biber J, Murer H (1998) Immunolocalization of SAT-1 sulfate/oxalate/bicarbonate anion exchanger in the rat kidney. Am J Physiol 275:F79–F87
Mount DB, Romero MF (2004) The SLC26 gene family of multifunctional anion exchangers. Pflugers Arch 447:710–721
Xie Q, Welch R, Mercado A, Romero MF, Mount DB (2002) Molecular characterization of the murine Slc26a6 anion exchanger: functional comparison with Slc26a1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 283:F826–F838
Green ML, Hatch M, Freel RW (2005) Ethylene glycol induces hyperoxaluria without metabolic acidosis in rats. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 289:F536–F543
Rozen S, Skaletsky H (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol Biol 132:365–386
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Steel RG, Torrie JH (1980) Principles and procedures of statistics, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York
SAS (1985) SAS User’s Guide: Basics, Version, 5th edn. SAS Institute Inc., Carey
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3:RESEARCH0034
Hatch M, Freel RW (2003) Angiotensin II involvement in adaptive enteric oxalate excretion in rats with chronic renal failure induced by hyperoxaluria. Urol Res 31:426–432
Aronson PS (1989) The renal proximal tubule: a model for diversity of anion exchangers and stilbene-sensitive anion transporters. Annu Rev Physiol 51:419–441
Regeer RR, Lee A, Markovich D (2003) Characterization of the human sulfate anion transporter (hsat-1) protein and gene (SAT1; SLC26A1). DNA Cell Biol 22:107–117
Markovich D, Murer H, Biber J, Sakhaee K, Pak C, Levi M (1998) Dietary sulfate regulates the expression of the renal brush border Na/Si cotransporter NaSi-1. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:1568–1573
Sagawa K, DuBois DC, Almon RR, Murer H, Morris ME (1998) Cellular mechanisms of renal adaptation of sodium dependent sulfate cotransport to altered dietary sulfate in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 287:1056–1062
Freel RW, Hatch M, Green M, Soleimani M (2006) Ileal oxalate absorption and urinary oxalate excretion are enhanced in Slc26a6-null mice. Am J Physiol (Gastrointest Liver Physiol) 290:G719–G728
Schnedler N, Burckhardt G, Burckhardt BC (2011) Glyoxylate is a substrate of the sulfate–oxalate exchanger, SAT-1, and increases its expression in HepG2 cells. J Hepatol 54:513–520
Fernandes I, Laouari D, Tutt P, Hampson G, Friedlander G, Silve C (2001) Sulfate homeostasis, NaSi-1 cotransporter, and SAT-1 exchanger expression in chronic renal failure in rats. Kidney Int 59:210–221
Green ML, Freel RW, Hatch M (2005) Lipid peroxidation is not the underlying cause of renal injury in hyperoxaluric rats. Kidney Int 68:1–10
Quondamatteo F, Krick W, Hagos Y, Kruger MH, Neubauer-Saile K, Herken R, Ramadori G, Burckhardt G, Burckhardt BC (2006) Localization of the sulfate/anion exchanger in the rat liver. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 290:G1075–G1081
Markovich D (2001) Physiological roles and regulation of mammalian sulfate transporters. Physiol Rev 81:1499–1533
Greger R (1981) In: Greger R, Lang F, Silbernagel S (eds) Renal transport of organic substances, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, p 224
Sigmon D, Kumar S, Carpenter B, Miller T, Menon M, Scheid C (1991) Oxalate transport in renal tubular cells from normal and stone-forming animals. Am J Kidney Dis 17:376–380
Chandhoke PS, Fan J (2000) Transport of oxalate across the rabbit papillary surface epithelium. J Urol 164:1724–1728
Acknowledgments
The technical assistance of Michael Green, Ph. D., Candi Morris, and Bonnie Murphey is greatly appreciated. This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (DK60544, DK56245).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freel, R.W., Hatch, M. Hyperoxaluric rats do not exhibit alterations in renal expression patterns of Slc26a1 (SAT1) mRNA or protein. Urol Res 40, 647–654 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-012-0480-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-012-0480-4