Abstract
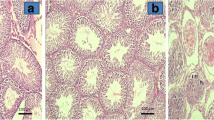
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) modulates Leydig cell proliferation, steroidogenesis, spermiogenesis, and Sertoli cell activity. It plays an important role in repairing ischemia-reperfusion injury in different tissues. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of sustained and local administration of EGF on improving bilateral testicular tissue after torsion. A total of 57 Wistar albino rats were used. For the EGF transport system, 1×2 cm gelatin films containing 2 µg EGF were used. Torsion was created by rotating the right testis 720° in a clockwise direction for 4 h in all groups except the control group. Then, in the torsion group, bilateral orchiectomy was performed. After returning the torsioned ipsilateral testes to their normal state, the bilateral testes were wrapped by 1×2 cm unloaded gelatin films in the gelatin (G7 and G21) groups and, by 2 µg EGF loaded gelatin films in the EGF 7 and EGF 21 groups. The testes were removed on the seventh and 21st days, respectively, for biochemical and histological examination. Histologically, Johnsen’s spermatogenesis criteria and mean seminiferous tubule diameter (MSTD) measurements were used. The EGF7 group did not show significant loss of Sertoli cells, while in the G7 group the number of these cells decreased. The ipsilateral ischemic testis of the EGF21 group showed Leydig cell hyperplasia, and the contralateral non-ischemic testes in this group were similar to the control group. In the G21 group, the bilateral testes showed Sertoli cell only syndrome in some sections, and most of the cells were undergoing apoptosis. The mean spermatogenesis scores and MSTD in the EGF7 and EGF21 groups were higher than in the G7 and G21 groups (P<0.05). Malondialdehyde levels were significantly lower in the EGF groups than in the G groups (P<0.05). Glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) levels in the G21 group were significantly higher than in the EGF21 group. Our study shows that local and sustained EGF release after testicular torsion improves bilateral testicular injury. EGF administration may be a new treatment choice for bilaterally injured testis after detorsion without removing the twisted testis.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krarup T (1978) Testis after torsion. Br J Urol 50: 43
Çiftçi AO, Müftüoğlu S, Çakar N, Tanyel FC (1997) Histological evidence of decreased contralateral testicular blood flow during ipsilateral testicular torsion. Br J Urol 80: 783
Sarica K, Küpeli B, Burak M et al. (1997) Influence of experimental spermatic cord torsion on the contralateral testis in rats. Urol Int 58: 208
Akgür FM, Kilinc K, Aktuğ T (1993) Reperfusion injury after detorsion of ipsilateral testicular torsion. Urol Res 21: 395
Nguyen L, Lievano G, Ghosh L, Radhakrishnan J, Fornell L, John E (1999) Effect of ipsilateral testicular torsion on blood flow and histology of contralateral testes. J Pediatr Surg 34: 680–683
Tanyel F, Büyükpamukçu N, Hiçsönmez A (1989) Contralateral testicular blood flow during ipsilateral testicular torsion. 63: 522
Bulkley GB (1987) Free radical mediated reperfusion injury: a selective review. Br J Cancer [Suppl] 8: 66
Madesh M, Balasubramanian KA (1997) Activation of liver mitocondrial phospholipase A2 by superoxide. Arch Biochem Biophys 346: 187
Turner TT, Tung KS, Tomomasa H (1997) Acute testicular ischemia results in germ cell-specific apoptosis in the rat. Biol Reprod 57: 1267
Traish AM, Wotiz HH (1987) Prostatic epidermal growth factors and their regulation by androgens. Endocrinology 121: 1461
Carpenter G, Cohen S (1979) Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem 48: 193
Caussanel V, Tabone E, Mauduit C, Dacheux F, Benahmed M (1996) Cellular distribution of EGF, TGFα and their receptor during postnatal development and spermatogenesis of the boar testis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 123: 61
Khan S, Teerds K, Dorrington J (1992) Growth factor requirements for DNA synthesis by Leydig cells from the immature rats. Biol Reprod 46: 335
Verhoeven G, Cailleau J (1986) Stimulatory effects of epidermal growth factor on steroidogenesis in Leydig cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 47: 99
Niederberger CS, Shubhada S, Kim SJ, Lamb DJ (1993) Paracrine factors and the regulation of spermatogenesis. World J Urol 11: 120
Nakazumi H, Sasano H, Maehara I, Orikasa S (1996) Transforming growth factor-α, epidermal growth factor, and epidermal growth factor receptor in human testis obtained from biopsy and castrastion: immunohistochemical study. Tohoku J Exp Med 178: 381
Peterson C, Boitani C, Froysa B, Soder O (2001) Transforming growth factor-alpha stimulates proliferation of rat Sertoli cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 5: 221
Levine E, Cupp AS, Miyashiro L, Skinner MK (2000) Role of transforming growth factor-alpha and the epidermal growth factor receptor in embryonic rat testis development. Biol Reprod 62: 477
Tsutsumi O, Kurachi H, Oka T (1986) A physiological role of epidermal growth factor in male reproductive function. Science 233: 975
Noguchi S, Ohba Y, Oka T (1990) Involvement of epidermal growth factor deficiency in pathogenesis of oligozoospermia in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Endocrinology 127: 2136
Fiore N, Ledniczky G, Liu Q, Orazi A, Du X, Williams DA, Grosfeld JL (1998) Comparison of interleukin-11 and epidermal growth factor on residual small intestine after massive small bowel resection. J Pediatr Surg 33: 24
Kuhn MA, Xia G, Mehta VB, Glenn S, Michalsky MP, Besner GE (2002) Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor decreases oxygen free radical production in vitro and in vivo. Antioxid Redox Signal 4: 639
Villa X, Kuluz JW, Schleien CL, Thompson JF (2002) Epidermal growth factor reduces ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat small intestine. Crit Care Med 30: 1576
Tomaszewska R, Dembinski A, Warzecha Z, Ceranowicz P, Konturek SJ, Stachura J (2002) The influence of epidermal growth factor on the course of ischemia-reperfusion induced pancreatitis in rats. J Physiol Pharmacol 53: 183
Taira T, Yoshimura A, Iizuka K, Inui K, Oshiden K, Iwasaki S, Ideura T, Koshikawa S (1996) Expression of epidermal growth factor and its receptor in rabbits with ischaemic acute renal failure. Virchows Arch 427: 583
Muvaffak A, Hasirci N (2002) Controlled release from glutaraldehyde crosslinked gelatin microspheres. Technol Health Care 10: 347
Cosentino MJ, Sheinfeld J, Erturk E, Cockett ATK (1986) The effect of graded ipsilateral testicular biopsy on the reproductive capacity of male rats. J Urol 135: 155
Johnsen SG (1970) Testicular biopsy score count. A method for registration of spermatogenesis in human testis: normal values and results in 335 hypogonadal males. Hormones 1: 2
Hadziselimovic F, Seguchi H (1974) Ultramikroskopische Undersuchungen an Tubules Seminiferus bei Kindern von der Geburt bis zur Pubertat II. Entwicklung und Morphologie der Sertolizellen. Verh Anat Ges 68: 149
França LR, Leal MC, Sasso-Cerri E, Vanconcelos A, Debeljuk L, Russell LD (2000) Cimetidine (Tagamet) is a reproductive toxicant in male rats affecting peritubuler cells. Biol Reprod 63: 1403
Uchiyama M, Mihara M (1978) Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by tiobarbituric acid test. Analyt Bioch 34: 271
Paglia DE, Valentina WN (1967) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70: 158
Draye JP, Delaey B, Van de Voorde A, Van Den Bulcke A, De Reu B, Schacht E (1998) In vitro and in vivo biocompatibility of dextran dialdehyde cross-linked gelatin hydrogel films. Biomaterials 19: 1677
Ulubayram K, Cakar AN, Korkusuz P, Ertan C, Hasirci N (2001) EGF containing gelatin-based wound dressings. Biomaterials 22: 1345
Ulubayram K, Eroglu I, Hasirci N (2002) Gelatin microspheres and sponges for delivery of macromolecules. J Biomater Applic 16: 227
Juhl CO, Vinter-Jensen L, Jensen LS, Nexo E, Djurhuus JC, Dajani EZ (1994) Recombinant human epidermal growth factor accelerates healing of sclerotherapy-induced esophageal ulcers and prevents esophageal stricture formation in pigs. Dig Dis Sci 39: 2671
Buckley A, Davidson JM, Kamerath TBW, Woodward SC (1985) Sustained release of epidermal growth factor accelerates wound repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 82: 7340
Sheardown H, Clark H, Wedge C, Apel R, Rootman D, Cheng YL (1997) A semi-solid drug delivery for epidermal growth factor in corneal epithelial wound healing. Curr Eye Res 16: 183
Radhakrishnan B, Suarez-Quian CA (1992) Characterization of epidermal growth factor receptor in testis, epididymis and vas deferens of non-human primates. J Reprod Fertil 96: 13
Robaire B, Hermo L (1998) Efferent ducts, epididymis, and vas deferens: structure, functions, and their regulation. In: Knobil E, Neill J (eds) The Physiology of reproduction. Raven Press, New York, p 999
Southorn PA, Powis G (1988) Free radicals in medicine. Chemical nature and physiologic reactions. Mayo Clin Proc 63: 3881
Halliwell B, Guueridge JMC (1989) Free radicals in biology and medicine, 2nd edn. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Aitken RJ, Irvine DS, Wu FC (1991) Prospective analysis of sperm-oocyte fusion and reactive oxygen species generation as criteria for the diagnosis of infertility. Am J Obstet Gynecol 164: 542
Roveri A, Casasco A, Maiorino M, Dalan P, Calligaro A, Ursini F (1992) Phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase of rat testis. J Biol Chem 267: 6142
Flamm ES, Demopoulas HB, Seligman ML, Poser RG, Ransohoff J (1978) Free radicals in cerebral ischemia. Stroke 9: 445
Cosentino MJ, Nishida M, Rabinowitz R, Cockett ATK (1986) Histopathology of prepubertal rat testes subjected to various durations of spermatic cord torsion. J Androl 7: 23
Cosentino MJ, Nishida M, Rabinowitz R, Cocckett AT (1985) Histological changes occurring in the contralateral testes of prepubertal rats subjected to various durations of ipsilateral spermatic cord torsion. J Urol 133: 906
Heindel RM, Pakyz RE, Cosentino JM (1990) Spermatic cord torsion. Contralateral testicular degeneration at various ages in the rat. J Androl 11: 506
Dokucu AI, Ozturk H, Ozdemir E (2000) The protective effects of nitric oxide on the contralateral testis in prepubertal rats with ipsilateral testicular torsion. BJU Int 85: 767
Karagüzel G, Tanyel FC, Kilinç K, Büyükpamukçu N, Hiçsönmez A (1994) The preventive role of chemical sympathectomy on contralateral testicular hypoxic parameters encountered during ipsilateral testicular torsion. Br J Urol 74: 507
Acknowledgement
This manuscript won the Professor Dr. Ihsan Numanoglu Scientific Experimental Research Prize at the XXIst National Pediatric Surgeon Congress, October 8–10, 2003, Urfa, Turkey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uguralp, S., Bay Karabulut, A., Mizrak, B. et al. The effect of sustained and local administration of epidermal growth factor on improving bilateral testicular tissue after torsion. Urol Res 32, 323–331 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-004-0418-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00240-004-0418-6