Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the possible protective role of syringic acid on torsion/detorsion-induced testicular injury using biochemical and histopathological approaches for the first time.
Methods
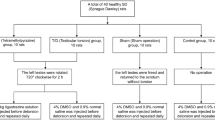
A total of 24 rats were divided into 4 groups: sham control, torsion/detorsion, torsion/detorsion + syringic acid (50 mg/kg and 100 mg/kg). Tissue malondialdehyde, total oxidant status and total antioxidant status levels were determined using colorimetric methods. Tissue 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine, superoxide dismutase, catalase, high mobility group box 1, nuclear factor kappa B protein 65, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, myeloperoxidase, 78-kDa glucose-regulated protein, activating transcription factor-6, C/EBP homologous protein and caspase-3 levels were determined using commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits. Johnsen’s testicle scoring system was used for histological evaluation.
Results
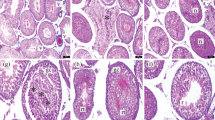
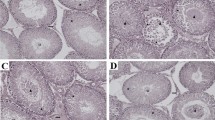
Compared with the control group, the levels of oxidative stress, inflammation, endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis were significantly increased in the torsion/detorsion group (p < 0.05). Syringic acid administrations statistically significantly restored these damage in a dose dependent manner (p < 0.05). Moreover, it was found that the results of histological examinations supported the biochemical results to a statistically significant extent.
Conclusion
The overall results suggest that syringic acid emerges as a potential compound for the treatment of testicular torsion and may be subject to clinical trials.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data presented in the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- 8-OHdG:
-
8-Hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine
- ATF6:
-
Activating transcription factor 6
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- CHOP:
-
C/EBP homologous protein
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- ERAD:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- GRP78:
-
78-KDa glucose-regulated protein
- H&E:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin
- HMGB1:
-
High mobility group box 1
- IP:
-
Intraperitoneal
- I/R:
-
Ischemia/reperfusion
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- IRE1:
-
Inositol requiring enzyme 1
- IRI:
-
Ischemia/reperfusion injury
- IQR:
-
Interquantile range
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- MPO:
-
Myeloperoxidase
- NF-κB p65:
-
Nuclear factor kappa B protein 65
- OSI:
-
Oxidative stress index
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffered saline
- PERK:
-
Protein kinase RNA-activated-like ER kinase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SA:
-
Syringic acid
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TAS:
-
Total antioxidant status
- TBA:
-
Thiobarbituric acid
- T/D:
-
Torsion/detorsion
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
- TOS:
-
Total oxidant status
- TT:
-
Testicular torsion
- UPR:
-
Unfolded protein response
References
Vaos G, Zavras N. Antioxidants in experimental ischemia-reperfusion injury of the testis: Where are we heading towards? World J Methodol. 2017;7(2):37–45.
Shunmugam M, Goldman RD. Testicular torsion in children. Can Fam Physician. 2021;67(9):669–71.
Unsal V, Kolukcu E, Gevrek F, Firat F. Sinapic acid reduces ischemia/reperfusion injury due to testicular torsion/detorsion in rats. Andrologia. 2021;53(8): e14117.
Sancak EB, Akbas A, Silan C, Cakir DU, Turkon H, Ozkanli SS. Protective effect of syringic acid on kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury. Ren Fail. 2016;38(4):629–35.
Karaguzel E, Kadihasanoglu M, Kutlu O. Mechanisms of testicular torsion and potential protective agents. Nat Rev Urol. 2014;11:391–9.
Li Y, Zhang L, Wang X, Wu W, Qin R. Effect of syringic acid on antioxidant biomarkers and associated inflammatory markers in mice model of asthma. Drug Dev Res. 2019;80(2):253–61.
Srinivasulu C, Ramgopal M, Ramanjaneyulu G, Anuradha CM, Kumar CS. Syringic acid (SA)-A review of its occurrence, biosynthesis, pharmacological and industrial importance. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;108:547–57.
Reyes-Fermín LM, Aparicio-Trejo OE, Avila-Rojas SH, Gómez-Sierra T, Martínez-Klimova E, Pedraza-Chaverri J. Natural antioxidants’ effects on endoplasmic reticulum stress-related diseases. Food Chem Toxicol. 2020;138: 111229.
Martucciello S, Masullo M, Cerulli A, Piacente S. Natural products targeting ER stress, and the functional link to mitochondria. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21:1905.
Tungalag T, Yang DK. Sinapic acid protects SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neurotoxicity. Biomedicines. 2021;9(3):295.
Güven M, Aras AB, Topaloğlu N, Özkan A, Şen HM, Kalkan Y, Okuyucu A, Akbal A, Gökmen F, Coşar M. The protective effect of syringic acid on ischemia injury in rat brain. Turk J Med Sci. 2015;45(1):233–40.
Liu G, Zhang BF, Hu Q, Liu XP, Chen J. Syringic acid mitigates myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury by activating the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;531(2):242–9.
Turner TT, Tung KS, Tomomasa H, Wilson LW. Acute testicular ischemia results in germ cell-specific apoptosis in the rat. Biol Reprod. 1997;57(6):1267–74.
Demir S, Kazaz IO, Kerimoglu G, Demir EA, Colak F, Yilmaz S, Mentese A. Astaxanthin protects testicular tissue against torsion/detorsion-induced injury via suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats. J Invest Surg. 2022;35(5):1044–9.
Kazaz IO, Demir S, Kerimoglu G, Colak F, Alemdar NT, Dogan SY, Bostan S, Mentese A. Chlorogenic acid ameliorates torsion/detorsion-induced testicular injury via decreasing endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Pediatr Urol. 2022;18(3):289.e1-e7.
Manjunatha S, Shaik AH, Prasad EM, Omar SYA, Mohammad A, Kodidhela LD. Combined cardio-protective ability of syringic acid and resveratrol against isoproterenol induced cardio-toxicity in rats via attenuating NF-kB and TNF-α pathways. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):3426.
Mihara M, Uchiyama M. Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by thiobarbituric acid test. Anal Biochem. 1978;86(1):271–8.
Demir EA, Mentese A, Kucuk H, Alemdar NT, Demir S. p-Coumaric acid alleviates cisplatin-induced ovarian toxicity in rats. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2022;48(2):411–9.
Johnsen SG. Testicular biopsy score count-A method for registration of spermatogenesis in human testes: Normal values and results in 335 hypogonadal males. Hormones. 1970;1:2–25.
Shahzad S, Mateen S, Kausar T, Naeem SS, Hasan A, Abidi M, Nayeem SM, Faizy AF, Moin S. Effect of syringic acid and syringaldehyde on oxidative stress and inflammatory status in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients of myocardial infarction. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020;393(4):691–704.
Ye Y, Zeng Z, Jin T, Zhang H, Xiong X, Gu L. The role of high mobility group box 1 in ischemic stroke. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:127.
Zhang B, Zhong Q, Chen X, Wu X, Sha R, Song G, Zhang C, Chen X. Neuroprotective effects of celastrol on transient global cerebral ischemia rats via regulating HMGB1/NF-κB signaling pathway. Front Neurosci. 2020;14:847.
Kim IH, Yan BC, Park JH, Yeun GH, Yim Y, Ahn JH, Lee JC, Hwang IK, Cho JH, Kim YM, Lee YL, Park JH, Won MH. Neuroprotection of a novel synthetic caffeic acid-syringic acid hybrid compound against experimentally induced transient cerebral ischemic damage. Planta Med. 2013;79(5):313–21.
Lin CL. Attenuation of endoplasmic reticulum stress as a treatment strategy against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(12):1930–1.
Xin Q, Ji B, Cheng B, Wang C, Liu H, Chen X, Chen J, Bai B. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in cerebral ischemia. Neurochem Int. 2014;68:18–27.
Li X, Zhang X, Xing R, Qi F, Dong J, Li D, Yu B, Huang M, Zhang L, Yuan X, Yang Y, Wu H, Zang L, Mao X, Sui R. Syringic acid demonstrates promising protective effect against tau fibrillization and cytotoxicity through regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated pathway as a prelude to Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;192:491–7.
Kazaz IO, Demir S, Kerimoglu G, Colak F, Alemdar NT, Akman AU, Cekuc OC, Mentese A. Effect of chrysin on endoplasmic reticulum stress in a rat model of testicular torsion. J Invest Surg. 2022;35(5):1106–11.
Demir S, Kazaz IO, Aliyazicioglu Y, Kerimoglu G, Teoman AS, Yaman SO, Arslan A, Mentese A. Effect of ethyl pyruvate on oxidative state and endoplasmic reticulum stress in a rat model of testicular torsion. Biotech Histochem. 2020;95(4):317–22.
Cikman O, Soylemez O, Ozkan OF, Kiraz HA, Sayar I, Ademoglu S, Taysi S, Karaayvaz M. Antioxidant activity of syringic acid prevents oxidative stress in L-arginine-induced acute pancreatitis: An experimental study on rats. Int Surg. 2015;100:891–6.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EAD: Conceptualization, data curation, validation, investigation, software, writing-original draft. SD: Conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, writing-original draft. IOK: Conceptualization, methodology and writing-original draft. HK: Methodology, investigation. NTA: Methodology, Formal analysis. OFG: Methodology. AM: Data curation, validation, investigation, software. YA: Investigation, writing-original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Experimental Animal Local Ethics Committee of Karadeniz Technical University (Protocol no: 2021/65) and performed according to the animal research reporting of in vivo experiments (ARRIVE) guidelines.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Demir, E.A., Demir, S., Kazaz, I.O. et al. Syringic acid ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion-induced testicular injury in rats via suppressing of HMGB1/NF-κB axis and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 49, 1595–1602 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-023-02227-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00068-023-02227-7