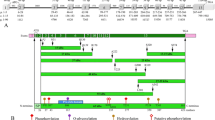
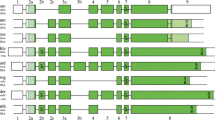
Abstract
Tuftelin (TUFT1) is an acidic, phosphorylated glycoprotein, initially discovered in developing enamel matrix. TUFT1 is expressed in many mineralized and non-mineralized tissues. We performed an evolutionary analysis of 82 mammalian TUFT1 sequences to identify residues and motifs that were conserved during 220 million years (Ma) of evolution. We showed that 168 residues (out of the 390 residues composing the human TUFT1 sequence) are under purifying selection. Our analyses identified several, new, putatively functional domains and confirmed previously described functional domains, such as the TIP39 interaction domain, which correlates with nuclear localization of the TUFT1 protein, that was demonstrated in several tissues. We also identified several sites under positive selection, which could indicate evolutionary changes possibly related to the functional diversification of TUFT1 during evolution in some lineages. We discovered that TUFT1 and MYZAP (myocardial zonula adherens protein) share a common ancestor that was duplicated circa 500 million years ago. Taken together, these findings expand our knowledge of TUFT1 evolution and provide new information that will be useful for further investigation of TUFT1 functions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Hashimi N, Sire JY, Delgado S (2009) Evolutionary analysis of mammalian enamelin, the largest enamel protein, supports a crucial role for the 32 kDa peptide and reveals selective adaptation in rodents and primates. J Mol Evol 69(6):635–656
Ashkenazy H, Erez E, Martz E, Pupko T, Ben-Tal N (2010) ConSurf 2010: calculating evolutionary conservation in sequence and structure of proteins and nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res 38(Web Server issue):W529–W533
Bashir MM, Abrams WR, Tucker T, Sellinger B, Budarf M, Emanuel B, Rosenbloom J (1998) Molecular cloning and characterization of the bovine and human tuftelin genes. Connect Tissue Res 39:13–24
Celniker G, Nimrod G, Ashkenazy H, Glaser F, Martz E, Mayrose I, Pupko T, Ben-Tal N (2013) ConSurf: using evolutionary data to raise testable hypotheses about protein function. Isr J Chem 53:199–206
Chan HC, Mai L, Oikonomopoulou A, Chan HL, Richardson AS, Wang SK, Simmer JP, Hu JC (2010) Altered enamelin phosphorylation site causes amelogenesis imperfecta. J Dent Res 89:695–699
Deutsch D (1989) Structure and function of enamel gene products. Anat Rec 224:189–210
Deutsch D, Palmon A, Fisher LW, Kolodny N, Termine JD, Young MF (1991) Sequencing of bovine enamelin (“tuftelin”) a novel acidic enamel protein. J Biol Chem 266:16021–16028
Deutsch D, Palmon A, Dafni L, Mao Z, Leytin V, Young M, Fisher LW (1998) Tuftelin – aspects of protein and gene structure. Eur J Oral Sci 106(Suppl. 1):315–323
Deutsch D, Shay B, Rosenfeld E, Leiser Y, Fermon E, Taylor A, Charuvi K, Cohen Y, Haze A, Fuks A, Dafni L, Mao Z (2002) The human tuftelin gene and the expression of tuftelin in mineralizing and nonmineralizing tissues. Connect Tissue Res 43:425–434
Deutsch D, Silverstein N, Shilo D, Lecht S, Lazarovici P, Blumenfeld A (2011) Biphasic influence of hypoxia on tuftelin expression in mouse mesenchymal C3H10T1/2 stem cells. Eur J Oral Sci 119(suppl. 1):55–61
Dinkel H, Van Roey K, Michael S, Kumar M, Uyar B, Altenberg B, Milchevskaya V, Schneider M, Kühn H, Behrendt A, Dahl SL, Damerell V, Diebel S, Kalman S, Klein S, Knudsen AC, Mäder C, Merrill S, Staudt A, Thiel V, Welti L, Davey NE, Diella F, Gibson TJ (2016) ELM 2016-data update and new functionality of the eukaryotic linear motif resource. Nucleic Acids Res 44(D1):D294–D300
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32(5):1792–1797
Endo T, Ikeo K, Gojobori T (1996) Large-scale search for genes on which positive selection may operate. Mol Biol Evol 13:685–690
Hasegawa M, Kishino H, Yano T (1985) Dating of the human-ape splitting by a molecular clock of mitochondrial DNA. J Mol Evol 22(2):160–174
Higgins DG, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ (1996) Using CLUSTAL for multiple sequence alignments. Methods Enzymol 266:383–402
Jeremias FL, Koruyucu M, Küchler EC, Bayram M, Tuna EB, Deeley K, Pierri RA, Souza JF, Fragelli CM, Paschoal MA, Gencay K, Seymen F, Caminaga RM, dos Santos-Pinto L, Vieira AR (2013) Genes expressed in dental enamel development are associated with molar-incisor hypomineralization. Arch Oral Biol 58:1434–1442
Leiser Y, Blumenfeld A, Haze A, Dafni L, Taylor AL, Rosenfeld E, Fermon E, Gruenbaum-Cohen Y, Shay B, Deutsch D (2007) Localization, quantification, and characterization of tuftelin in soft tissues. Anat Rec 290:449–454
Leiser Y, Silverstein NC, Blumenfeld A, Shilo D, Haze A, Rosenfeld E, Shay B, Tabakman R, Lecht S, Lazarovici P, Deutsch D (2010) The induction of tuftelin expression in PC12 cell line during hypoxia and NGF induced differentiation. J Cell Physiol 226:165–172
MacDougall M, Simmons D, Dodds A, Knight C, Luan X, Zeichner-David M, Zhang C, Ryu OH, Qian Q, Simmer JP, Hu C-C (1998) Cloning, characterization, and tissue expression pattern of mouse tuftelin cDNA. J Dent Res 77:1970–1978
Mao Z, Shay B, Hekmati M, Fermon E, Taylor A, Dafni L, Heikenheimo K, Lustmann J, Fisher LW, Young MF, Deutsch D (2001) The human tuftelin gene: cloning and characterization. Gene 279:181–196
Meredith RW, Janečka JE, Gatesy J, Ryder OA, Fisher CA, Teeling EC, Goodbla A, Eizirik E, Simão TL, Stadler T, Rabosky DL, Honeycutt RL, Flynn JJ, Ingram CM, Steiner C, Williams TL, Robinson TJ, Burk-Herrick A, Westerman M, Ayoub NA, Springer MS, Murphy WJ (2011) Impacts of the cretaceous terrestrial revolution and KPg extinction on mammal diversification. Science 334(6055):521–524
Paine CT, Paine ML, Luo W, Okamoto CT, Lyngstadaas SP, Snead ML (2000) A tuftelin-interacting protein (TIP39) localizes tothe apical secretory pole of mouse ameloblasts. J Biol Chem 275:22284–22292
Patir A, Seymen F, Yildirim M, Deeley K, Cooper ME, Marazita ML, Vieira AR (2008) Enamel formation genes are associated with high caries experience in Turkish children. Caries Res 42:394–400
Pieperhoff S, Rickelt S, Heid H, Claycomb WC, Zimbelmann R, Kuhn C, Winter-Simanowski S, Kuhn C, Frey N, Franke WW (2012) The plaque protein myozap identified as a novel major component of adhering junctions in endothelia of the blood and the lymph vascular systems. J Cell Mol Med 16:1709–1719
Pond SLK, Frost SDW (2005) A genetic algorithm approach to detecting lineage-specific variation in selection pressure. Mol Biol Evol 22:478–485
Pond SLK, Muse SV (2005) HyPhy: Hypothesis testing using Phylogenies. In Statistical Methods for Molecular Evolution. Statistics for Biology and Health, Part II. Springer, New York, p 125–181
Pond SLK, Frost SDW, Muse SV (2005) HyPhy: hypothesis testing using phylogenies. Bioinformatics 21:676–679
Rickelt S, Kuhn C, Winter-Simanowski S, Zimbelmann R, Frey N, Franke WW (2011) Protein myozapa late addition to the molecular ensembles of various kinds of adherens junctions. Cell Tissue Res 346:347–359
Schmid K, Yang Z (2008) The trouble with sliding windows and the selective pressure in BRCA1. PLoS ONE 3:e3746
Shay B, Gruenbaum-Cohen Y, Tucker AS, Taylor AL, Rosenfeld E, Haze A, Dafni L, Leiser Y, Fermon E, Danieli T, Blumenfeld A, Deutsch D (2009) High yield expression of biologically active recombinant full length human tuftelin protein in baculovirus-infected insect cells. Protein Expr Purif 68:90–98
Sigrist CJA, Cerutti L, de Castro E, Langendijk-Genevaux PS, Bulliard V, Bairoch A, Hulo N (2010) PROSITE, a protein domain database for functional characterization and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res 38(Database issue):D161–D166
Silvent J, Sire JY, Delgado S (2013) The Dentin matrix acidic phosphoprotein 1 (DMP1) in the light of mammalian evolution. J Mol Evol 76(1–2):59–70
Stanek D, Pridalova-Hnilicova J, Novotny I, Huranova M, Blazikova M, Wen X, Sapra AK, Neugebauer KM (2008) Spliceosomal small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles repeatedly cycle through Cajal bodies. Mol Biol Cell 19:2534–2543
Stern A, Doron-Faigenboim A, Erez E, Martz E, Bacharach E, Pupko T (2007) Selecton 2007: advanced models for detecting positive and purifying selection using a Bayesian inference approach. Nucleic Acids Res 35(Web Server issue):W506–W511
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Tsunoyama K, Gojobori T (1998) Evolution of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits. Mol Biol Evol 15:518–527
Wen X, Lei Y-P, Zhou YL, Okamoto CT, Snead ML, Paine ML (2005) Structural organization and cellular localization of tuftelin-interacting protein 11 (TFIP11). Cell Mol Life Sci 62:1038–1046
Yang Z, Nielsen R, Goldman N, Pedersen AM (2000) Codon-substitution models for heterogeneous selection pressure at amino acid sites. Genetics 155:431–449
Acknowledgements
This collaborative study was initiated at the Tooth Morphogenesis and Differentiation conference in Lalonde-les-Maures (France) in Spring 2013. We thank the Université Pierre et Marie Curie, CNRS, and ANR (Jaws project, 12-BSV7-0020) for their financial support. We also thank Dr. Kurt Liittschwager (USA) for his English correction.
Funding
The funding was provided by Agence Nationale de la Recherche (Grant No. 12-BSV7-0020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delgado, S., Deutsch, D. & Sire, J.Y. Evolutionary Analysis of the Mammalian Tuftelin Sequence Reveals Features of Functional Importance. J Mol Evol 84, 214–224 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-017-9789-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-017-9789-5