Abstract
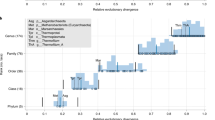
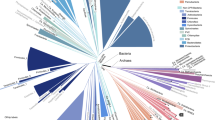
In this study, we have calculated distances between genomes based on our previously developed compositional spectra (CS) analysis. The study was conducted using genomes of 39 species of Eukarya, Eubacteria, and Archaea. Based on CS distances, we produced two different consensus dendrograms for four- and two-letter (purine-pyrimidine) alphabets. A comparison of the obtained structure using purine-pyrimidine alphabet with the standard three-kingdom (3K) scheme reveals substantial similarity. Surprisingly, this is not the case when the same procedure is based on the four-letter alphabet. In this situation, we also found three main clusters—but different from those in the 3K scheme. In particular, one of the clusters includes Eukarya and thermophilic bacteria and a part of the considered Archaea species. We speculate that the key factor in the last classification (based on the A-T-G-C alphabet) is related to ecology: two ecological parameters, temperature and oxygen, distinctly explain the clustering revealed by compositional spectra in the four-letter alphabet. Therefore, we assume that this result reflects two interdependent processes: evolutionary divergence and superimposed ecological convergence of the genomes, albeit another process, horizontal transfer, cannot be excluded as an important contributing factor.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aravind L, Tatusov RL, Wolf YI, Walker DR, Koonin EV (1998) Evidence for massive gene exchange between archaeal and bacterial hyperthermophiles. Trends Genet 14:442–444
Baldi P, Basnee PF (2000) Sequence analysis by additive scale: DNA structure for sequences and repeats of all lengths. Bioinformatics 16:865–889
Bird AP (1980) DNA methylation and the frequency of CpG in animal. DNA Nucleic Acids Res 8:1499–1504
Blair JE, Shah P, Hedges SB (2005) Evolutionary sequence analysis of complete eukaryote genomes. BMC Bioinformatics 6:53
Brendel V, Busse HG (1984) Genome structure described by formal languages. Nucleic Acids Res 12:2561–2568
Brendel V, Beckmann JS, Trifonov EN (1986) Linguistics of nucleotide sequences: morphology and comparison of vocabularies. J Biomol Struct Dyn 4(1):11–21
Brocchieri L (2001) Phylogenetic inference from molecular sequences: review and critique. Theor Pop Biol 59(1):27–40
Burg C, Campbell AM, Karlin S (1992) Over- and underrepresentation of short oligonucleotides in DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:1358–1362
Bussemaker HJ, Li H, Siggia ED (2000) Building a dictionary for genomes: identification of presumptive regulatory sites by statistical analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(18):10096–10100
Daubin V, Gouy M, Perri’ere G (2001) Bacterial molecular phylogeny using supertree approach. Genome Inform 12:155–164
Deckert G, Warren PV, Gaasterland T, et al. (1988) The complete genome of the hyperthermophilic bacterium Aquifex aeolicus. Nature 392:353–358
Dekker J, Rippe K, Dekker M, Kleckner N (2002) Capturing chromosome conformation. Science 295:1306–1311
Doolittle WF (1999) Phylogenetic classification and the universal tree. Science 284:2124–2128
Eichler EE, Sankoff D (2003) Structural dynamics of eukaryotic chromosome evolution. Science 301:793–797
Feng D, Cho G, Doolittle RF (1997) Determining divergence times with a protein clock: update and reevaluation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:13028–13033
Foerstner KU, Mering CV, Hooper SD, Bork P (2005) Environments shape the nucleotide composition of genomes. EMBO Reports 6(12):1208–1213
Gelfand MS (1993) Genetic language: Metaphore or analogy? Biosystems 30:277–288
Gogarten JP, Doolittle WF, Lawrence JG (2002) Prokaryotic evolution in light of gene transfer. Mol Biol Evol 19(12):2226–2238
Golding GB, Gupta RS (1995) Protein-based phylogenies support a chimeric origin for the eukaryotic genome. Mol Biol Evol 12(1):1–6
Gribaldo S, Philippe H (2002) Ancient phylogenetic relationships. Theor Popul Biol 61(4):391–408
Gupta RS (1998a) Protein phylogenies and signature sequences: a reappraisal of evolutionary relationships among archaebacteria, eubacteria, and eukaryotes. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:1435–1491
Gupta RS (1998b) Life’s third domain (Archaea): An established fact or an endangered paradigm? Theor Popul Biol 54(2):91–104
Gupta RS, Griffiths E (2002) Critical issues in bacterial phylogeny. Theor Popul Biol 61(4):423–434
Healy J, Thomas EE, Schwartz JT, Wigler M (2003) Annotating large genomes with exact word matches. Genome Res 13(10):2306–2315
Hedges SB (2002) The origin and evolution of model organisms. Nat Rev Genet 3(11):838–849
Holmquist GP (1989) Evolution of chromosome bands: molecular ecology of noncoding DNA. J Mol Evol 28:469–486
Hsiao WW, Ung K, Aeschliman D, Bryan J, Finlay BB, Brinkman FS (2005) Evidence of a large novel gene pool associated with prokaryotic genomic islands. PLoS Genetics 1(5):e62:0540–e62:0550
Karlin S, Cardon R (1994) Computational DNA sequence analysis. Annu Rev Microbiol 48:619–654
Karlin S, Mrazek J, Campbell AM (1997) Compositional biases of bacterial genomes and evolutionary implications. J Bacteriol 179(12):3899–3913
Kaufman L, Rousseeuw PJ (1990) Finding groups in data: an introduction to cluster analysis. Wiley, New York
Kirzhner VM, Korol AB, Bolshoy A, Nevo E (2002) Compositional spectrum—revealing patterns for genomic sequence characterization and comparison. Physica A 312:447–457
Kirzhner VM, Nevo E, Korol AB, Bolshoy A (2003) One promising approach to a large scale comparison of genomic sequences Acta Biotheor 51(2):73–89
Kirzhner V, Bolshoy V, Volkovich Z, Korol A, Nevo E (2005) Large scale genome clustering across life based on a linguistic approach. BioSystem 81(3):208–222
Kendall MG (1970) Rank correlation methods. Charles Griffin, London
Korol AB, Preygel IA, Preygel SI (1994) Recombination variability and evolution. Chapman & Hall, London
Lerat E, Daubin V, Moran NA (2003) From gene trees to organismal phylogeny in prokaryotes: the case of the γ-proteobacteria. PLoS Biol 1(1):e19
Li YC, Korol AB, Fahima T, Beiles A, Nevo E (2002) Microsatellites: genomic distribution, putative functions and mutational mechanisms: a review. Mol Ecol 11(12):2453–2465
Li YC, Korol AB, Fahima T, Beiles A, Nevo E (2004) Microsatellites within genes: structure, function, and evolution. Mol Biol Evol 21:991–1007
Lin J, Gerstein M (2000) Whole-genome trees based on the occurrence of folds and orthologs: implications for comparing genomes on different levels. Genome Res 10(6):808–818
Lobry JR, Chessel D (2003) Internal correspondence analysis of codon and amino-acid usage in thermophilic bacteria. J Appl Genet 44(2):235–261
Logsdon JM, Faguy DM (1999) Thermotoga heats up lateral gene transfer. Curr Biol 9(19):R747–R751
Lyubetsky VA, V’yugin VV (2003) Methods of horizontal gene transfer determination using phylogenetic data. In Silico Biol 3:0003
Mayr E (1998) Two empires or three? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(17):9720–9723
Naya H, Romero H, Zavala H, Alvarez B, Musto H (2002) Aerobiosis increases the genomic guanine plus cytosine content (GC%) in prokaryotes. J Mol Evol 55:260–264
Nelson KE, Clayton RA, Gill SR, et al. (1999) Evidence for lateral gene transfer between Archaea and bacteria from genome sequence of Thermotoga maritima. Nature 399(6734):323–329
Nussinov R (1980) Some rules in the ordering of nucleotides in the DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 10:4545–4562
Paz A, Mester D, Baca I, Nevo E, Korol A (2004) Adaptive role of increased frequency of polypurine tracts in mRNA sequences of thermophilic prokaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:2951–2956
Paz A, Kirzhner V, Nevo E, Korol A (2006) Coevolution of DNA-interacting proteins and genome “dialect.” Mol Biol Evol 23:56–64
Pietrokovski S, Hirshon J, Trifonov EN (1990) Linguistic measure of taxonomic and functional relatedness of nucleotide sequences. J Biomol Struct Dyn 7:1251–1268
Rocha EP, Viari A, Danchin A (1998) Oligonucleotide bias in Bacillus subtilis: general trends and taxonomic comparisons. Nucleic Acids Res 2(12):2971–2980
Rogozin IB, Makarova KS, Natale DA, Spiridonov AN, Tatusov RL, Wolf YI, Koonin EV (2002) Congruent evolution of different classes of non-coding DNA in procariotic genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 30(19):4264–4271
Omelchenko MV, Wolf YI, Gaidamakova EK, Matrosova VY, Vasilenko A, Min Zhai, Daly MJ, Koonin EV, Makarova KS (2005) Comparative genomics of Thermus thermophilus and Deinococcus radiodurans: divergent routes of adaptation to thermophily and radiation resistance. BMC Evol Biol 5:57
Robins H, Krasnitz M, Barak H, Levine AJ (2005) A relative-entropy algorithm for genomic fingerprinting captures host-phage similarities. J Bacteriol 187(24):8370–8374
Sneath PHA, Sokal RR (1973) Numerical taxonomy, the principles and practice of numerical classification. W. H. Freeman, San Francisco
Snel B, Bork P, Huynen MA (1999) Genome phylogeny based on gene content. Nat Genet 21(1):108–110
Tekaia F, Lazcano A, Dujon B (1999) The genomic tree as revealed from whole proteome comparisons. Genome Res 9:550–557
Trifonov EN (1989) The multiple codes of nucleotide sequences. Bull Math Biol 51(4):417–432
Trifonov EN, Brendel V (1986) Gnomics—a dictionary of genetic codes. Balaban, Rehovot
Volkovich Z, Kirzhner V, Bolshoy A, Korol A, Nevo E (2005) The method of N-grams in large-scale clustering of DNA texts. Pattern Recogn 38(11):1902–1912
Woese CR (1987) Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev 51:221–271
Woese CR (2000) Interpreting the universal phylogenetic tree. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(15):8392–8396
Woese CR (2002) On the evolution of cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(13):8742–8747
Woese CR, Kandler O, Wheelis ML (1990) Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:4576–4579
Wolf YI, Rogozin IB, Grishin NV, Tatusov RL, Koonin EV (2001a) Genome trees constructed using five different approaches suggest new major bacterial clades. BMC Evol Biol 1:8
Wolf YI, Rogozin IB, Kondrashov AS, Koonin EV (2001b) Genome alignment, evolution of prokaryotic genome organization, and prediction of gene function using genomic context. Genome Res 11(3):356–372
Wolf YI, Rogozin IB, Grishin NV, Koonin EV (2002) Genome trees and the tree of life. Trends Genet 18(9):472–479
Xia X, Wei T, Xie Z, Danchin A (2002) Genomic changes in nucleotide and dinucleotide frequencies in Pasteurella multocida cultured under high temperature. Genetics 161(4):1385–1394
Acknowledgments
We thank Stuart Newfeld and three anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments and suggestions. This work was supported by the Israeli Ministry of Absorption. A.P. was supported by a scholarship in Bioinformatics from the Eshkol Foundation of the Israeli Ministry of Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
[Reviewing Editor: Dr. Stuart Newfeld]
Appendix: List of Depicted Genomic Sequences
Appendix: List of Depicted Genomic Sequences
Each record in the list is represented by species name. If only a DNA fragment rather than entire genome was taken for a species, the corresponding accession number is also presented to avoid incorrect identification.
Eukarya
Homo sapiens chromosome (chr) X (NT 011528); Homo sapiens chr Y (NT011864); Mus musculus chr 7 (AC012382); Caenorhabditis elegans chr 1; Drosophila melanogaster chr 2; Arabidopsis thaliana chr 1 (NC 003071); A thaliana mitochondrial genome (NC 001284.1); Saccharomyces cerevisiae chr ii; Leishmania major (AE001274).
Eubacteria
Bacillus subtilis; Streptococcus pyogenes; Mycoplasma genitalium; Mycoplasma pneumoniae; Mycobacterium tuberculosis; Synechocystis sp.; Helicobacter pylori; Escherichia coli; Deinococcus radiodurans; Thermotoga maritima; Aquifex aeolicus; Neisseria meningitides; Neisseria gonorrhoeae; Campylobacter jejuni; Haemophilus influenzae; Clostridium acetobutylicum; Treponema pallidum; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans strain HK1651; Rickettsia prowazekii; Borrelia burgdorferi; Thermus thermophilus; Enterococcus faecalis.
Archaea
Halobacterium sp. NRC-1; Pyrococcus horikoshii; Pyrococcus abyssi; Archaeoglobus fulgidus; Methanococcus jannaschii; Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum; Aeropyrum pernix; Sulfolobus solfataricus.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirzhner, V., Paz, A., Volkovich, Z. et al. Different Clustering of Genomes Across Life Using the A-T-C-G and Degenerate R-Y Alphabets: Early and Late Signaling on Genome Evolution?. J Mol Evol 64, 448–456 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-006-0178-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-006-0178-8