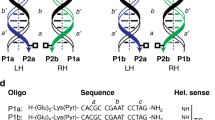
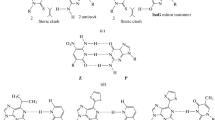
Abstract
The ability to maximize the use of available nucleic acid sequence space would have been crucial during the presumed RNA world and confers selective advantage in many contemporary organisms. One way to access sequence space at a higher density would be to make use of both strands of a duplex nucleic acid for the production of functional molecules. As a demonstration of this possibility, two pairs of nucleic acid enzymes were engineered to be perfect complements, each with the capacity to adopt a distinct structure and catalyze a particular chemical transformation. Both members of each pair of enzymes exhibited nearly the same level of activity as the canonical form of the corresponding catalytic motif. The ability to generate functional nucleic acids encoded by both strands of a duplex has implications for the evolution of catalytic nucleic acids and the prospects for realizing maximum functionality from a given genetic sequence.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
JP Adelman CT Bond J Douglass E Herbert (1987) ArticleTitleTwo mammalian genes transcribed from opposite strands of the same DNA locus. Science 235 1514–1517
JM Buzayan WL Gerlach G Bruening (1986) ArticleTitleNon-enzymatic cleavage and ligation of RNAs complementary to a plant virus satellite RNA. Nature 323 349–353 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XlvVGjsLg%3D
JM Comeron (2001) ArticleTitleWhat controls the length of noncoding DNA? Curr Opin Genet Dev 11 652–659 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXnslajtLw%3D Occurrence Handle11682309
J Compton (1991) ArticleTitleNucleic acid sequence-based amplification. Nature 350 91–92 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By6C28zmsVc%3D Occurrence Handle1706072
WF Doolittle (1978) ArticleTitleGenes in pieces: Were they ever together? Nature 272 581–582
M Fedor (2000) ArticleTitleStructure and function of the hairpin ribozyme. J Mol Biol 297 269–291 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXhs1Gns7g%3D Occurrence Handle10715200
AC Forster RH Symons (1987) ArticleTitleSelf-cleavage of virusoid RNA is performed by the proposed 55-nucleotide active site. Cell 50 9–16 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXltVaisQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle3594567
RF Gesteland TR Cech JF Atkins (Eds) (1999) The RNA world, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press New York
JC Guatelli KM Whitfield DY Kwoh KJ Barringer DD Richman TR Gingeras (1990) ArticleTitleIsothermal in vitro amplification of nucleic acids by a multienzyme reaction modeled after retroviral replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87 7797–7802 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXps1ahsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle2217213
A Hampel R Tritz M Hicks P Cruz (1990) ArticleTitle‘Hairpin’ catalytic RNA model: Evidence for helices and sequence requirement for substrate RNA. Nucleic Acids Res 18 299–304 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXitFejs70%3D Occurrence Handle2183177
S Henikoff MA Keene K Fechtel JW Fristrom (1986) ArticleTitleGene within a gene: Nested Drosophila genes encode unrelated proteins on opposite DNA strands. Cell 44 33–42 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XitVWnsrg%3D Occurrence Handle3079672
Hill CS (1996) Gen-Probe transcription-mediated amplification: System principles. Gen-Probe Incorporated Technical Document; available at http://www.gen-probe.com/pdfs/tma_whiteppr.pdf
A Mira H Ochman NA Moran (2001) ArticleTitleDeletional bias and the evolution of bacterial genomes. Trends Genet 17 589–596 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXnt1Wju7g%3D Occurrence Handle11585665
SR Misener VK Walker (2000) ArticleTitleExtraordinarily high density of unrelated genes showing overlapping and intraintronic transcription units. Biochim Biophys Acta 1492 269–270 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXltVCqtL8%3D Occurrence Handle10858562
S Normark S Bergstrom T Edlund T Grundstrom B Jaurin FP Lindberg O Olsson (1983) ArticleTitleOverlapping genes. Annu Rev Genet 17 499–525
Y Okazaki et al. (2002) ArticleTitleAnalysis of the mouse transcriptome based on functional annotation of 60,770 full-length cDNAs. Nature 420 563–573 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nature01266 Occurrence Handle12466851
P Ordoukhanian GF Joyce (1999) ArticleTitleA molecular description of the evolution of resistance. Chem Biol 6 881–889 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXotVygsro%3D Occurrence Handle10631516
GA Prody JT Bakos JM Buzayan IR Schneider G Bruening (1986) ArticleTitleAutolytic processing of dimeric plant virus satellite RNA. Science 231 1577–1580 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XhsVCisb8%3D
SW Santoro GF Joyce (1997) ArticleTitleA general purpose RNA-cleaving DNA enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94 4262–4266 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXjtVyit7w%3D Occurrence Handle9113977
SW Santoro GF Joyce (1998) ArticleTitleMechanism and utility of an RNA-cleaving DNA enzyme. Biochemistry 37 13330–13342 Occurrence Handle10.1021/bi9812221 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXlsFKhu7k%3D Occurrence Handle9748341
EA Schultes DP Bartel (2000) ArticleTitleOne sequence, two ribozymes: Implications for the emergence of new ribozyme folds. Science 289 448–452 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXlsV2gtLg%3D Occurrence Handle10903205
F Sleutels R Zwart DP Barlow (2002) ArticleTitleThe non-coding Air RNA is required for silencing autosomal imprinted genes. Nature 415 77–81 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xkt1OrsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11780120
N Sugimoto S Nakano M Katoh A Matsumura H Nakamuta T Ohmichi M Yoneyama M Sasaki (1995) ArticleTitleThermodynamic parameters to predict stability of RNA/DNA hybrid duplexes. Biochemistry 34 11211–11216 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXnsVKktLs%3D Occurrence Handle7545436
J Tang RR Breaker (2000) ArticleTitleStructural diversity of self-cleaving ribozymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97 5784–5789 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjvFakt7k%3D Occurrence Handle10823936
C Vanhee-Brossollet C Vaquero (1998) ArticleTitleDo natural antisense transcripts make sense in eukaryotes? Gene 211 1–9 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-1119(98)00093-6 Occurrence Handle9573333
EG Wagner RW Simons (1994) ArticleTitleAntisense RNA control in bacteria, phages, and plasmids. Annu Rev Microbiol 48 713–742 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.micro.48.1.713 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXmslKhtro%3D Occurrence Handle7826024
MC Wright GF Joyce (1997) ArticleTitleContinuous in vitro evolution of catalytic function. Science 276 614–617 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXivVKis7c%3D Occurrence Handle9110984
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grant NAG5-9386 from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration and by The Skaggs Institute for Chemical Biology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuhns, S.T., Joyce, G.F. Perfectly Complementary Nucleic Acid Enzymes . J Mol Evol 56, 711–717 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-002-2445-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-002-2445-7